Power distribution units are essential devices that manage and deliver electrical power to various IT equipment. They ensure a consistent and dependable power supply within data centers and server rooms. These units distribute, monitor, and control power for critical infrastructure like servers and networking devices. Power-related outages account for 43% of significant data center downtime. An Intelligent PDU helps prevent such disruptions by providing advanced monitoring and control capabilities.
Key Takeaways
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs) deliver and manage electricity to IT equipment. They prevent power outages in data centers.
- PDUs are better than power strips. They offer rack-mount designs, circuit protection, and advanced power management.
- Different PDU types exist for various needs. These include Basic, Metered, Monitored, Switched, and Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) PDUs.
- Intelligent PDUs offer advanced features. They monitor power use, allow remote control, and provide environmental data.
- PDUs ensure reliable power. They prevent system downtime and help with power redundancy.
- PDUs help manage power efficiently. They balance electrical loads and plan for future power needs.
- PDUs improve rack organization. They reduce cable clutter and optimize airflow for better cooling.
- Choose the right PDU by checking its location, power needs, and outlet types. Consider advanced features like network connectivity.
Understanding the Core Function of Power Distribution Units

Power distribution units perform a critical task. They take power from a single source and distribute it to multiple devices. This process ensures each piece of equipment receives the necessary electrical current.
Basic Power Distribution Principles
Input Power Connection
A power distribution unit begins its operation by connecting to a primary power source. This connection typically uses a heavy-duty input cable. The source can be a wall outlet, an uninterruptible power supply (UPS), or a generator. Different regions and power requirements dictate the type of input plug and voltage. For example, some units use NEMA plugs, while others use IEC connectors. The PDU acts as a central hub for power intake.
Output Receptacles
After receiving power, the PDU delivers it to connected IT equipment through various output receptacles. These outlets are specifically designed for data center environments. Common types include IEC C13 and C19 receptacles. Each receptacle provides a secure connection. This design prevents accidental disconnections, which could lead to downtime. The PDU efficiently channels power to servers, switches, and other critical hardware.
Beyond Standard Power Strips
Power distribution units offer capabilities far beyond those of a common power strip. They provide robust power management for demanding IT environments. Their design and features cater to professional infrastructure needs.
Rack-Mount Design
Most PDUs feature a rack-mount design. This allows for seamless integration into standard server racks. They can mount horizontally across a rack’s width or vertically along its side. This design optimizes space within crowded data centers. It also helps organize cables, reducing clutter and improving airflow. The sturdy construction ensures durability in continuous operation.
Integrated Circuit Protection
Power distribution units incorporate advanced safety features. These features protect connected equipment from electrical anomalies. They include integrated circuit breakers for overload protection. If a circuit draws too much current, the breaker trips automatically. This prevents damage to the PDU and attached devices. Many PDUs also feature locking outlets. These outlets secure power cords, preventing accidental unplugging. This table highlights key differences between PDUs and standard power strips:
| Feature | Power Distribution Unit (PDU) | Standard Power Strip |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Distributes electrical power with advanced management | Extends available electrical outlets |
| Functionality | Load balancing, real-time monitoring, overload prevention, remote management, stable and uninterrupted power | Basic outlet extension, often with surge protection |
| Environment | Professional settings (data centers, server rooms, industrial facilities) | Homes, offices, residential, and commercial sectors |
| Construction | Heavy-duty, durable aluminum alloy housing | Compact, lightweight, portable |
| Outlet Capacity | High (e.g., 24 locking outlets) | Typically 4 to 8 outlets |
| Safety Features | Overload protection (automatic trip-off), locking outlets (prevents accidental disconnections) | Surge protection (guards against voltage spikes), temperature resistance |
| Purpose | Reliable and efficient power management, prevents costly disruptions, reduces downtime/damage | Convenience, powers multiple devices from one socket |
This comprehensive protection ensures reliable power delivery. It minimizes the risk of costly disruptions.
Diverse Types of Power Distribution Units
Organizations deploy various power distribution units to meet specific power management needs. Each type offers distinct features, ranging from basic power delivery to advanced monitoring and control.
Basic Power Distribution Units
Basic power distribution units represent the most straightforward option for power delivery. They provide essential functionality without complex features.
