
The right rack mount power distribution unit forms the backbone of server room reliability and operational efficiency. Power-related problems significantly contribute to data center outages. For instance, the Uptime Institute’s 2025 report indicates that power-related issues are responsible for 54% of impactful outages. Such downtime carries substantial financial consequences across industries.
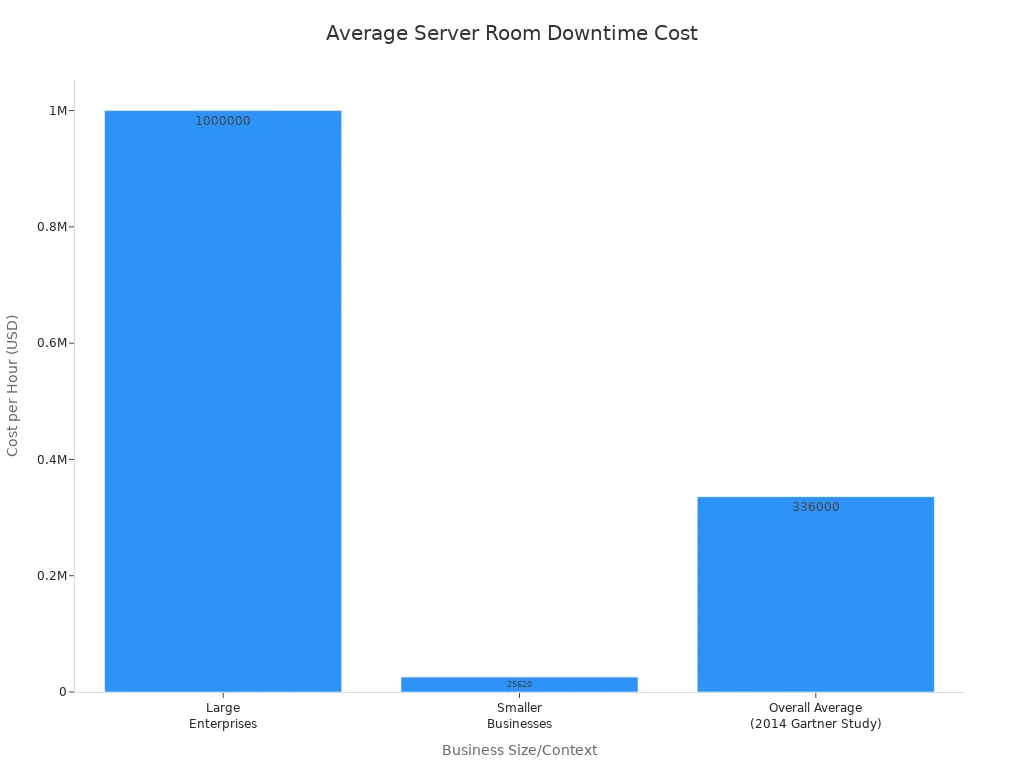
Large enterprises often face costs exceeding $1 million per hour during downtime. Therefore, selecting the optimal PDU is a critical decision.
Key Takeaways
- Choose the right PDU type for your needs. Basic, metered, monitored, and switched PDUs offer different features.
- Understand your power needs. Check voltage, amperage, and plug types for all your equipment.
- Follow the 80% rule for safety. Do not load a PDU beyond 80% of its total power capacity.
- Plan for future growth. Add extra capacity to your PDU for new equipment.
- Look for advanced features. Remote monitoring, surge protection, and locking outlets improve reliability.
- Consider physical factors. Mounting style, outlet count, and high-temperature ratings are important.
- Check for safety standards. Ensure the PDU meets international safety and quality rules.
- Balance cost with features. A good PDU saves money over time by preventing downtime and improving energy use.
Understanding Rack Mount Power Distribution Unit Types

Choosing the correct rack mount PDU begins with understanding the different types available. Each type offers distinct functionalities, catering to various operational needs within a server room or data center.
Basic Power Distribution Units
Core Functionality and Simplicity
Basic power distribution units represent the simplest form of power distribution. They primarily distribute electric power from an input source to multiple outlets. These devices are equipped with multiple outputs, specifically designed to power racks of computers and networking equipment. Their core function focuses on effective power delivery without advanced monitoring or control features. Some models even include plug clips to prevent accidental disconnections, enhancing reliability.
Best Use Cases for Basic Power Distribution
Basic PDUs are ideal for environments where local power distribution is the primary requirement and advanced monitoring is not critical. They significantly contribute to organizing rack cabling, making them suitable for smaller server rooms, remote telecom sites, or non-critical applications. These units provide essential power distribution, ensuring equipment receives the necessary electricity.
