
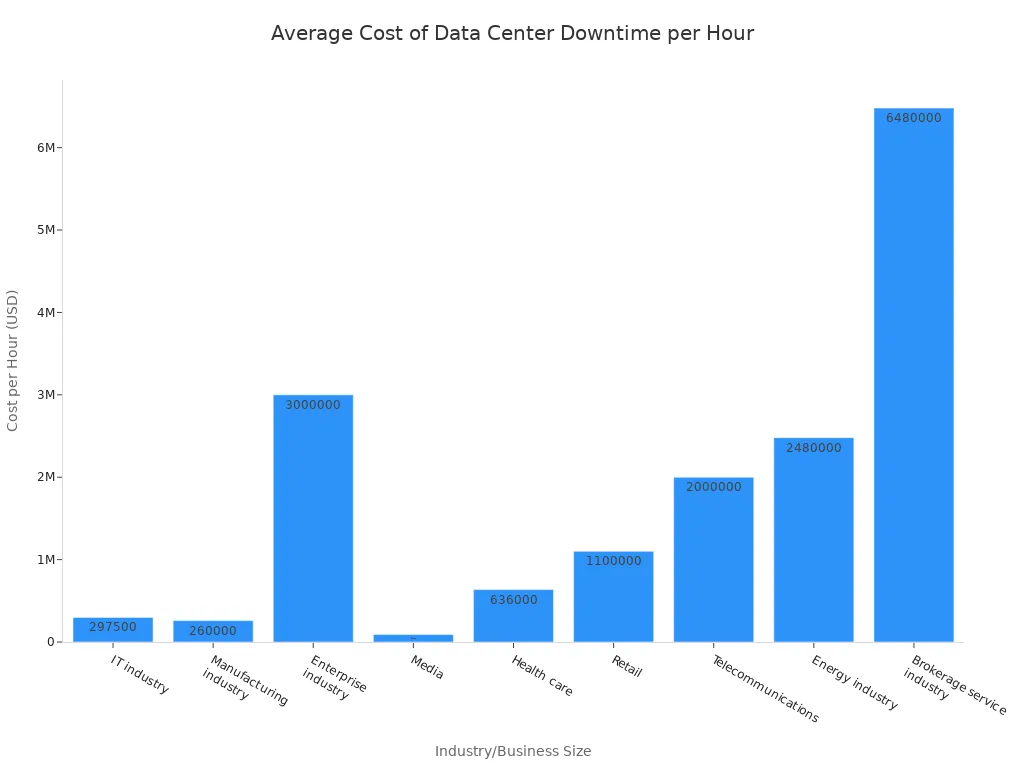
Advanced Rack Power Distribution Units serve as the primary defense against costly downtime. Power-related issues account for over half of all major data center outages. Such disruptions carry significant financial consequences for businesses. For instance, the average cost of data center downtime per hour varies greatly across industries:
These units move beyond a basic PDU. They offer essential features for uninterrupted operations. An Intelligent PDU provides real-time monitoring and control. This helps maintain system stability and prevents financial losses.
Key Takeaways
- Advanced Rack PDUs are like smart power strips for data centers. They do more than just give power.
- These smart PDUs watch power use and room conditions in real-time. This helps stop problems before they start.
- You can control these PDUs from far away. You can turn devices on or off without being in the server room.
- Advanced PDUs protect your equipment from power surges and too much power. This keeps your devices safe.
- They send alerts if something goes wrong. This helps you fix issues quickly and avoid shutdowns.
- Some PDUs can switch to a backup power source if the main one fails. This keeps everything running smoothly.
- Choosing the right PDU means looking at how much power you need now and in the future. It also means picking a good brand.
Understanding Advanced Rack Power Distribution Units for Uptime

Beyond Basic Power Strips: The Evolution of Rack PDUs
Core Functions: Power Distribution and Delivery
Basic power strips simply distribute electricity. They provide power to multiple devices from a single source. However, modern data centers demand more than just basic power delivery. They require sophisticated power management. This need led to the evolution of the Rack Power Distribution Unit. These units offer advanced capabilities. They ensure stable and efficient power delivery to critical IT equipment.
