
Understanding the differences between a PDU, a Basic PDU, and a power strip is crucial for effective power management. While both PDUs and power strips distribute electricity, they serve distinct purposes and contexts. PDUs, particularly in data centers and industrial facilities, provide advanced features for monitoring and optimizing power usage. The Intelligent PDU takes this a step further by offering enhanced capabilities for energy management. In contrast, power strips typically cater to home offices and small businesses for basic electronic devices. Recognizing these differences can enhance safety and improve energy efficiency.
| Environment Type | Common Usage of PDUs | Common Usage of Power Strips |
|---|---|---|
| Data Centers | Monitoring power usage, energy efficiency | N/A |
| High-Density Data Centers | Power management optimization, energy initiatives | N/A |
| Corporate Offices | Advanced features, compliance | N/A |
| Industrial Facilities | Stabilizing power supply, minimizing accidents | N/A |
| Home Offices | N/A | Powering computers, printers, lamps |
| Small Businesses | N/A | Basic electronics, temporary setups |
| Temporary Workspaces | N/A | Quick power access |
Key Takeaways
- Understand that PDUs and power strips serve different purposes. PDUs are designed for high-demand environments like data centers, while power strips are suitable for home and small office use.
- Recognize the advanced features of PDUs, such as monitoring and overload protection. These features enhance safety and efficiency in power management.
- Consider the number of outlets needed. PDUs can offer 4 to 48 outlets, making them ideal for environments with multiple devices, while power strips typically provide 2 to 8 outlets.
- Evaluate your power needs carefully. Assess factors like energy monitoring, output capacity, and redundancy requirements before choosing between a PDU and a power strip.
- Be aware of the safety features. PDUs often include industrial-grade circuit protection, while power strips may only offer basic surge protection.
- Think about the environment where the device will be used. PDUs are best for industrial settings, while power strips work well in residential or light commercial spaces.
- Budget considerations are important. While PDUs may have a higher initial cost, their long-term energy efficiency can lead to savings over time.
- Make informed decisions based on your specific needs. Choosing the right device can improve performance and reliability in your electrical systems.
Definitions

What is a PDU?
A Power Distribution Unit (PDU) is a critical device in managing electrical power within data centers and industrial environments. It distributes alternating current (AC) from a power source to multiple devices, such as servers and networking equipment. According to industry standards, a PDU receives electrical power from sources like utility power suppliers or generators. It then channels this power to various equipment, ensuring efficient energy distribution.
PDUs come in various types, each designed for specific needs:
- Basic PDUs: These units provide simple power distribution without advanced features, making them suitable for small setups.
- Metered PDUs: These models measure power consumption, aiding in load balancing and capacity planning.
- Switched PDUs: They allow remote control of outlets, which is useful for managing power during outages.
- Managed PDUs: These feature-rich units include monitoring and control capabilities, often used interchangeably with switched PDUs.
- Universal PDUs: They offer flexible connection options for various power sources, making them adaptable for global use.
What is a Power Strip?
A power strip is a common electrical device that provides multiple outlets for connecting various electronic devices. It typically consists of a long plastic or metal housing with several electrical sockets. Power strips are widely used in homes, offices, and temporary workspaces to extend the number of available outlets.
Smart power strips have gained popularity due to their advanced features. They include circuitry that monitors and controls the power supplied to each outlet. For instance, when a printer connected to a smart strip enters standby mode, the strip detects the reduced power consumption and cuts off electricity to that outlet. This functionality helps lower overall electricity use.
Common features of power strips include:
- Durable plastic or metal housings in various styles.
- Up to 24 outlets and power cords that can extend up to 25 feet.
- Transformer outlet options for accommodating larger AC adapters.
Power strips serve as a practical solution for powering multiple devices in various settings, from homes to commercial environments.
Key Differences

Design and Configuration
The design and configuration of PDUs and power strips differ significantly. PDUs typically feature a robust construction, often made from steel, which enhances durability and safety in demanding environments. In contrast, power strips usually consist of plastic housings, making them lighter but less resilient.
| Feature | Power Strips | PDUs |
|---|---|---|
| Gauge Ratings | Typically 14 AWG | Ranges from 14 AWG to 6 AWG |
| Voltage Ratings | 110V/208V/230V single-phase | 208V/400V three-phase |
| Safety Features | Often include surge protectors | Usually have overload protectors and MCBs |
This table illustrates the differences in electrical architecture between the two devices. PDUs are designed to handle higher loads and more complex configurations, making them suitable for industrial applications.