Metered Power Distribution Units
Local Power Monitoring Capabilities
Metered power distribution units offer enhanced capabilities beyond basic power distribution. They distribute electricity to multiple devices while sensors track current, ensuring operation within safe limits. A built-in display panel shows real-time readings such as voltage, current, and total power draw. This allows quick action on spikes or dips. These PDUs also provide circuit monitoring, measuring energy at the outlet or branch level. This identifies power consumption by specific devices, aiding in load balancing and fault detection.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Tracking | Tracks power consumption data via a local display. |
| Metrics Display | Provides metrics such as current, voltage, and power factor. |
| Monitoring Level | Allows monitoring at the outlet level for detailed insights. |
Ideal Applications for Metered PDUs
Metered PDUs are perfect for environments requiring local, real-time power consumption data. They help identify inefficiencies and reduce energy waste, leading to enhanced energy management. Monitoring metrics like voltage and current ensures devices operate within safe limits, improving equipment protection. The detailed data allows for better planning and resource allocation, offering valuable operational insights. Many models also offer network connectivity for remote monitoring of power statistics and alarms, though their primary focus remains local display.
Monitored Power Distribution Units
Remote Power Monitoring and Data Collection
Monitored power distribution units elevate power management by providing robust remote monitoring and data collection capabilities. They track power usage in real-time at the unit or outlet level. These PDUs incorporate the GE Smart IP Meter for precise and real-time energy monitoring, tracking energy consumption at the outlet level, and monitoring critical parameters like voltage, current, and power factor. They also offer robust remote management capabilities, enabling control and monitoring via LAN, WAN, or the Internet.
Advanced Data Insights for Your Power Distribution Unit
Monitored PDUs provide advanced data insights crucial for optimizing server room performance. They offer alarming capabilities, alerting users to power anomalies or threshold breaches. Users can remotely monitor voltage, power, frequency, and load levels in real-time through built-in networking. These units allow for reviewing historical data and identifying trends in power usage. They also integrate with Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) systems for centralized control and monitor environmental factors like temperature and humidity. An alarm notification system delivers alerts via email, SMS, or SNMP traps, ensuring rapid response to potential issues.
Switched Power Distribution Units
Remote Outlet Control and Management
Switched power distribution units offer advanced control over individual outlets. They provide remote power management, allowing users to control devices from any location. This capability includes turning devices on or off and rebooting malfunctioning equipment. Users manage individual outlets without needing physical presence. This feature eliminates costly site visits, saving both time and resources. It is especially beneficial for troubleshooting unresponsive servers remotely, restoring functionality in seconds. Switched PDUs allow for efficient power allocation and prioritization of critical equipment during peak usage.
Power Cycling and Automation Benefits
Switched PDUs significantly contribute to energy efficiency. They allow monitoring of power consumption at the outlet level. This data helps identify underutilized equipment. Users can turn off devices not in use, reducing unnecessary power consumption and lowering energy bills. Power sequencing prevents inrush currents when multiple devices power on simultaneously. This conserves energy and protects equipment from power surges. Switched PDUs enhance equipment safety and longevity through advanced features like surge protection and power monitoring. These features prevent damage from voltage fluctuations or power spikes. They also allow setting thresholds for power usage, ensuring devices operate within safe limits. Power cycling extends equipment lifespan by preventing overheating and reducing wear and tear on critical components. This improves reliability and reduces maintenance costs. Switched PDUs offer unmatched scalability and flexibility, adapting seamlessly to changing IT infrastructure needs.
Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) Power Distribution Units
Ensuring Redundant Power Sources
Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) power distribution units are crucial for ensuring power redundancy. They minimize system downtime by providing the ability to switch to a backup power source. This occurs when the primary source becomes unavailable. For instance, WTI’s PTS Series Automatic Transfer Switches prevent downtime by instantly switching to backup power. This happens when the primary source interrupts. These devices also switch power back to the primary input once it restores. They offer cost-efficient power redundancy and seamless failover for single power inlet devices. These devices include routers, firewalls, and switches from various manufacturers.
Seamless Power Failover for Critical Loads
ATS PDUs ensure redundant power sources and seamless failover through several key components and mechanisms:
- Dual Power Interfaces: These connect the ATS PDU to both a primary power source and a backup power source. Examples include utility lines and generators.
- Sensors and Monitoring Equipment: These continuously check critical parameters. They monitor voltage, frequency, and phase to detect any power anomalies or issues.
- Mechanical or Semiconductor Switch: This component rapidly and safely transfers the power load between the primary and backup sources.
- Control Logic: A microprocessor-based system monitors the power status from both sources. It triggers switching operations automatically when a problem detects.
- Rapid Transfer Technology: This technology allows the ATS PDU to switch between power sources in milliseconds. Mechanical switches achieve transfer times of 10 to 16 milliseconds. Solid-state devices switch in less than 4 milliseconds. This ensures continuous power without interruption.