The Role of Intelligent Rack PDUs in Modern Data Centers
Intelligent Rack PDUs are essential for modern data centers. They move beyond simple power distribution. They provide advanced power management features. These features are crucial for maintaining uptime and operational efficiency. The table below highlights the key differences between basic and intelligent PDUs:
| Feature | Basic PDUs | Intelligent PDUs |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Straightforward power distribution | Advanced power management |
| Monitoring | None | Real-time monitoring (voltage, current, power consumption, outlet-level metering) |
| Control | Manual | Remote control and automation (reboot servers, schedule power cycles) |
| Environmental Monitoring | None | Advanced (sensors track temperature, humidity, airflow) |
| Integration | None | Seamless integration with data center management tools |
| Application Suitability | Small-scale applications, low-density environments | High-density environments, data centers |
| Additional Features | Master on/off switch | Local digital display, advanced reporting, remote rebooting, asset tracking |
Intelligent PDUs offer continuous oversight. They capture metrics like voltage and energy consumption. They also allow remote control. This helps manage devices over a secure network. They can reboot unresponsive servers. They can also schedule power cycles. This proactive management prevents many power-related issues.
Real-time Monitoring Capabilities of Advanced Rack PDUs
Granular Power Consumption Tracking
Advanced Rack PDUs provide detailed insights into power usage. They offer granular power consumption tracking. This allows data center managers to monitor power at various levels. They can track overall rack consumption. They can also monitor individual outlet usage. This detailed tracking helps identify inefficiencies. It also prevents overloads. Key metrics include:
- Voltage
- Current
- Active power
- Energy consumption (kWh)
- Status of circuit breakers
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS)
- Energy consumption for each outlet
- Voltage for each outlet
- Current for each outlet
This granular data helps optimize power usage. It also aids in capacity planning.
Environmental Sensor Integration for Proactive Alerts
Beyond power monitoring, advanced Rack PDUs integrate environmental sensors. These sensors provide crucial data about the rack environment. They help maintain optimal operating conditions. They also prevent equipment damage from environmental factors. When conditions exceed safe thresholds, the PDU generates alerts. This allows for rapid response to potential issues. Common integrated sensors include:
- Vibration Sensors (DX-VBR): Detects vibrations along three axes. This helps identify issues like earthquakes or damaged fans.
- Water/Leak Sensors (DPX-WSF-KIT, DPX-WSC-35-KIT, DPX-WSC-70-KIT): Monitors for leaks on floors or around liquid-cooled racks. They can also detect condensation.
- Rack Inlet Temperature and Humidity Sensors (DX2-T3H1): Monitors temperature and humidity at different levels of the cool air inlet side.
- Airflow Sensors (DPX-AF1): Measures airflow in plenum spaces. This includes areas under raised floors.
- Differential Air Pressure Sensors (DPX-T1DP1): Measures air pressure differences. This helps prevent thermal leaks between hot and cold aisles.
- Contact Closure Sensors (DX2-CC2): Used with third-party devices like smoke detectors. They monitor risky conditions.
- Tethered Temperature Sensor: A remote sensor for precise monitoring closer to heat sources.
- Fluid Detection Sensor: Detects fluid leaks and provides early warnings.
- Door Sensor: Monitors access to rooms, racks, and other containers.
- AC Voltage Sensor: Detects the presence of AC voltage in power cables.
These sensors provide a comprehensive view of the data center environment. They enable proactive alerts. This ensures equipment safety and continuous operation.
Proactive Downtime Prevention with Advanced Rack PDU Features
Advanced Rack Power Distribution Units offer robust remote control capabilities. These features allow data center managers to manage power from any location. This significantly reduces the need for on-site intervention.
Remote Power Control and Management
Individual Outlet Switching and Power Cycling
Intelligent PDUs provide real-time control over individual power outlets. This allows remote management to reduce downtime and enhance efficiency. Managers can remotely turn outlets on or off. They can also power cycle devices. This means they can reboot servers and network equipment without stepping into the server room. This action cuts downtime and keeps business moving. Remote troubleshooting capabilities help solve problems faster. These include power cycling devices, monitoring power issues, and managing equipment from anywhere. This saves time and money. It eliminates the need to send staff to the server room for every issue.