Simple Power Delivery
Basic power distribution units are the simplest form of PDU. They perform their core function of distributing power effectively. These units do not possess the advanced features found in other PDU types. They help organize rack cabling, which reduces clutter. Some models include plug clips. These clips prevent accidental disconnections, ensuring continuous power to devices.
Cost-Effective Solutions
Basic power distribution units offer a cost-effective and easy-to-deploy solution. They are the most traditional option for power distribution. These units provide essential features for distributing power to rack-mounted equipment. They lack advanced management or monitoring capabilities. Companies use them in scenarios where only basic power distribution is necessary. Remote monitoring and control are not required for these applications. They suit small data centers or less critical applications well.
Metered Power Distribution Units
Metered power distribution units offer local power monitoring capabilities. They provide real-time data directly at the rack.
Local Power Monitoring
Metered power distribution units allow administrators to monitor power usage directly at the unit. A digital LCD meter often displays the current draw for connected equipment in amps. This feature enables real-time load monitoring. For example, CyberPower Metered Power Distribution Units feature such a digital LCD meter. This helps prevent overloads and ensures stable operation.
Real-time Current and Voltage Display
These power distribution units provide real-time displays of critical electrical parameters. Users can view voltage, current, and power (kW). More advanced models also show active power (kW), apparent power (kVA), reactive power (kVAr), and power factor (PF). This detailed information helps users understand power consumption patterns. It also assists in making informed decisions about power capacity.
Monitored Power Distribution Units
Monitored power distribution units take power management a step further. They offer remote monitoring capabilities.
Remote Power Monitoring Capabilities
Monitored power distribution units allow users to track power usage from a remote location. They connect to a network, providing access to power data through a web interface or network management system. This capability enables proactive management of power resources. It helps identify potential issues before they cause downtime.
Environmental Sensor Integration
Many monitored power distribution units integrate with environmental sensors. These sensors provide crucial data about the data center environment. Common sensors include temperature and humidity sensors. Some units also support heat sensors or liquid detection sensors. This integration helps maintain optimal operating conditions. It also alerts staff to environmental changes that could affect equipment performance.
Switched Power Distribution Units
Switched power distribution units offer advanced control over individual outlets. They provide capabilities beyond simple power delivery and monitoring.
Remote Outlet Control
Switched PDUs give users full remote access through a network connection. Administrators can power on or off individual outlets using a web interface or management software. This remote control saves time and travel. It allows immediate shutdown or restart of malfunctioning devices from any location. Remote management possibilities include rebooting servers, activating backup systems, and powering down devices for disaster preparedness. Users can perform these actions with a few clicks or keystrokes.
Power Cycling for Devices
A switched PDU specifically adds the ability to control outlets. Users can turn them on, off, or cycle them as needed. This capability enables powerful applications. These include rebooting unresponsive equipment, scheduling power usage, and sequencing startups to prevent overloads. Power cycling, the process of turning devices off and on to clear faults, becomes simpler and safer with switched PDUs. They allow remote reboots with a few clicks. Automated sequences can be programmed to follow a specific order during power-up or shutdown. For example, critical systems can turn on first.
Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) Power Distribution Units
Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) power distribution units provide critical redundancy for power delivery. They ensure continuous operation by managing multiple power sources.
Redundant Power Source Management
ATS power distribution units connect to both primary and backup power sources through dual power interfaces. Internal control logic, often a microprocessor, continuously monitors these sources. It checks for voltage and frequency. This monitoring identifies any failure in the primary power source. Sensors for voltage and frequency monitoring continuously detect irregularities. This enables proactive measures and optimizes load management.
Seamless Power Transfer
When the primary power source fails, the ATS checks the secondary source for stability. It ensures the power is within acceptable voltage and frequency tolerance levels. The ATS then automatically and near-instantaneously switches the load circuit to the secondary source. When the primary source restores, the ATS returns the load from the secondary source to the primary source. Some ATS units use a "closed transition" or "make-before-break" method. This momentarily parallels primary and backup sources to eliminate power interruptions. Static Transfer Switches (STS) use solid-state components like thyristors or SCRs. They achieve rapid, millisecond-level power transfers without moving parts. This ensures uninterrupted power for critical systems.