- Automated Failover Mechanisms: The control logic constantly monitors both power sources. If the primary source fails, the unit automatically switches to the backup source within milliseconds. This happens without requiring manual intervention. Once the primary source stabilizes, the system returns the load to it.
Assessing Your Server Room’s Power Distribution Needs
Properly assessing a server room’s power distribution needs is crucial for operational stability and efficiency. This involves understanding voltage and amperage, calculating total power capacity, and implementing robust circuit breaker protection.
Voltage and Amperage Requirements for Your PDU
Understanding the voltage and amperage requirements of IT equipment is fundamental for selecting the correct power distribution unit. These values dictate the electrical current’s volume and pressure.
Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase Power Distribution
Server room equipment typically operates with common voltage ratings of 120-volt or 208-volt power. Modern IT equipment operates within a range of 100V to 250V. This ensures worldwide compatibility, accommodating North American 120/208V, Japanese 100/200V, and 230V used elsewhere. Using higher voltages, such as 240V, is more efficient. It offers benefits like reduced wiring, smaller transformers, and lower costs compared to 120V distribution. Moving from 120V to 240V can increase efficiency by 2-3.5% per server. This leads to significant energy savings in large data centers.
To calculate the power draw (watts), multiply the amperage by the voltage. For example, a server pulling 8 amps on a 208-volt circuit consumes 1,664 watts. The same server on a 120-volt circuit consumes 960 watts.
| Branch Circuit | Voltage | Amperage | Max Load 80% | Phase | Total Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120v Single-Phase | 120v | 20A | 16A | SP | 1.92 kW |
| 120v Single-Phase | 120v | 30A | 24A | SP | 2.88 kW |
| 208v Single-Phase | 208v | 20A | 16A | SP | 3.33 kW |
| 208v Single-Phase | 208v | 30A | 24A | SP | 4.99 kW |
| 208v Single-Phase | 208v | 50A | 40A | SP | 8.32 kW |
| 208v Single-Phase | 208v | 60A | 48A | SP | 9.98 kW |
| 208v Single-Phase | 208v | 100A | 80A | SP | 16.64 kW |
| 208v Three-Phase | 208v | 20A | 16A | 3PH | 5.76 kW |
| 208v Three-Phase | 208v | 30A | 24A | 3PH | 8.65 kW |
| 208v Three-Phase | 208v | 50A | 40A | 3PH | 14.41 kW |
| 208v Three-Phase | 208v | 60A | 48A | 3PH | 17.29 kW |
| 208v Three-Phase | 208v | 100A | 80A | 3PH | 28.82 kW |

- Amperage (Amps): Represents the volume or strength of electrical current. This value is often found on the server’s faceplate or in its technical specifications.
- Voltage (Volts): Represents the pressure or force pushing the electrical current. Common data center voltages include 120V (standard single-phase) and 208V (common three-phase for higher-density racks).
Input Plug Types and Compatibility
Ensuring input plug compatibility is critical for rack mount PDUs. The PDU’s input plug must precisely match the available power receptacle in the facility. Mismatched plugs will prevent proper connection and can lead to unsafe workarounds. It is essential to always verify the power source’s receptacle type before selecting a PDU to ensure a secure and functional setup.
- NEMA Plugs: Standard in North America (US and Canada). Examples include NEMA 5-15P (for 15-amp circuits) and NEMA 5-20P (for 20-amp circuits). These are suitable for typical office and data center environments in these regions.
- IEC Connectors: Offer global compatibility, adhering to International Electrotechnical Commission standards. Common types are IEC 60320 C14 and C20 inlets, which pair with C13 and C19 power cords, respectively. Many servers and network devices utilize these.
- CEEFORM Plugs: Robust, round connectors designed for high-power applications, often found in industrial settings and large data centers. They come in various configurations indicating voltage and amperage ratings, ensuring secure connections for demanding loads.
Calculating Total Power Capacity for Your Rack Mount PDU
Accurately calculating total power capacity is essential for preventing overloads and ensuring system stability. This involves applying industry rules and planning for future expansion.
The 80% Rule for Safe Power Distribution
The 80% rule, as per NEC code, states that continuous electrical loads should not exceed 80% of a circuit’s or PDU’s maximum current rating. This rule is crucial for preventing overheating, inefficiency, and circuit breaker trips.
Application in server rooms, especially with redundant power, involves:
- Method 1: Under Normal Operation, Do Not Exceed 40% of Each PDU’s Rating. This method is suitable when power supplies are balanced and loads are equally shared. For example, in a dual 20A PDU setup, neither PDU should exceed 8 Amps (40% of 20A) under normal operation. This ensures that if one power source fails, the remaining PDU can handle the full load without exceeding 80% of its rating.