Automated Power Sequencing for System Stability
Advanced PDUs support automated power sequencing. This feature ensures devices power on in a specific order. This prevents inrush current issues and maintains system stability. Detailed reports on power usage for each device allow managers to schedule powering down equipment when not needed. They can also balance loads to prevent overloads. Proactive power monitoring provides real-time data on every outlet. This helps balance loads, prevent overloads, avoid overheating, and track energy use for cost reduction.
Enhanced Power Protection Mechanisms
Advanced Rack Power Distribution Units integrate several mechanisms. These protect IT equipment from power fluctuations and failures.
Overload Protection and Circuit Breaker Functionality
Overload protection is crucial for equipment safety. Basic PDUs integrate circuit protection through thermal-magnetic breakers. These breakers trip during overload conditions. This prevents damage and ensures safe power delivery. They provide essential overcurrent safeguards. Advanced PDUs also feature hydraulic magnetic circuit breakers. These breakers maintain their trip current across a wide temperature range. This enhances availability. Circuit breaker monitoring allows managers to track the total load on each breaker. This detects potential overloads. The PDU’s metering IC disables all outlets during excessive load or short circuit conditions. This enhances protection beyond the PDU’s circuit breaker.
| Safety Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Overload Protection | Circuit breakers disconnect power during overcurrent or short circuit events. This prevents overheating and electrical fires. |
| Surge Protection | This feature absorbs or diverts excess voltage from events like lightning strikes or power spikes. It protects sensitive electronics. |
| Manual Reset | Most PDUs require a manual reset after tripping. This ensures system inspection before power restoration. |
| Durable Housing | Materials like aluminum alloy resist fire and impact. This adds an extra layer of safety. |
Integrated Surge Suppression for Equipment Safety
Power surge protection is vital for sensitive electronics. Advanced PDUs utilize robust mechanisms. These include 15kV cable electrostatic discharge (ESD) and 2kV cable surge protection. They also feature UL 1449/EN 61643 type 3 SPD 6kV/3kA surge protection. These handle lightning strikes or high voltage impulses. Safe-voltage protection includes over-voltage and under-voltage protection. It automatically shuts down outlets if voltage falls outside a user-defined safe range. Specialized circuitry also filters AC power for cleanliness. This extends device lifespan and stability. It can also detect improper AC input grounding. Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) measurements allow visualization of electrical load distortion. This includes voltage dips, swells, and crest factor. This ensures efficient rack power.
Intelligent Alerting and Notification Systems
Intelligent alerting systems in advanced Rack Power Distribution Units play a critical role. They prevent downtime by providing timely information.
Customizable Thresholds for Critical Events
Intelligent rack PDUs prevent downtime with built-in power load monitoring. They also offer remote reboot capabilities. Alarm thresholds in the system provide proactive alerts. This prevents circuit overloads and enhances reliability. Managers define clear and actionable alert thresholds. They leverage historical baselines to inform threshold settings. This ensures threshold customization and flexibility to adapt to changing needs. Combining static thresholds for critical alerts with dynamic thresholds for warning/error levels creates a comprehensive monitoring strategy. This allows for early detection of anomalies.
Multi-channel Notifications for Rapid Response
Real-time alerts enable quick responses to power issues. Automated alerts for power issues, with custom thresholds for current, voltage, or temperature, enable instant notification. This allows for quick response to avoid outages and equipment damage. Advanced PDUs integrate with sensors to monitor temperature and humidity. They generate alarms if user-specified thresholds are exceeded. This allows for quick adjustments. These PDUs support additional sensors for monitoring water leaks or unexpected enclosure door openings. Rapid response capabilities through remote access and control allow managers to reboot devices, shift loads, or isolate faults without entering the server room. This ensures quick problem resolution.
Ensuring Redundancy and Reliability with Advanced Rack Power Distribution Units

Advanced Rack Power Distribution Units (PDUs) are crucial for maintaining continuous operation in data centers. They build redundancy and reliability directly into the power infrastructure. This prevents single points of failure and ensures uninterrupted service.
Dual Power Input and Automatic Transfer Switching (ATS)
Power redundancy is a cornerstone of high availability. Advanced PDUs achieve this through dual power inputs and Automatic Transfer Switching (ATS).