High-Density and Specialized Power Distribution Units
High-density and specialized power distribution units address the unique demands of modern IT environments. They cater to specific equipment like blade servers.
Optimized for Blade Servers
High-density racks, especially those with blade servers exceeding 50% capacity, present significant challenges. These challenges involve power distribution and cooling compared to traditional server racks. Three-phase power systems are crucial for efficiently meeting high-power demands. These demands can reach 20-30 kW per rack in densely packed server environments. They support higher capacities and use smaller, more manageable wiring. This reduces installation costs and complexity. Redundant A/B power feeds with granular circuit-level monitoring are essential. They maintain uptime and ensure efficient energy usage in these high-density environments.
Custom Configuration Options
Specialized PDUs offer custom configuration options to fit diverse infrastructure needs. Tall and deep racks accommodate vertical PDUs, structured cabling, airflow management tools, and liquid cooling systems. Accessible placement ensures breakers, PDUs, and cable trays remain operational and accessible. This holds true even when racks are fully populated. Switched Rack PDUs (rPDUs) offer remote management capabilities. They enhance performance and reliability for demanding applications like AI and High-Performance Computing (HPC), which include blade servers.
The Role of Intelligent Power Distribution Units
Intelligent Power Distribution Units (iPDUs) represent a significant advancement in power management. They offer capabilities far beyond basic power distribution units. These devices provide advanced features for monitoring, control, and environmental insights within IT environments.
Advanced Monitoring Capabilities
Intelligent PDUs provide comprehensive visibility into power usage. They help administrators make informed decisions and prevent potential issues.
Remote Power Usage Tracking
Intelligent PDUs enable remote monitoring of power usage. Administrators can track real-time data on energy consumption, voltage, and current for each outlet. This remote access allows for proactive management. It helps identify abnormal energy consumption patterns. Users can also receive real-time alarms for critical events. This capability ensures administrators stay informed about their power infrastructure from any location.
Real-time Data on Energy Consumption
These advanced units offer detailed real-time data. They provide metrics like Neutral Voltage, Total Harmonic Distortion (THD), and Voltage Dips and Swells. This data helps assess power quality with high accuracy, often ±0.5% for energy metering. Some intelligent PDUs also offer waveform capture. This feature provides intuitive visualizations. It helps users understand the health of power sources and connected devices. Furthermore, they offer circuit breaker trip forensics. This gives insights into which outlet and device caused a trip event. It also includes Trip Cause Outlet Handling to isolate defective equipment. Intelligent PDUs can integrate with Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) solutions. This provides a single access point to view real-time power and environmental data. It also allows for generating trend reports.
Enhanced Power Control
Intelligent PDUs offer significant control over power delivery. This enhances operational efficiency and troubleshooting.
Remote Outlet Switching
Switched PDUs provide remote control over individual outlets. Administrators can turn outlets on or off using a web interface or management software. This feature allows for immediate shutdown or restart of malfunctioning devices. It saves time and reduces the need for on-site intervention. Remote management possibilities include rebooting servers or activating backup systems.
Troubleshooting and Energy Saving
The ability to remotely control outlets simplifies troubleshooting. Users can power cycle unresponsive equipment with a few clicks. This clears faults and restores functionality. Intelligent PDUs also support scheduled power usage. This helps in energy saving. For example, administrators can power down non-critical devices during off-peak hours. This reduces power wastage and optimizes overall energy consumption.
Environmental Insights
Intelligent PDUs extend their capabilities to environmental monitoring. They help maintain optimal operating conditions within data centers.
Temperature and Humidity Sensors
Intelligent PDUs often include built-in sensors. These sensors monitor environmental conditions like temperature and humidity within the data center. They provide crucial data for maintaining equipment performance and longevity. For instance, Raritan PX Intelligent PDUs offer granular environmental monitoring. They use a full set of plug-and-play environmental sensors. These sensors can monitor any environmental conditions in the data center.
Data Center Condition Monitoring
By collecting and analyzing environmental data, operators can identify cooling inefficiencies, hot spots, or airflow recirculation in IT equipment. The PX follows ASHRAE 90.4 guidelines. It integrates sensors directly with the Xerus technology platform’s advanced alerting and threshold intelligence. This allows for immediate alerts in case of abnormal environmental changes. Such alerts enable quick responses. They prevent potential equipment failures. Panduit Intelligent PDUs (iPDUs) continuously scan for physical environmental conditions. This protects critical IT equipment from risk.