Power Capacity
Power capacity is another critical difference. PDUs can manage higher power loads compared to standard power strips. For example, a server with a 1400-watt power supply at 208V will draw approximately 6.7 amps. This demonstrates how PDUs can accommodate significant electrical demands, which is essential in data centers and industrial settings.
| Device Type | Power Capacity (Amps) | Power Capacity (Watts) |
|---|---|---|
| PDU | 15A, 20A, 30A | Up to 7200W |
| Power Strip | 15A | Up to 1800W |
Commonly ordered PDUs include models such as the 15A APC PDU (AP7900) and the 20A 110V PDUs (AP7930, AP7901). These specifications highlight the capacity differences that users must consider when selecting a device for their power needs.
Number of Outlets
The number of outlets available also varies between PDUs and power strips. PDUs typically offer a greater range of outlets, accommodating anywhere from 4 to 48 connections. This flexibility is crucial for environments that require multiple devices to be powered simultaneously.
| Device Type | Number of Outlets |
|---|---|
| PDU | 4 to 48 |
| Power Strip | 2 to 8 |
This table clearly shows that power strips provide fewer outlets, making them more suitable for smaller setups or temporary arrangements.
Understanding these key differences helps users make informed decisions about which device best meets their power distribution needs.
Circuit Protection
Circuit protection is a vital aspect of electrical devices, ensuring safety and preventing damage from overloads or surges. PDUs and power strips differ significantly in their circuit protection features. Understanding these differences can help users make informed decisions about which device best suits their needs.
PDUs typically include advanced circuit protection mechanisms designed for high-demand environments. They often feature industrial-grade resettable circuit breakers or miniature circuit breakers (MCBs). These components automatically disconnect power when they detect an overload, preventing potential hazards. In contrast, power strips usually offer basic surge protection and may lack overload protection altogether.
The following table summarizes the standard circuit protection features found in PDUs compared to power strips:
| Feature | PDU | Power Strip |
|---|---|---|
| Surge Protection | Usually absent | Typically included |
| Overload Protection | Yes, with overload protectors | Often absent |
| Circuit Breakers | Industrial-grade resettable fuses or MCBs | Not present |
The effectiveness of these circuit protection mechanisms varies significantly. PDUs are designed to handle high power demands, making them suitable for industrial settings. They often include advanced monitoring capabilities that allow users to track power usage and identify potential issues before they escalate. On the other hand, power strips generally provide basic surge protection, which may not suffice in high-load environments.
The following table illustrates the effectiveness of circuit protection in PDUs compared to power strips based on safety testing data:
| Feature | PDUs | Power Strips |
|---|---|---|
| Overload Protection | Industrial-grade overload protection | Basic surge protection |
| Circuit Breakers | Resettable circuit breakers included | Simple fuses or basic circuit breakers |
| Monitoring Capabilities | Advanced monitoring capabilities | Limited monitoring |
| Suitability for High Power | Designed for high power demands | Less suitable for industrial settings |
Applications
Where to Use a PDU
PDUs excel in environments that demand reliable and efficient power management. They are ideal for:
- Data Centers: These facilities require stable power for high-tech equipment. PDUs ensure that power distribution remains consistent, preventing downtime.
- Server Rooms: Similar to data centers, server rooms rely on PDUs to manage complex electrical systems. They help maintain stability and avoid power-related problems.
- Manufacturing Plants: Efficient power distribution is crucial for machinery operations. PDUs support the intricate power setups needed in these environments.
- Healthcare Facilities: Critical medical equipment depends on stable power. PDUs provide the reliability necessary for life-saving devices.
- Financial Institutions: Sensitive financial systems require power stability to function correctly. PDUs help maintain this stability, ensuring smooth operations.
Where to Use a Power Strip
Power strips serve well in less demanding environments. They are suitable for:
- Home Offices: Power strips provide a convenient way to connect multiple devices like computers, printers, and lamps.
- Small Businesses: These devices offer a quick solution for powering basic electronics and temporary setups.