Seamless Power Source Failover
An Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) provides critical equipment with both a primary and a secondary power feed. If the primary power source fails, the ATS automatically switches to the secondary feed. This ensures a continuous power supply. This feature is especially useful for industrial equipment with single power inputs. It allows them to use dual power sources. For example, equipment can draw power from two separate breaker panels or dual power grids. The ATS connects both sources and distributes power. It then switches to the secondary source if the primary fails.
This automatic switching offers several key benefits:
- Minimized Downtime: Automatic switching ensures an instant transition to a secondary power source. This happens upon primary failure. It is crucial for continuous operation and minimizes disruptions.
- Enhanced Equipment Protection: It safeguards sensitive equipment from power fluctuations and sudden outages. It maintains a stable power supply. This prevents damage and data loss.
- Operational Efficiency: Automating the switching process reduces human error. It simplifies management through integrated monitoring. This allows for quicker responses.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By ensuring continuous operation and protecting equipment, automatic switching lowers operational costs. These costs are associated with downtime and equipment replacement.
Dual power automatic transfer switches are crucial for modern electrical systems. They ensure continuous power by seamlessly transitioning between power sources. This automatic switching protects sensitive equipment. It significantly boosts overall system reliability and redundancy. ATS devices eliminate the need for manual intervention. This reduces response times and human error in critical situations. They safeguard against power fluctuations, voltage sags, surges, and complete outages. This extends equipment lifespan and prevents costly repairs. In mission-critical applications, ATS provides a robust backup system. It allows for scheduled maintenance without disrupting operations. This ensures continuous uptime.
Maintaining Power to Single-Corded Devices
Many critical IT devices, especially older models, only have a single power input. This creates a vulnerability. If that single power source fails, the device goes down. An ATS within an advanced Rack Power Distribution Unit solves this problem. It allows a single-corded device to effectively draw power from two independent sources. The ATS monitors both inputs. If the primary input loses power, the ATS instantly switches the device to the secondary input. This provides the same level of redundancy as a dual-corded device. It ensures continuous operation for all equipment, regardless of its power input design.
Hot-Swappable Components and Serviceability
Even the most reliable systems require maintenance. Advanced Rack Power Distribution Units incorporate features that minimize disruption during these essential tasks.
Minimizing Disruption During Maintenance
Hot-swappable components are a significant advantage in advanced PDUs. They allow technicians to replace or upgrade parts without shutting down the entire system. This ensures continuous power distribution. It also simplifies maintenance tasks. In high-demand environments, such as telecom, a failed module can be replaced immediately. This happens without affecting the rest of the system. It minimizes downtime and keeps operations running smoothly.
By using hot-swappable components, you can reduce the time and effort required for maintenance, enhancing overall system reliability. This feature not only improves operational efficiency but also supports scalability. As your telecom network grows, you can easily upgrade your PDU system without disrupting existing operations. ESTEL PDUs make maintenance a seamless process, ensuring that your telecom cabinets remain efficient and reliable.
This capability significantly reduces the time and effort needed for maintenance. It enhances overall system reliability. It also improves operational efficiency and supports scalability. For example, Eaton’s ePDU G3 Series includes a hot-swap network meter module. This allows for maintenance without downtime. Vertiv Geist rPDU models offer a hot-swappable monitoring device. This, combined with dual Ethernet ports, supports operational flexibility. It delivers high power capacity and advanced remote management.
Design for Continuous Operation
The design of advanced PDUs prioritizes continuous operation. Hot-swappable components are a key part of this philosophy. They allow for proactive maintenance and rapid repair. This means data center managers can address issues with specific modules without impacting the power supply to other critical equipment. This design approach optimizes energy usage. It improves operational efficiency. It also supports sustainability goals by extending the lifespan of the PDU system. The ability to perform maintenance without interruption is vital for environments that demand 24/7 uptime.
Securing Your Infrastructure with Advanced Rack Power Distribution Units
Advanced Rack Power Distribution Units (PDUs) protect critical IT infrastructure. They implement robust security measures. These measures safeguard against unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Robust Access Control and Authentication
User Role Management and Secure Login Protocols
Advanced rack PDUs prevent unauthorized access to critical power management functions. They employ secure authentication methods. These methods include password protection and user role assignments. This approach restricts access to authorized users only. It minimizes the risk of unauthorized changes to power settings. Such changes could lead to equipment damage or data loss. This maintains the integrity and reliability of data center operations. Features like TACACS+ protocols at the PDU level provide access control. They permit approved personnel while keeping unauthorized individuals out. Enforced password policies require strong, current passwords. They have minimum character requirements and forced updates. These policies serve as a primary defense against hacking.