Energy Efficiency Optimization
Intelligent Power Distribution Units play a crucial role in optimizing energy efficiency within IT infrastructure. They provide the tools necessary to understand, control, and reduce power consumption. This leads to significant cost savings and a smaller environmental footprint.
Identifying Power Wastage
Intelligent PDUs, often called ‘smart’ PDUs, give data center managers the ability to remotely monitor real-time power usage. They track data and event logs, along with the current drawn by each PDU and individual outlet. This capability helps pinpoint equipment that uses a lot of energy. It also detects servers that are underutilized or "comatose," meaning they consume power but do little work. This information is vital for effective capacity planning. Intelligent PDUs can also alert managers to potential equipment failure or when a PDU approaches its total power capacity. This allows for proactive measures to prevent outages.
For example, Target, in one of its ENERGY STAR certified data centers, powered down two unloaded 300 kVA PDUs. This action resulted in an annual saving of 261,000 kWh. This demonstrates the real energy efficiency improvements possible by actively managing PDU usage. Metered PDUs specifically measure data center power usage at the unit or outlet level. This enables accurate tracking of energy consumption and helps prevent overloads. They reveal power consumption for each piece of equipment. This helps identify devices contributing to inefficiency.
Improving Overall Efficiency
Intelligent PDUs offer remote on/off switching for each outlet. This allows administrators to shut down equipment not in use, conserving energy. They also enable remote power cycling of connected devices. This helps address inefficiency by rebooting unresponsive systems. Switched PDUs provide the added benefit of remote control over individual outlets. Operators can turn devices on or off as needed to optimize workflow. This enhances monitoring for precise billing in colocation facilities. It also provides real-time alerts for potential overloads. This helps distribute power effectively and avoids downtime.
Intelligent PDUs provide real-time current (amps), voltage, power (kVA, kW), and energy consumption (kWh) data. Managers can monitor power usage at the device or PDU level. Environmental sensors attached to intelligent PDUs help data center managers improve efficiency. They provide optimal control over AC, heat, and humidity. By monitoring power consumption down to the device level, iPDUs help identify energy hogs. They also find equipment that is no longer needed, such as servers running at low average power.
Remote power cycling and control allow for remote rebooting of crashed systems. It also enables powering down IT equipment not in use during off-hours. This reduces costs and power consumption. Intelligent PDUs help in understanding power consumption. They baseline utilization to predict equipment failure. They also identify stranded capacity and accurately plan for future power needs. They can alert IT administrators to potential issues like nearing capacity or equipment failure. This allows for proactive intervention to maintain uptime and optimize power distribution. Intelligent PDUs work with Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) solutions. This provides comprehensive insights into power loads, trends, and capacity forecasts. This contributes to a greener data center. Metering at the unit, inlet, or outlet level allows users to understand and trend power usage and capacity data. This enables more accurate provisioning of resources and improved efficiency by tracking metrics like Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE). Alerts can trigger based on conditions like out-of-threshold temperature and load. This enables proactive management of potential issues.
Why Power Distribution Units are Essential for IT Infrastructure

Power distribution units are vital components for modern IT infrastructure. They ensure the smooth and efficient operation of critical equipment. These devices provide numerous benefits, from preventing costly downtime to optimizing space within data centers.
Ensuring Reliable Power Delivery
Reliable power delivery forms the backbone of any stable IT environment. Power distribution units play a critical role in maintaining this reliability.
Preventing System Downtime
Reliable power delivery from these units significantly improves system availability. It enhances scalability and boosts power efficiency. This also increases cooling efficiency and reduces network downtime. Ultimately, it leads to higher data center productivity. Power distribution units offer reliable power distribution, which prevents interruptions. Their remote monitoring capabilities allow real-time oversight of power usage. This helps identify issues proactively. Alarming capabilities notify users of power threshold breaches, enabling quick intervention. Environmental monitoring proactively detects conditions like heat and moisture. These conditions could lead to equipment failure. Remote connectivity enables off-site access to monitor and configure alerts. This prevents downtime from afar.