- Temporary Workspaces: In situations where power access is needed quickly, power strips can be easily deployed to meet immediate needs.
Industry-Specific Uses
Different industries have unique power management requirements. PDUs are particularly beneficial in sectors that face challenges with power distribution. Here are some industry-specific uses:
- Complex Electrical Systems: Industries with intricate power setups benefit from PDUs. They help manage power loads effectively, ensuring stability.
- Data Centers: These facilities prioritize power reliability to prevent outages and equipment failures. PDUs provide the necessary infrastructure.
- Manufacturing: Efficient power distribution is vital for machinery operations. PDUs support the high demands of manufacturing environments.
- Healthcare: Medical facilities rely on PDUs for critical equipment, ensuring that power remains stable and reliable.
- Finance and Government: Both sectors utilize PDUs for secure and reliable power management, essential for sensitive operations.
Physical Differences
Size and Form Factor
The size and form factor of PDUs and power strips significantly influence their installation and usability. PDUs typically range from 4 to 48 outlets, making them suitable for environments with high power demands, such as data centers and industrial settings. In contrast, power strips usually offer between 2 to 8 outlets, catering to smaller setups in homes and offices.
| Feature | PDUs | Power Strips |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Outlets | 4 to 48 | 2 to 8 |
| Application Environment | Industrial, data centers, server rooms | Homes, offices |
The larger size of PDUs allows for more complex configurations, which is essential in environments where multiple devices require power simultaneously.
Mounting Options
Mounting options vary greatly between PDUs and power strips, affecting their deployment in different settings. PDUs are designed for rack or cabinet mounting, allowing for both horizontal and vertical installations. This flexibility helps save space and improves organization within server racks.
- PDUs can be installed vertically to save space and improve organization in racks.
- Tool-less installation allows for easy securing of multiple PDUs next to each other.
- Smaller PDUs can be mounted horizontally, but this may reduce available rack space.
Power strips, on the other hand, are primarily designed to lie flat on surfaces. However, some models come with mounting tabs, enabling them to be secured to walls or desks.
- Rack mount power strips offer flexible mounting options, including 0U to 4U configurations.
- Standard button mounts and custom mounting brackets are available for different installation needs.
- Ensure correct mounting brackets are used to avoid interference with server mounting space.
Cable Lengths
Cable lengths also differ between PDUs and power strips, impacting their usability in various environments. PDUs often feature longer cables, which can extend up to 25 feet. This length allows for greater flexibility in positioning the unit within a data center or industrial facility.
Power strips typically have shorter cables, usually ranging from 6 to 12 feet. While this length is sufficient for home and office use, it may limit placement options in larger spaces.
Safety Features
Surge Protection
Surge protection is a critical feature in both PDUs and power strips. It safeguards connected devices from voltage spikes, which can occur due to lightning strikes or power surges. PDUs often include advanced surge protection mechanisms, while power strips typically offer basic protection.
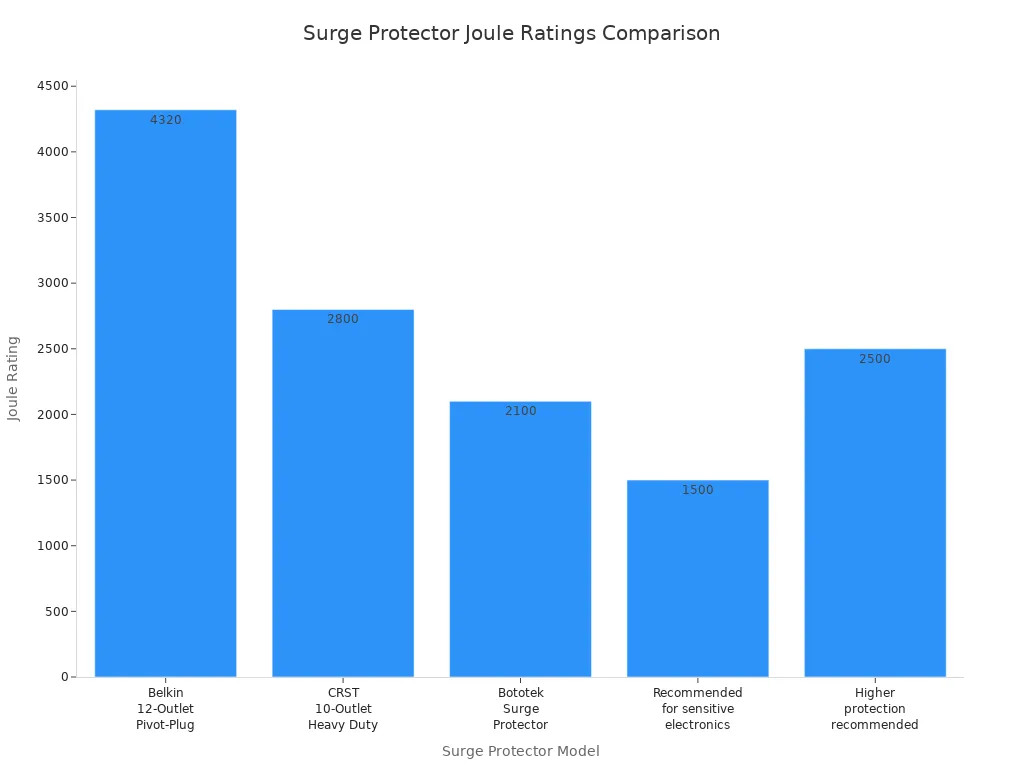