Integration with Centralized Authentication Systems
PDUs connect to networks. Therefore, data transmission must be encrypted. Products secured with HTTPS or SSH encryption by default enhance security. They also offer additional encrypted connection capabilities and protocols. Firewalls are crucial for protecting PDUs from unauthorized access. This is especially true when multiple systems and users need network access. Utilizing IP-based access control lists and role-based access control rules can block unauthorized access. This safeguards power quality and uptime. X.509 digital certificates ensure secure connections from authorized users. This is particularly important when accessing PDUs over public networks. They act as a main line of defense against man-in-the-middle attacks.
Data Security and Firmware Integrity
Encrypted Communication Channels
Advanced PDUs prioritize data security. They encrypt data sent or received. They use the strongest industry encryption for secure communication. This protects sensitive information from cyber threats. This ensures that all management and operational data remains confidential and secure.
Secure Firmware Updates and Vulnerability Management
Intelligent PDU solutions protect against malware. They use internal, chip-level secure boot processes. PRO4X PDUs include Secure Boot features. They have an onboard Secure Element cryptographic security module. This ensures the integrity and authenticity of the boot process. It prevents untampered firmware from running if validation fails. This hardware root of trust provides a strong foundation for system security. It ensures that only trusted software operates the PDU. This protects the device from malicious code and unauthorized modifications.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Encryption | Protects data from cyber threats through secure communication. |
| Firewalls | Shields the system from unauthorized access and attacks. |
| Secure Boot Processes | Ensures that only trusted software is loaded during startup. |
| Password Policies | Restricts access to authorized personnel only. |
Selecting the Right Advanced Rack Power Distribution Unit
Choosing the correct advanced Rack Power Distribution Unit is a critical decision. It directly impacts data center uptime and operational efficiency. Organizations must carefully assess several factors to ensure they select the best solution.
Assessing Power Requirements and Scalability
Total Load Capacity and Future Expansion Needs
Organizations must first define current and future power needs. Calculate total power consumption for all IT equipment. This includes servers, switches, and other devices. Use the formula: Power (Watts) = Voltage (Volts) × Current (Amps). Add a 20-30% safety margin for power surges or future expansions. US data centers consume over 20 GW annually. Projections show a 32% growth by 2025. This emphasizes the need for future-proofing. Consider higher capacity PDUs, like three-phase units, for loads exceeding 22 kW.
Voltage, Amperage, and Plug Compatibility
Evaluate the PDU’s voltage, amperage, and power ratings. Match the PDU’s voltage (e.g., 120V, 208V, 240/415V) to your equipment. Ensure the amperage rating (e.g., 16A) exceeds the total current draw. This prevents overheating and allows for expansion. Power ratings in watts combine voltage and amperage. They indicate total capacity. This is crucial for high-density environments. The PDU’s outlets should match your devices. Examples include IEC C13 and IEC C19 for high-power devices. Future-proof by selecting a mix of outlet types. Distribute devices evenly across outlets for load balancing. This also ensures accurate power monitoring. Implement redundant setups with two PDUs per rack. This ensures continuous power if one fails. Downtime can cost nearly $9,000 per minute. Redundancy is a critical investment.
Evaluating Redundancy and Advanced Features
N, N+1, and 2N Configurations for Critical Systems
Redundancy configurations are vital for critical systems. They ensure continuous operation.