Power Redundancy Implementation
Many IT environments require redundant power sources to ensure continuous operation. Power distribution units facilitate this by connecting to multiple power feeds. Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) PDUs, for example, seamlessly switch between primary and backup power sources. This ensures that equipment receives uninterrupted power even if one source fails. This redundancy is crucial for mission-critical applications. It protects against power outages and maintains business continuity.
Optimizing Power Management
Effective power management is key to operational efficiency and cost savings in data centers. Power distribution units provide the tools for this optimization.
Effective Load Balancing
Modern power distribution units offer advanced power management and metering capabilities. This functionality is crucial for data centers. It helps identify inefficiencies, effectively balance loads, and support strategic capacity planning. Built-in meters in rack PDUs provide continuous power quality monitoring. They measure power consumption and identify stranded capacity. They also provide IT load information for calculating parameters like PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness). This is vital for strategic capacity planning. Monitoring capabilities exist at both the PDU infeed and outlet/device level. This helps detect potentially harmful power events.
Strategic Capacity Planning
Metered rPDUs provide local power consumption data. This includes current, voltage, and power factor. This data aids in capacity planning and electrical load balancing. Monitored rPDUs offer remote real-time power consumption metrics. These are accessible via a secure web interface. This enables more precise load balancing. It limits stranded power without risking shorts. It also improves billing accuracy by tracking power usage with greater precision. Switched rPDUs allow remote management. They can limit power usage at individual outlets. This prevents accidental overloads.
Improving Space and Cable Management
Efficient space and cable management are essential for organized and maintainable IT infrastructure. Power distribution units contribute significantly to these aspects.
Organized Rack Layouts
Rack-mounted PDUs are crucial for optimizing space. They streamline layouts and keep IT infrastructure organized. They provide more room, improve airflow, and facilitate faster maintenance. By mounting directly in the server rack, PDUs help keep cables neat. They prevent tangles and simplify installation. This eliminates the need to run cables across the floor or behind equipment. This allows for grouping power cords and network cables. It makes connections easier to trace. Rack-mounted PDUs maximize space efficiency. They allow more devices to be installed in server racks without clutter.
Reducing Cable Clutter
Good cable management with rack-mounted PDUs enhances airflow within the rack. This helps keep servers cool and prolongs equipment life. Rack-mounted PDUs offer a significant advantage over floor-mounted units and basic power strips. They save space because they install directly within server racks. This setup ensures equipment remains organized and cables stay tidy. It contributes to an efficient and manageable IT environment. Their ability to mount easily in a 19-inch server rack or cabinet makes them an ideal solution for environments with limited space.
Selecting the Right Power Distribution Unit
Choosing the correct power distribution unit is crucial for optimizing IT infrastructure. This decision impacts efficiency, reliability, and scalability. Organizations must consider several factors to ensure they select the best PDU for their specific needs.
Installation Location and Form Factor
The physical characteristics and placement of a PDU significantly affect its utility within a data center.
Horizontal vs. Vertical Mounting
PDUs come in various form factors designed for different installation methods. Vertical PDUs, often called Zero U PDUs, mount vertically at the rear or side of the rack. They save space and are ideal for high-density racks. They also offer easy access to outlets and efficient cable management. Horizontal PDUs, typically 1U or 2U, mount horizontally within the rack’s 19-inch mounting rails. They are easy to install and suit racks with lower power density. They can mount at the front or rear.
| Form Factor | Installation Location | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical PDUs (Zero U) | Mounted vertically at the rear or side of the rack, typically on the rack’s uprights or within the side panels. | Space-saving, ideal for high-density racks, easy access to outlets, efficient cable management, available in various lengths and outlet configurations. |
| Horizontal PDUs (1U/2U) | Mounted horizontally within the rack’s 19-inch mounting rails, occupying 1U or 2U of rack space. | Easy to install, suitable for racks with lower power density, can be mounted at the front or rear, may obstruct airflow if mounted at the front. |
Rack Unit Requirements
Rack unit requirements dictate the physical space a PDU occupies. Horizontal PDUs consume 1U or 2U of rack space. Vertical PDUs, however, utilize the unused vertical space at the side or rear of the rack. This makes them ideal for maximizing rack density.
Power Requirements and Capacity
Understanding the power needs of connected equipment is fundamental for PDU selection.