- Method 2: Total Rack Power ≤ 80% of PDU Rating. This approach is recommended when loads are not equally shared or when maintaining less than 40% PDU utilization is not feasible. It requires ensuring that the total current consumption of all equipment in the rack does not exceed 80% of each PDU’s current rating. This accounts for a worst-case scenario where one PDU might need to power the entire load independently. To apply this, determine the total current consumption of all equipment (from datasheets or by measurement) and confirm it is within 80% of each PDU’s rating.
Planning for Future Growth and Scalability
To calculate total power capacity, use the formula: Total Power (Watts) = Voltage × Current × Power Factor × √3. For instance, a system operating at 208V with 30A and a power factor of 0.95 would have a total power capacity of approximately 10,260 Watts. A 3-phase PDU calculator is an excellent tool for planning future expansions. It helps assess if a current PDU can handle additional devices and determine if an upgrade is necessary.
When using the calculator, avoid common mistakes such as:
- Ignoring load imbalances, which can cause equipment failure and waste energy.
- Using incorrect input values for voltage, current, or power factor, leading to inaccurate calculations.
- Overlooking future growth, which risks insufficient capacity as power demand increases.
- Relying only on nameplate power values, which can lead to oversizing.
- Ignoring actual current draw under real operating conditions.
- Overlooking startup surges or simultaneous equipment startups, which can cause underestimating power needs.
- Failing to consider failure scenarios, such as when half of the power supplies fail and the remaining ones must handle the full load.
- Not using power measurement tools or vendor recommendations, which provide more accurate data than theoretical maximums.
To ensure proper planning:
- Confirm Power Calculations: Ensure accurate power calculations by using reliable tools like 3-phase PDU calculators, regularly reviewing power needs with real-time monitoring, applying derating factors, and load balancing across all phases. Consulting experts like electrical engineers can further improve accuracy.
- Add a Safety Margin: Industry standards recommend a 20% safety margin above the total power draw. This buffer accounts for unexpected surges and additional loads, keeping the load below 80% of the PDU’s rated capacity to reduce overload risk and extend equipment lifespan. For example, if the total equipment load is 80 kW, select a PDU rated at 100 kW.
- Ensure Redundancy and Future Expansion: Plan for 20-30% extra capacity beyond current needs to accommodate growth and prevent overloads. Consider modular PDUs and monitoring features for easy expansion. Investing in redundancy (e.g., N+1 with dual inputs) and modularity can lower long-term costs by reducing maintenance and enabling future upgrades.
Circuit Breaker Protection in Your Power Distribution Unit
Circuit breaker protection is a vital component of any power distribution unit, safeguarding equipment from electrical faults.
Overload Prevention Mechanisms
Circuit breakers prevent overloads by discriminating between normal and damaging overcurrents through their unique ‘delay curves’. These curves dictate how long a breaker will tolerate an overcurrent before tripping. For instance, they are designed not to trip during momentary, short-term overcurrent events like server inrush currents, which are normal. However, if an overload persists for more than a few minutes, the breaker will open to prevent overheating and potential damage to equipment.
- Real-time Power Monitoring: Local monitored PDUs provide detailed metrics (current, voltage, power consumption) on their display. This allows immediate insight into energy usage at outlet and circuit levels. This visibility helps identify inefficiencies and potential overloads, enabling proactive redistribution of loads or adjustment of equipment usage to prevent disruptions. Real-time monitoring systems have been shown to reduce energy consumption by up to 20%.
- Setting Power Thresholds: Monitored PDUs allow users to configure specific warning thresholds for power usage. These thresholds act as safeguards, triggering visual or audible alerts when energy consumption approaches critical levels. This proactive alerting minimizes the risk of overloading phases, which can lead to equipment damage or downtime.
- Load Balancing and Optimization: Monitored PDUs simplify load balancing by providing real-time data to distribute power loads evenly across circuits. This prevents specific outlets or circuits from becoming overburdened, reducing the likelihood of failures and optimizing energy usage. Effective load balancing can lead to significant cost savings, with examples like IBM reporting a 30% reduction in energy costs through similar strategies.
Individual vs. Bank Protection for Outlets
Different types of circuit breakers offer varying levels of protection:
- Thermal Circuit Breakers: Utilize a heat-responsive bimetal strip or disk. They have a slower characteristic curve to differentiate between safe, temporary surges and prolonged overloads. They are a low-cost solution for appliances and printed circuit board protection but are sensitive to ambient temperature and may have limitations in high-current applications, often being UL 1077 devices.
- Thermal-Magnetic Circuit Breakers: Combine the benefits of thermal and magnetic breakers. They include a delay to prevent nuisance tripping from normal inrush current and a solenoid actuator for rapid response to higher currents. Like thermal breakers, they are sensitive to ambient temperature.
- Magnetic Circuit Breakers: Operate via a solenoid and trip almost instantly once the threshold current is reached. This type is suitable for sensitive installations but not ideal for equipment with significant inrush currents (e.g., servers).