The effectiveness of surge protectors varies significantly. For example, the joule rating indicates how much energy a surge protector can absorb before failing. Higher joule ratings generally correlate with better protection. The following table illustrates the joule ratings and effectiveness levels of various surge protector models:
| Surge Protector Model | Joule Rating | Effectiveness Level |
|---|---|---|
| Belkin 12-Outlet Pivot-Plug | 4320 joules | Highest protection for extended use |
| CRST 10-Outlet Heavy Duty | 2800 joules | Good protection for sensitive devices |
| Bototek Surge Protector | 2100 joules | Adequate for general use |
| Recommended for sensitive electronics | 1000-2000 joules | Generally sufficient for most users |
| Higher protection recommended | >2000 joules | For expensive or critical equipment |
Power strips with lower joule ratings may not provide adequate protection for sensitive electronics. Therefore, users should consider their specific needs when selecting a surge protector.
Overload Protection
Overload protection is another essential safety feature. It prevents devices from drawing more power than the circuit can handle. PDUs typically include industrial-grade resettable circuit breakers or miniature circuit breakers (MCBs). These components automatically disconnect power when they detect an overload, reducing the risk of fire or equipment damage.
In contrast, many power strips lack robust overload protection. Some may include basic fuses, but these often do not provide the same level of safety as the mechanisms found in PDUs. Users should prioritize devices with reliable overload protection, especially in environments with high power demands.
Thermal Protection
Thermal protection is vital for preventing overheating, which can lead to equipment failure or fire hazards. PDUs often feature built-in thermal protection systems that monitor temperature levels. If the temperature exceeds a safe threshold, the PDU will automatically shut down to prevent damage.
Power strips, however, may not always include this feature. While some models offer basic thermal protection, they often lack the advanced monitoring capabilities found in PDUs. Users should be cautious when using power strips in high-heat environments or with devices that generate significant heat.
Advanced Functions
Monitoring and Management Features
Advanced PDUs, particularly intelligent models, offer a range of monitoring and management features that significantly enhance data center operations. These capabilities include:
- Real-time power distribution monitoring
- Alerts for power anomalies like surges and outages
- Improved energy efficiency and reduced downtime
These features enable data center operators to effectively manage power distribution and consumption. With real-time monitoring, operators can track energy usage and identify inefficiencies. Advanced reporting tools provide insights into power consumption patterns, aiding in capacity planning. Environmental monitoring features also help maintain optimal conditions for sensitive equipment.
Remote Access Capabilities
Remote access capabilities in PDUs enhance power management compared to traditional power strips. The following table highlights key differences:
| Feature | Smart PDUs | Traditional Power Strips |
|---|---|---|
| Remote Monitoring | Yes | No |
| Remote Control of Outlets | Yes | No |
| Energy Usage Analytics | Yes | No |
| Alerts and Notifications | Yes | Limited |
| Surge Protection | Yes | Limited |
Smart PDUs allow users to monitor energy usage in real-time and control individual outlets remotely. This capability enables quick responses to potential issues, such as alerts for temperature or humidity changes. Operators can also receive notifications for power anomalies, ensuring they can act swiftly to avoid downtime.