Voltage and Amperage Ratings
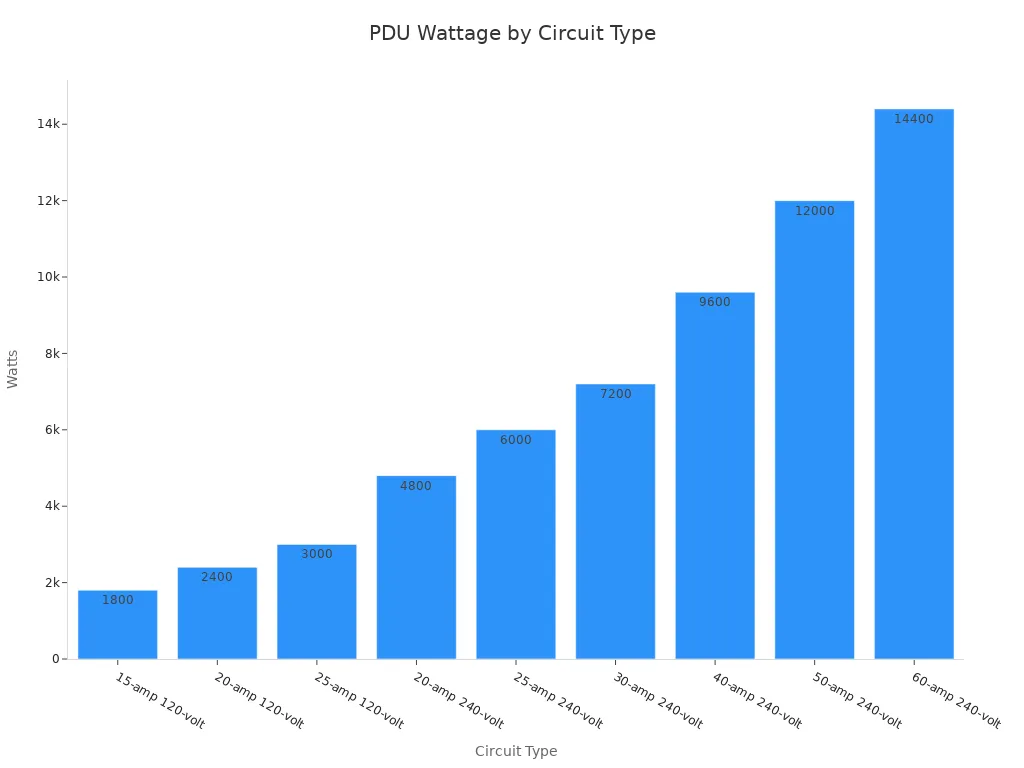
Administrators must match the PDU’s voltage and amperage ratings to the input power source and the equipment’s requirements. Common voltage ratings include 120V, 208V, and 240V. Amperage ratings vary widely, from 15A to 60A or higher. Selecting a PDU with appropriate ratings prevents overloads and ensures stable power delivery.
Total Wattage Calculation
Calculating total wattage helps determine the PDU’s capacity. The fundamental electrical formula, Amps × Volts = Watts, determines power consumption. For example, a server drawing 8 Amps on a 208V circuit consumes 1,664 Watts of power. Watts measure the actual energy being used. For 3-phase PDUs, the total power capacity is calculated by multiplying the voltage, current, and power factor of the system. A setup operating at 208V with a current of 30A and a power factor of 0.95, for instance, has a total power capacity of approximately 10,260 watts.
Outlet Types and Quantity
The types and number of outlets on a PDU must align with the equipment it powers.
NEMA and IEC Standards
PDUs feature various outlet types conforming to NEMA (North American) or IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards. NEMA outlets are common in North America, while IEC C13 and C19 outlets are standard in data centers worldwide. Ensure the PDU’s outlets match the power cords of the equipment.
Number of Receptacles Needed
Determine the exact number of receptacles required by counting all devices needing power. It is advisable to include a few extra outlets for future expansion. This prevents the need for additional PDUs later.
Advanced Features and Connectivity
Advanced power distribution units offer sophisticated features. These features enhance their functionality and integration within IT environments. They provide more than just power delivery.