| Configuration | Description | Redundancy Level | Failure Tolerance | Cost/Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Minimum capacity for full IT load (e.g., 4 UPS units if 4 are needed). | None | Cannot tolerate any disruption; susceptible to single points of failure. | Lower initial cost, but high risk of downtime. |
| N+1 | N capacity plus one additional component (e.g., 5 UPS units if 4 are needed). | Minimal | Tolerates a single component failure or allows for single component maintenance. | Cheaper and more energy-efficient than 2N; presents risk with multiple simultaneous failures. |
| 2N | A mirror image of the original N architecture (e.g., 8 UPS units if 4 are needed), with two independent distribution systems. | Full fault tolerance | Allows an entire set of components to be taken offline for maintenance without interruption; secondary architecture takes over if primary fails. | Higher cost due to duplicated infrastructure, but greatly diminishes downtime likelihood. |
Integration with Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM)
Integrating advanced PDUs with Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) systems offers significant benefits. DCIM provides an accurate ‘asset truth’. It details what is in each rack unit, its power draw, and the specific power path. This path includes utility, switchgear, UPS, PDU, Rack PDU, and IT loads. Integrating an ecosystem explicitly supported by DCIM from the outset is a sensible strategy. This includes Power Distribution Units (PDUs), Static Transfer Switches (STS), and other ancillary equipment. This approach allows seamless communication. It enhances overall data center management. DCIM helps monitor power consumption, assess available power capacity, ensure system uptime, and facilitate high-density deployments. It supports monitoring and data collection for tens of thousands of nodes. This includes Intelligent Rack PDUs, Floor PDUs, RPPs, Busways, UPS, CRACs, and environmental sensors. It supports multiple protocols like SNMP, ModBus, and BacNet.
Considering Manufacturer Expertise and Support
Importance of a Reputable Rack PDU Supplier
Choosing a reputable supplier for your Rack Power Distribution Unit is paramount. A reliable manufacturer offers proven quality and adherence to industry standards. They provide products designed for durability and performance. This ensures the PDU meets the demanding requirements of modern data centers. Such suppliers often have extensive experience and a strong track record in the industry. This expertise translates into more robust and dependable products.
Long-term Support and Product Longevity
Long-term support and product longevity are crucial considerations. A good supplier offers ongoing technical assistance and regular firmware updates. This keeps the PDU secure and functional over its lifespan. It also ensures the unit remains compatible with evolving IT infrastructure. Investing in a PDU from a manufacturer committed to long-term support protects your investment. It also guarantees continued operational efficiency and security for years to come.
Implementing and Maintaining Advanced Rack Power Distribution Units for Maximum Uptime
Strategic Deployment and Cabling Best Practices
Optimal Rack Placement and Cable Management
Strategic deployment of advanced rack PDUs is crucial. It involves proper placement and mounting. Consider available rack space, outlet accessibility, and airflow. This prevents obstruction. Capacity planning is also vital. Calculate equipment wattage. Add a 20% buffer. Select a PDU with sufficient capacity. This avoids tripping breakers. Load balancing across racks should also occur. For future growth, plan for scalability. Choose a larger PDU initially if more servers are anticipated. Remote management best practices include setting secure admin passwords. Configure alerts to appropriate staff. Regularly review power consumption. This identifies trends and issues.
Future-proofing PDU installations involves planning for scalability. Evaluate current setups. Identify areas for expansion. Key metrics to monitor include power load readings from rack PDUs. This locates stranded capacity. Resource capacity KPIs provide real-time information on power, cooling, and connectivity. Space utilization metrics track available floor and cabinet space. Regularly reviewing these metrics ensures adaptability. It minimizes disruptions. Choosing modular and expandable PDU options is also vital. They allow for component upgrades. This includes higher-capacity modules or intelligent features like IoT-based monitoring. This reduces the need for complete system overhauls. It optimizes energy usage.
Effective cable management is essential for an organized and efficient server rack. Plan cable routes before installation. Group cables by function. This includes power, data, and network. Assign specific paths. This minimizes clutter and facilitates access. Use cable ties for permanent installations. Use Velcro straps for setups requiring frequent adjustments. This helps maintain tidiness. It prevents tangling. Choose durable materials for ties. Use reusable options for Velcro. Avoid overtightening. Leave some slack in cables. This accommodates future changes. It prevents strain. Label connections with durable, heat-resistant labels. Use color-coding. Include detailed information at both ends. This simplifies maintenance and troubleshooting. It ensures compliance with industry standards.