- Hydraulic-Magnetic Circuit Breakers: Combine a magnetic circuit breaker with a hydraulic delay, making them tolerant of current surges. They offer a two-step response curve, providing a delay for normal overcurrents but tripping quickly on short circuits. These breakers are not affected by ambient temperature and are often preferred for IT infrastructure equipment due to their customizable delay curves.
Physical and Environmental Considerations for Your Rack Mount PDU

Choosing the right rack mount PDU involves careful consideration of its physical attributes and how it interacts with the server room environment. These factors directly impact space utilization, accessibility, and overall operational efficiency.
Mounting Orientation and Rack Space Utilization
The way a PDU mounts in a rack significantly affects available space and cable management.
Vertical (0U) Power Distribution Units
Vertical PDUs, often called 0U PDUs, mount along the side of the rack. They do not consume any valuable rack units (U). This design makes them ideal for high-density environments and modern data centers. They offer better airflow and more organized cable routing. Vertical PDUs can accommodate a higher number of outlets, sometimes up to 54 or 60, without using rack space. This supports future expansion.
Horizontal (1U/2U) Power Distribution Units
Horizontal PDUs mount within the rack, occupying 1U or 2U of space. They suit less constrained spaces, smaller racks, or shallow IT equipment. While they are easy to access for frequent changes, they can limit space for other critical equipment.
| Feature | Horizontal PDU | Vertical PDU |
|---|---|---|
| Orientation | Mounted horizontally | Mounted vertically |
| Rack Space Usage | Occupies 1U or 2U of rack space | Takes up no rack units (ZeroU) |
| Outlet Capacity | Typically 8 to 16 outlets | Can accommodate up to 54 outlets |
| Cable Management | More challenging due to limited space | Better airflow and organized routing |
| Application Suitability | Suitable for less constrained spaces, smaller racks, or shallow IT equipment | Ideal for high-density environments, modern data centers |
Various Bracket Types for Installation
Various bracket types exist to meet diverse installation needs. These brackets ensure secure mounting for both horizontal and vertical PDUs, adapting to different rack designs and space constraints.
Outlet Count and Connector Types
The number and type of outlets on a PDU are crucial for connecting all equipment and planning for future growth.
NEMA Outlets for Power Distribution
In North America, NEMA-style plugs are common on rack PDUs. These often include locking types like L5, L6, and L15, which are prevalent in data centers. California-style plugs also appear in North American data centers, typically for 50A circuits.
IEC Outlets for International Standards
IEC-style plugs are another common option, offering global compatibility. Connectors like C13 and C19 are standard for IT equipment. IEC 60309 connectors are also used.
| Feature | NEMA Standard | IEC Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Connectors | L5, L6, L15 (locking types common in data centers) | C13, C19 (common for IT equipment), IEC 60309 |
| Current Ratings | 15A to 60A | Typically 16A to 63A for IT equipment (standards allow up to 250A) |
Mixed Outlet Configurations for Versatility
Many PDUs offer mixed outlet configurations for greater versatility. For example, PX4 Rack PDUs provide configurations with up to 54 outlets per chassis, including a mix of HDOT Cx* and HDOT C13 outlets. HDOT Cx Outlets are hybrid IEC C13 and C19 outlets that accommodate both C14 and C20 plugs. PX3 Rack PDUs offer up to 60 outlets, typically a mix of C13 and C19. The number of receptacles should account for current devices and future rack growth. Vertically mounted PDUs, being longer, tend to offer more receptacles. Receptacle counts often balance per phase, leading to common counts like 24, 30, and 42 for 3-phase power.
| Connector Type | Maximum Current (Amps) | Voltage Type |
|---|---|---|
| C13 | 10 | AC |
| C19 | 16 | AC |
| C21 | 16 | DC |
Cable Management Features for Your Power Distribution Unit
Effective cable management is essential for maintaining an organized server room, improving airflow, and simplifying maintenance.
Cord Retention Mechanisms
Cord retention mechanisms prevent accidental power cord disconnections. Integrated locking mechanisms in eConnect® PDUs secure cords without proprietary hardware. The APC AP9569 Cord Retention Bracket also prevents accidental disconnections. It reduces cable clutter, which improves organization and enhances airflow for better thermal management.
Optimized Cable Routing Options
Optimized cable routing options help organize cables and improve airflow. Vertical cable managers, installed at rack edges, control up to 200 cables per channel to prevent overcrowding. Horizontal cable managers, designed with D-rings or brush strips, organize patch cables for equipment above and below them. Adhering to cable bend radius compliance, such as 5 times the diameter for Cat6, mitigates signal degradation and microfractures. Color-coded outlets aid in quick identification and organization of connections, reducing errors during maintenance and changes. High-power PDUs streamline cable management by reducing the number of units needed per rack, thereby decreasing cable congestion and improving airflow.