Network Connectivity Options
Modern PDUs include robust network connectivity. This allows remote management and data access. Gigabit Ethernet provides seamless connections to modern switching infrastructure. Some PDUs offer network cascading. This feature allows a single network connection to be shared across multiple intelligent PDUs. It reduces the number of required Ethernet ports. Users can also find built-in wireless options. A Wi-Fi adapter enables completely wireless deployments. This eliminates the need for physical network cables. These PDUs are compatible with a vast ecosystem of environmental sensors. This allows monitoring of various parameters. They also offer extensive DCIM interoperability. An open API allows integration with any DCIM or BMS software. This provides centralized control. Mass configuration options are available. These include TFTP, PXE over DHCP, and JSON-RPC. These options help configure numerous PDUs efficiently.
Management Software Integration
Intelligent PDUs integrate with various management software solutions. This integration centralizes power management. Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) software is a common example. DCIM platforms collect data from PDUs. This includes power consumption, temperature, and humidity. They present this data in a unified dashboard. This allows administrators to monitor the entire IT infrastructure. The software can also trigger alerts for critical events. For instance, it notifies staff if a PDU approaches its power limit. This proactive approach helps prevent outages. Integration with management software streamlines operations. It improves decision-making for power capacity and efficiency. This connectivity transforms PDUs into intelligent components of a smart data center.
Best Practices for Power Distribution Unit Deployment and Management
Effective deployment and diligent management of power distribution units are crucial for maintaining a robust and efficient IT infrastructure. These practices ensure optimal performance, prevent downtime, and extend equipment lifespan.
Strategic PDU Placement
Proper placement of power distribution units within racks significantly impacts operational efficiency.
Optimizing Airflow within Racks
Strategic PDU placement directly influences airflow. Vertical power distribution units, for example, mount along the side or rear of a rack. This positioning keeps cables organized and out of the way. It prevents cable clutter from obstructing airflow. Good airflow is essential for cooling IT equipment. It helps maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Accessibility for Maintenance
Accessibility is another key consideration. Technicians need easy access to power distribution units for maintenance, troubleshooting, and equipment changes. Placing PDUs where they are easily reachable simplifies these tasks. It reduces the time required for interventions. This also minimizes disruption to other rack components.
Effective Load Balancing Strategies
Implementing effective load balancing strategies prevents power-related issues and optimizes energy use.
Distributing Power Evenly
Real-time power monitoring provides immediate insights into energy consumption. It tracks power usage at both outlet and circuit levels. This visibility helps identify inefficiencies. It also enables corrective actions before issues escalate. Local monitored PDUs display metrics like current, voltage, and power consumption. This helps pinpoint areas nearing capacity. It allows for early detection of potential overloads. Load balancing and optimization involve distributing power loads evenly across circuits using this real-time data. This prevents specific outlets or circuits from becoming overburdened. It reduces the likelihood of failures. IBM achieved a 30% reduction in energy costs in its data centers by implementing real-time monitoring and predictive analytics to effectively balance loads. Studies indicate that real-time monitoring systems can reduce energy consumption by up to 20%.
Preventing Overloads
Configuring specific warning thresholds for power usage acts as a safeguard. These thresholds trigger visual or audible alerts when energy consumption approaches critical levels. This enables timely intervention. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of overloading phases and potential equipment damage. Power distribution units often integrate safety features. Circuit breakers automatically interrupt electrical flow when a circuit draws too much current. This protects connected equipment from damage. Surge protection shields sensitive electronic equipment from voltage spikes. Overcurrent protection detects excessive current and shuts off power. Overvoltage protection guards against high voltage levels. Short circuit protection immediately cuts power during sudden current surges. Proper grounding provides a safe path for electricity to dissipate.
Leveraging Remote Management
Remote management capabilities of power distribution units offer significant advantages for proactive infrastructure oversight.
Proactive Monitoring and Alerts
Intelligent power distribution units provide real-time environmental monitoring. Integrated sensors track temperature and humidity. This offers a comprehensive view of rack health. These units send instant alerts via email or SNMP trap when power thresholds or environmental conditions are exceeded. Per-outlet power metering identifies specific devices causing power spikes. This allows for immediate detection of anomalies. Logging every reboot on a dashboard helps understand the cause, such as updates or power surges.