| Benefit | Why It Matters | Installer Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| High-Density Mounting | Accommodates more equipment in less space | Efficient use of floor area and easier scalability |
| Enhanced Airflow Management | Prevents overheating and improves efficiency | Lowers cooling costs and prolongs equipment life |
| Modular Components | Quick addition or removal of accessories | Faster deployments and simpler upgrades |
| Integrated Cable Management | Organized, accessible cable routing | Easier troubleshooting and fewer installation errors |
| Security and Compliance | Protects assets and meets industry standards | Peace of mind and simplified audits |
| Edge-Ready Design | Supports remote and distributed IT setups | Reduced travel time and rapid issue resolution |
Phased Rollout for Minimal Disruption
A phased rollout strategy minimizes disruption. It allows for gradual integration of new PDUs. This approach reduces risk. It ensures continuous operation during upgrades. Teams can test new units in stages. This identifies and resolves issues before full deployment.
Configuration, Calibration, and Ongoing Monitoring
Initial Setup and Baseline Establishment
Proper initial setup and baseline establishment are critical. They ensure optimal PDU performance. Follow these steps:
- Confirm the Infrastructure Voltage: Identify the input voltage. This includes 120V single phase, 208V single phase, 208V three phase, or 400V three phase for North America.
- Establish the Rack Kilowatt Budget: Estimate the total power required (kW, kVA). Calculate the sum of device nameplate values multiplied by 70%. Consider headroom for future growth.
- Determine the Circuits, Phase, and Amperage for the Rack: Identify the PDU input voltage, number of phases, and amperage. This dictates the PDU plug type. For existing setups, check the receptacle type.
- Find Out What Devices will be in the Rack: This determines the necessary PDU outlet types. Examples include C-14 and C-20. It also determines the total number of outlets.
- Decide if Switching is Desired and What Level of Metering is Required: Evaluate the need for remote power control. This includes rebooting servers or preventing unauthorized access. Choose between inlet-level or outlet-level metering.
- Learn the Rack PDU Installation Options: Consider the PDU form factor. Examples include 1U, 2U, or Zero U. Consider power inlet location, input power cord length, and methods to prevent accidental unplugging.
- Figure Out if Advanced Features are Needed: Determine if environmental monitoring, specific LAN connectivity (hardwire Ethernet, Wi-Fi, Gigabit Ethernet), or color-coding for power feeds are required.
Regular Health Checks and Performance Audits
Routine visual inspections are essential for maintaining the health of server room PDUs. Focus on visible signs. This includes frayed cables, loose connections, or physical damage to outlets. Check for dust accumulation. It can interfere with airflow and cooling. Dust can clog cooling fans. It can insulate components. This causes temperature increases of up to 30°F. Contaminants like food debris, skin particles, and clothing fibers can enter the system. They affect performance. A cleaner environment protects electrical components. It extends their lifespan.
| Inspection Focus Areas | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Cable Connections | Prevents electrical hazards. |
| Cooling Systems | Ensures stable temperatures. |
| Firmware Updates | Keeps PDUs secure and efficient. |
Regular updates provide access to the latest features. They improve functionality. Security patches protect systems from vulnerabilities. They reduce risks. Updated firmware enhances reliability. It ensures uninterrupted operations.
| Performance Improvement | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Reliability | Real-time monitoring allows for timely decision-making, reducing the likelihood of failures. |
| Reduced Operational Costs | Efficient power distribution leads to lower energy bills and maintenance costs. |
| Improved Worker Safety | Alerts for abnormal conditions help prevent accidents and ensure a safer working environment. |
| Greater Customer Satisfaction | Reliable power distribution enhances service quality, leading to higher customer satisfaction. |
| Proactive Maintenance | Trend analysis helps identify issues before they escalate, allowing for timely maintenance. |
| Energy Efficiency | Intelligent power distribution minimizes energy waste, contributing to overall efficiency. |
Hospitals in Taiwan should conduct regular safety audits. This ensures their power distribution systems remain compliant and functional. Inspections should focus on verifying that all medical grade PDUs meet local and international safety standards. Scheduling these checks quarterly or semi-annually helps maintain a safe environment for patients and staff.