High-Temperature Rating for Server Room Environments
Server room environments often present challenging thermal conditions. Equipment generates significant heat. This requires PDUs to withstand high temperatures for reliable operation.
Suitability for Operating Environments
Rack mount PDUs must endure elevated temperatures. This is especially true in higher power racks. Exhaust temperatures from IT equipment can become very high in these areas. Some intelligent rack PDUs are certified to operate at 60°C (140°F). This certification accommodates these demanding conditions. Manufacturers test and approve these PDUs for safe and reliable operation in 60°C (140°F) environments. This indicates a necessary high-temperature rating for server room applications.
Performance in Data Center Hot Spots
Data centers often have "hot spots." These are areas where heat accumulates due to airflow issues or dense equipment. A PDU with a high-temperature rating performs consistently in these challenging zones. It prevents thermal degradation of components. This ensures continuous power delivery to critical IT infrastructure. High-temperature rated PDUs maintain their performance specifications. They do not falter under the stress of extreme heat. This capability is vital for maintaining uptime and equipment longevity.
Housing Material and Heat Dissipation
The physical construction of a PDU plays a crucial role in its thermal performance. Material choice directly impacts heat management.
Premium Aluminum Alloy Casings
PDU casings often feature high-strength aluminum alloy. This material offers several benefits. It provides lightweight durability. Aluminum also has excellent thermal dissipation properties. This construction ensures ruggedness. It also keeps the PDU light for easier installation. The aluminum housing facilitates passive heat dissipation. This lowers the internal temperature under load.
Effective Heat Management
An optimized internal structure design ensures ample space for heat dissipation. This design works with the aluminum casing. It prevents heat buildup. This ensures stable power delivery to connected devices. Even under full load for one hour, the temperature rise in these PDUs is only 13-28 ℃. This is significantly lower than the national standard of 45 ℃. This demonstrates effective heat dissipation. A venting design further prevents heat accumulation. This contributes to the PDU’s overall stability and reliability.
Essential Advanced Features for Your Power Distribution Unit
Modern server rooms demand more than basic power delivery. Advanced features in power distribution units provide critical insights, control, and protection. These capabilities enhance operational efficiency and safeguard valuable IT infrastructure.
Remote Monitoring Capabilities of a Smart PDU
Smart PDUs transform power management by offering comprehensive remote monitoring. They provide detailed visibility into power consumption and environmental conditions.
Real-time Data Access and Alerts
Smart PDUs stream real-time and historical power and environmental data, accessible through a web browser. They offer granular monitoring, including Per Outlet Power Sensing (POPS), which provides data for individual outlets or devices. This data includes current, voltage, power (kW), apparent power, crest factor, and power factor. Per Inlet Power Sensing (PIPS) offers similar comprehensive monitoring for the entire inlet or infeed, adding reactance and accumulated energy to the metrics. These units also support temperature and humidity monitoring. Smart PDUs can be configured with user-defined power thresholds. They trigger notifications via various channels such as SMS, SNMP traps, or email when these thresholds are breached. This proactive alerting helps prevent issues like overloads and ensures optimal operating conditions. Email alerts notify users about log, event, authorization, power, and configuration messages. SNMP traps based on status, changes, load, temperature, and humidity also provide critical warnings.
Environmental Sensor Integration (Temperature, Humidity)
Smart PDUs directly support environmental sensors for temperature and humidity monitoring. This capability allows for monitoring without a separate solution. SmartSensors are engineered for easy deployment and provide accurate data for environmental monitoring. They are plug-and-play ready with intelligent rack PDUs, making installation quick and non-disruptive. SmartSensors support customizable configurations. They allow a cascade of up to 32 sensor heads linked with standard CAT5/6 cables through a single control device. This comprehensive environmental data helps maintain optimal operating conditions within the rack.
Remote Control and Automation with Switched PDUs
Switched PDUs provide unparalleled control over power at the outlet level. This enables efficient management and automation of connected equipment.
Individual Outlet Switching and Control
Switched PDUs enable remote switching of individual or groups of outlets via web or command-line interfaces. This capability assists data center operators in troubleshooting, managing power consumption, and enhancing security. They offer outlet-level power control, enabling remote management and automated device recovery for various IT and distributed environments. Users can remotely reboot unresponsive equipment, reducing the need for on-site maintenance and preventing downtime. CyberPower Switched Metered-by-Outlet PDUs combine network-grade power distribution with outlet-level monitoring and remote control for advanced energy management. They allow for remote switching of outlets for unscheduled reboots, load shedding, and controlled power-cycling. Risk mitigation is supported through power event notifications via email and SMS text.