Remote Troubleshooting Capabilities
Remote management enables efficient troubleshooting. Administrators can remotely reboot individual outlets. This allows for remote restoration of service without requiring on-site intervention. This capability saves time and reduces the need for physical presence in the data center. It ensures rapid response to issues.
Regular Maintenance and Monitoring
Regular maintenance and diligent monitoring of power distribution units are paramount. These practices ensure the continuous reliability and optimal performance of IT infrastructure. They prevent unexpected failures and maximize the lifespan of critical equipment.
Firmware Updates and Patches
Firmware represents the embedded software controlling a PDU’s operations. Manufacturers frequently release updates for this firmware. These updates often introduce new features, enhance security protocols, or fix identified bugs. Administrators must apply these updates promptly.
- Security Enhancements: Updates patch vulnerabilities, protecting the PDU and connected devices from cyber threats.
- Feature Improvements: New firmware versions can unlock advanced functionalities, improving power management capabilities.
- Bug Fixes: Updates resolve software glitches, ensuring stable and error-free operation.
Ignoring firmware updates can leave PDUs vulnerable to security breaches or operational inefficiencies. Organizations establish a regular schedule for reviewing and applying these patches. This proactive approach maintains the PDU’s integrity and performance.
Performance Reviews and Adjustments
Regularly reviewing PDU performance data is crucial for effective power management. Administrators analyze various metrics to assess operational health and efficiency.
They examine power consumption trends, identifying any anomalies or sudden spikes. This review helps pinpoint underutilized equipment or potential overloads. They also monitor power quality data, such as voltage stability and current draw. This ensures the PDU delivers clean, consistent power to connected devices. Environmental data from integrated sensors, like temperature and humidity, also undergoes scrutiny. This helps maintain optimal operating conditions within the rack.
Based on these performance reviews, administrators make necessary adjustments. They might rebalance loads across different PDU outlets to prevent overstressing specific circuits. They could also modify power thresholds or alert settings to better align with current operational needs. This continuous cycle of review and adjustment optimizes energy usage. It also extends the life of IT equipment. Proactive management ensures the PDU consistently meets the demands of the evolving IT environment. It prevents costly downtime.
Power distribution units are indispensable components for modern IT environments. They ensure the efficient and reliable operation of servers and networking equipment. Advanced PDU solutions offer comprehensive benefits. They reduce energy waste by up to 20%. They also improve reliability by 25% in installations with backup power. Downtime can decrease by 15%. These units provide enhanced reliability, efficiency, and scalability. Therefore, informed selection and diligent management of power distribution units are crucial. This ensures optimal airflow, supports future expansion, and maintains safety standards within the data center.
FAQ
What is a Power Distribution Unit (PDU)?
A PDU distributes electrical power from a single source to multiple IT devices. It ensures a consistent and dependable power supply within data centers and server rooms. PDUs manage and deliver power to critical infrastructure.
How does a PDU differ from a standard power strip?
PDUs offer robust power management for demanding IT environments. They feature rack-mount designs, integrated circuit protection, and advanced monitoring. Standard power strips primarily extend available electrical outlets for basic use.
What are the main types of Power Distribution Units?
Main types include Basic, Metered, Monitored, Switched, and Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) PDUs. Each type offers specific features for power delivery, monitoring, or control, catering to diverse IT needs.
Why are Intelligent PDUs essential for IT infrastructure?
Intelligent PDUs provide advanced monitoring, remote control, and environmental insights. They track power usage, enable remote outlet switching, and integrate environmental sensors. This optimizes energy efficiency and prevents downtime.
How do PDUs help with cable management in server racks?
Rack-mount PDUs integrate directly into server racks. This design keeps cables neat and organized. It prevents tangles and simplifies installation. This setup also improves airflow and maximizes space efficiency within the rack.
What is the function of an Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) PDU?
An ATS PDU provides power redundancy. It connects to primary and backup power sources. The ATS automatically and seamlessly switches the load to the secondary source if the primary source fails. This ensures continuous operation.
How do PDUs prevent electrical overloads?
PDUs incorporate integrated circuit breakers. These breakers automatically trip if a circuit draws too much current. This prevents damage to the PDU and connected devices. Many PDUs also offer real-time load monitoring to detect potential overloads.
Post time: Dec-30-2025