| Inspection Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Scheduled Inspections | Identify signs of wear and tear, such as loose connections and dust buildup. |
| Automated Monitoring | Track temperature, humidity, and power usage to respond swiftly to anomalies. |
Firmware Updates and Proactive Maintenance
Staying Current with Security Patches and Feature Enhancements
Firmware stability directly impacts the reliability of advanced rack PDUs. Outdated or buggy firmware can lead to unexpected reboots. It can also cause loss of configuration settings. This disrupts network operations. It requires immediate attention. Regular firmware updates are essential for maintaining both security and functionality. They fix bugs. They patch vulnerabilities. Proper firmware management ensures reliable operation. It protects against cyber threats. Insecure firmware update mechanisms can expose PDUs to remote code execution risks. This highlights the necessity of using secure update methods, strong authentication, and regular audits. This protects PDU infrastructure. A thorough evaluation of firmware and support ensures the PDU remains secure, up-to-date, and manageable throughout its lifecycle.
Security patches are crucial for safeguarding intelligent power devices from cyberattacks. Unpatched devices are vulnerable to exploitation. Documented risks include authentication bypass flaws. These grant remote administrative control. Operational disruption can occur through remote power-offs. Physical destruction can result from malicious rapid power cycling. Compromised devices can also serve as stealthy entry points for attackers. They move laterally within a network. Applying security patches promptly helps prevent these threats. Isolate devices on secure networks. Enforce strong authentication. This maintains system resilience. It reduces costly downtime. Manufacturers regularly release firmware and software updates. They address performance issues and security risks. Staying current with these updates helps maintain device stability. It ensures compatibility with evolving data center technologies.
Scheduled Inspections and Component Checks
Scheduled inspections and component checks are vital for PDU longevity. The frequency depends on the potential for damage.
| Degree of Potential Damage | Recommended Inspection Interval |
|---|---|
| High | Monthly |
| Medium | Quarterly |
| Low | Twice a year |
Inspect for deformed columns. They may require the ’1-2-3 Rule’ for assessment. Check for in-house repairs and welds not designed by professionals. Ensure upright columns are vertically aligned. Look for rust formation on racking components due to environmental factors. Verify proper clearance between racking systems and building components. Check for missing, loose, or inadequate safety pins securing beams. Inspect for deformed or detached beams affecting stability. Look for deformed and/or twisted columns impacting load capacity. Examine damaged racking braces compromising stability.
Advanced Rack Power Distribution Units form the foundation of resilient IT operations. They represent a strategic investment. These units ensure uninterrupted performance and enhance data center security. Businesses elevate their uptime strategy with intelligent rack PDU solutions. This proactive approach safeguards critical infrastructure.
FAQ
What is an Advanced Rack PDU?
An Advanced Rack PDU distributes power to IT equipment in a rack. It offers intelligent features. These include real-time monitoring, remote control, and enhanced security. These units go beyond basic power strips. They ensure stable and efficient power delivery.
How do Advanced Rack PDUs prevent downtime?
Advanced Rack PDUs prevent downtime through proactive monitoring. They offer remote power control and robust protection mechanisms. Features like overload protection, surge suppression, and intelligent alerts help avoid power-related issues. They ensure continuous operation.
Can Advanced Rack PDUs monitor environmental conditions?
Yes, Advanced Rack PDUs integrate environmental sensors. These sensors track temperature, humidity, and airflow. They provide proactive alerts if conditions exceed safe thresholds. This helps maintain optimal operating environments. It prevents equipment damage.
What is Automatic Transfer Switching (ATS) in a PDU?
Automatic Transfer Switching (ATS) provides seamless power source failover. If the primary power source fails, the ATS automatically switches to a secondary feed. This ensures continuous power. It is crucial for maintaining uptime for critical equipment.
How do Advanced Rack PDUs enhance security?
Advanced Rack PDUs enhance security with robust access control. They use secure login protocols and user role management. They also feature encrypted communication channels. Secure firmware updates protect against cyber threats. This safeguards critical infrastructure.
Why is granular power consumption tracking important?
Granular power consumption tracking provides detailed insights into power usage. It monitors power at the rack and individual outlet levels. This helps identify inefficiencies. It also prevents overloads and aids in capacity planning.
What are hot-swappable components in a PDU?
Hot-swappable components allow technicians to replace or upgrade parts. They do this without shutting down the entire system. This minimizes disruption during maintenance. It ensures continuous power distribution. It simplifies maintenance tasks.
Post time: Dec-02-2025