Scheduled Power Cycling for Maintenance
Switched PDUs support power cycling and rebooting of connected equipment. This control facilitates powerful applications such as rebooting unresponsive equipment, scheduling power usage, and sequencing startups to prevent overloads. CyberPower’s Switched PDU Series provides network-grade power distribution, remote/local monitoring, and outlet control. They allow for remote management and monitoring of PDU vitals, as well as control of individual outlets and networked clients. Outlets can be switched on and off remotely to reboot connected equipment using the CyberPower Management Console. Planned power cycling of attached equipment can be performed without performance disruption.
Surge Protection and Power Filtering in Your PDU
Protecting sensitive IT equipment from electrical disturbances is paramount. Surge protection and power filtering features in PDUs provide this essential safeguarding.
Equipment Safeguarding Against Spikes
Surge protection diverts excess voltage away from connected devices during power surges. This prevents damage to critical components like servers and routers. This feature enhances equipment protection, preventing damage from sudden voltage fluctuations. ESTEL PDUs utilize rapid voltage change detection. They identify and respond to fluctuations instantly, ensuring operational continuity even during unstable power conditions.
Improving Power Quality for Sensitive Gear
Power filtering eliminates electrical noise and harmonics, ensuring a clean and stable power supply. This improves performance by reducing electrical noise, ensuring consistent operation of sensitive devices. It also increases uptime by minimizing disruptions caused by power disturbances. Voltage harmonics monitoring helps maintain power quality, enhancing system efficiency. These integrated features provide a comprehensive solution for reliable power distribution, protecting equipment and contributing to overall stability and efficiency. Audio/video professionals recognize power conditioners and filters as essential for providing a clean, consistent power supply necessary for reliable A/V performance. Intelligent PDUs are key to a power strategy that ensures resilience and optimal performance in enterprise A/V systems. Best-in-class A/V-specific PDUs deliver advanced features that reduce susceptibility to power fluctuations and protect systems against performance degradation and damage.
Locking Outlets for Enhanced Reliability
Preventing Accidental Disconnections
Accidental power cord disconnections pose a significant risk in server rooms. Such incidents can lead to unexpected downtime and operational disruptions. Locking power cables and secure power connections in PDUs are crucial for preventing these accidental disconnections. This directly contributes to keeping systems operational without interruption. U-Lock Outlets in PDUs are specifically designed to secure power cords. They avoid accidental disconnections and ensure reliable power delivery to connected equipment. This feature is vital for maintaining continuous and secure power delivery.
Ensuring Secure Power Delivery
Locking outlets provide a robust solution for maintaining power integrity. They physically secure power cords to the PDU. This prevents them from being inadvertently pulled out or loosened. This physical security is especially important in dynamic data center environments. Technicians often work in tight spaces. Equipment vibration can also occur. By preventing accidental disconnections, locking outlets ensure a stable and uninterrupted power supply to critical IT infrastructure. This enhances overall system reliability and reduces the risk of costly outages.
Universal Design and Modularity for Your Power Distribution Unit
Future-Proofing Your Investment
A universal design and modularity in a PDU offer significant advantages for future-proofing an investment. These features allow a PDU to adapt to evolving server room needs. They accommodate new technologies and increased power demands without requiring a complete overhaul of the power infrastructure. This flexibility extends the lifespan of the PDU. It also reduces the total cost of ownership over time. Investing in a PDU with a universal design ensures compatibility with a wide range of equipment and rack configurations. This includes horizontal (1U/2U) or vertical (0U) mounting in standard 19” server racks or network cabinets.
Scalability and Functional Module Combinations (e.g., A/V meter, overload protector)
Modularity provides excellent scalability. It allows users to customize PDUs with various functional modules. These modules can include surge protectors, overload protectors, or A/V meters. This capability means a PDU can grow and change with the server room’s requirements. Users can add or swap modules as needed. This avoids the need to replace the entire unit. For example, a basic PDU can become a smart PDU by adding monitoring modules. This adaptability ensures the power distribution system remains efficient and effective. It also supports future expansion and technological advancements.
Safety and Compliance Standards
Adherence to International Regulatory Compliances (CE, GS, RoHS, REACH)
Adherence to international regulatory compliances is paramount for rack mount PDUs. These standards ensure product safety, quality, and environmental responsibility.
- CE Mark: This mark is essential for electronic devices sold in the European Union (EU). It confirms compliance with consumer and workplace safety standards.
- GS: This certification signifies tested safety and quality, often exceeding basic CE requirements.
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): This standard limits the use of hazardous materials in electronic products. It promotes environmental responsibility.
- REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals): This regulation also ensures environmental responsibility. It limits hazardous materials in electronic products.
- UL: This confirms compliance with international safety standards.
- ISO9001: This confirms compliance with international quality standards.
PDUs should also conform to standards like IEC 60905-1. IEC 62368-1 replaced IEC 60950-1 in December 2020. It emphasizes product safety evaluation during the design phase.
Newsunn’s Commitment to Quality and Performance
Newsunn demonstrates a persistent commitment to quality, performance, and safety. The company assures strict adherence to international regulatory compliances. Newsunn’s manufacturing unit has acquired and maintained various approval standards, regulations, and certifications. This makes their products acceptable and highly reliable across the world. Their engineers possess extensive experience. They work with various regulatory compliance and requirements. This ensures all products meet global benchmarks for safety and performance.
Making the Right Power Distribution Unit Selection
Choosing the correct power distribution unit requires careful consideration. Decision-makers must align PDU capabilities with specific operational needs. This ensures optimal performance and long-term reliability for the server room.
Budget Allocation and Value Proposition
Balancing Cost with Feature Set
Organizations must balance the cost of a PDU with its feature set. They evaluate specific needs. Basic PDUs offer cost-effective solutions for smaller-scale operations. Smart PDUs provide better long-term value. They include advanced features like remote control or environmental monitoring. Managed rack PDUs, despite higher upfront costs, lead to significant savings. They achieve this through optimized energy usage and reduced downtime. Prioritize essential features like power capacity and outlet configurations if the budget is limited.
Assessing Long-term Value and ROI
Assessing long-term value involves looking beyond the initial purchase price. Managed rack PDUs improve energy efficiency through real-time monitoring. They also reduce downtime risks with consistent power delivery and alarming capabilities. For high-density environments, features like outlet-level monitoring and environmental sensors are crucial. They protect equipment and ensure optimal performance. A well-built PDU reduces the need for frequent replacements. Safety features, such as surge protection, prevent costly equipment damage and downtime. Investing in superior durability and features avoids frequent replacements and equipment damage. This leads to overall savings.
Vendor Reputation and Support for Your PDU
Reliability, Warranty, and After-Sales Service
A reputable PDU vendor offers strong reliability, warranty, and after-sales service. Key indicators include a strong uptime track record and a high Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) rating. Comprehensive support and warranty coverage are also vital. Manufacturers often provide a standard warranty. For example, Eaton offers 3-5 years, Tripp Lite 2-5 years, CyberPower up to 5 years, and Geist 3 years. Warranty coverage and maintenance programs indicate a company’s commitment to product reliability. Leading PDU manufacturers offer extensive warranties covering parts and labor for several years. Some extend coverage to specific components. Routine maintenance, including scheduled inspections and firmware updates, helps prevent failures. It also prolongs equipment lifespan.
Technical Assistance and Expertise
Reputable PDU vendors prioritize reliable customer support. They establish global service networks for round-the-clock technical assistance. They offer multiple contact channels like phone, email, and live chat. Often, dedicated portals provide troubleshooting and documentation. Strong service availability minimizes downtime. It quickly resolves issues, especially in mission-critical environments. This significantly influences purchasing decisions. Technical assistance and expertise ensure smooth operation and quick problem resolution.
Selecting the optimal rack mount PDU is paramount for maximizing server room performance and ensuring continuous operation. This involves careful consideration of power requirements, the necessary number of outlets, and robust monitoring capabilities. A strategic PDU choice, considering current needs and future growth, safeguards infrastructure and optimizes energy management. It requires assessing total load, planning for future expansion, and ensuring physical fit with appropriate mounting options. A well-chosen power distribution unit is a critical investment in the longevity and efficiency of your data center. It offers significant energy cost reductions and improved uptime, leading to a strong return on investment.
FAQ
What is a rack mount PDU’s main purpose?
A rack mount PDU distributes electrical power to multiple devices within a server rack. It ensures organized and efficient power delivery to IT equipment.
How do basic and metered PDUs differ?
Basic PDUs simply distribute power. Metered PDUs add local monitoring capabilities. They display real-time power usage on a built-in screen.
Why is the 80% rule crucial for PDU capacity?
The 80% rule prevents overloading circuits. It ensures continuous electrical loads do not exceed 80% of the PDU’s maximum current rating. This prevents overheating and trips.
What advantages do switched PDUs offer?
Switched PDUs provide remote control over individual outlets. Users can remotely power cycle equipment. This improves troubleshooting and energy management.
How do ATS PDUs ensure power redundancy?
ATS PDUs automatically switch to a backup power source. They do this when the primary source fails. This ensures continuous power for critical loads.
Why are high-temperature ratings important for PDUs?
High-temperature ratings ensure PDUs operate reliably in hot server room environments. They withstand exhaust heat from IT equipment. This prevents thermal degradation.
What compliance standards should a PDU meet?
A PDU should meet international standards like CE, GS, RoHS, and REACH. These ensure safety, quality, and environmental responsibility. Newsunn adheres to these.
Post time: Jan-13-2026