Smart PDUs vs. Traditional Power Strips
Smart PDUs provide advanced functionalities that traditional power strips lack. The following table summarizes the key differences in functionality:
| Feature | Traditional Power Strips | Smart PDU Power Strips |
|---|---|---|
| Real-time Monitoring | No | Yes |
| Remote Management | No | Yes |
| Energy Consumption Tracking | No | Yes |
| Scalability and Flexibility | Limited | High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Smart PDUs offer outlet-level monitoring and remote management, essential for managing complex IT environments. These features help IT teams optimize power usage and quickly address issues. In contrast, traditional power strips only provide basic power distribution, making them less suitable for environments with demanding power needs.
Choosing the Right Option
Assessing Your Power Needs
When selecting between a PDU and a power strip, assessing power needs is crucial. Consider the following factors:
- Monitoring Energy Usage: PDUs can monitor energy consumption to prevent overloads. This feature is essential for maintaining equipment health.
- Downtime Reduction: PDUs help reduce downtime through advanced management features. Standard power strips lack these capabilities.
- Power Type: Determine if you need AC or DC power based on your equipment requirements.
- Output Capacity: Ensure the PDU has enough outputs for your devices, with some room for future growth.
- Redundancy Needs: Consider if your devices have redundant power supplies and how the PDU can manage them effectively.
- Mounting Options: Choose between rack-mounted or wall-mounted PDUs based on your space constraints.
- Additional Features: Look for features like monitoring capabilities to enhance functionality.
Evaluating Your Environment
The operating environment significantly influences the choice between a PDU and a power strip. Here are some considerations:
- PDUs are designed for industrial environments, suitable for heavy-duty equipment.
- Power strips are intended for residential and light commercial use, connecting everyday appliances.
- PDUs offer enhanced safety and flexibility for high-voltage applications, ideal for data centers.
- Power strips are used for common devices like home entertainment systems and desktop computers.
Understanding the specific requirements of your environment will guide you in making the right choice.
Budget Considerations
Budget plays a vital role in the decision-making process. Here are some financial aspects to consider:
- Initial Investment: PDUs typically have a higher initial cost compared to power strips. This upfront expense can be a deterrent for some users.
- Long-term Benefits: PDUs offer significant savings and efficiency over time. They often reduce energy costs and improve overall performance.
- Energy Efficiency: PDUs improve energy efficiency with monitoring capabilities, unlike basic power strips. This efficiency can lead to lower utility bills in the long run.
By weighing these budget considerations, users can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals.
In summary, PDUs and power strips serve distinct purposes in power management. PDUs excel in high-demand environments, offering advanced features like monitoring and overload protection. Power strips provide basic power distribution for everyday devices.
Selecting the right device is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. Users should assess their specific needs and environments before making a choice.
Tip: Consider your power management strategies to optimize energy use and reduce costs. Making informed decisions can lead to better performance and reliability in your electrical systems.
FAQ
What is the main purpose of a PDU?
A Power Distribution Unit (PDU) distributes electrical power to multiple devices in environments like data centers. It ensures efficient energy management and provides advanced features for monitoring power usage.
Can I use a power strip in a data center?
Using a power strip in a data center is not recommended. Power strips lack the necessary capacity and safety features required for high-demand environments, which can lead to overloads and equipment failure.
How do I choose between a PDU and a power strip?
Consider your power needs, environment, and budget. PDUs suit high-demand settings requiring monitoring and safety features, while power strips work well for basic setups in homes or small offices.
Are PDUs more expensive than power strips?
Yes, PDUs generally have a higher initial cost than power strips. However, their advanced features and energy efficiency can lead to long-term savings, making them a worthwhile investment.
Do power strips provide surge protection?
Most power strips include basic surge protection. However, the level of protection varies. Users should check the joule rating to ensure adequate protection for sensitive devices.
How many outlets do PDUs typically have?
PDUs can offer between 4 to 48 outlets, depending on the model. This range allows for flexible power distribution in environments with multiple devices.
Can I mount a PDU?
Yes, PDUs are designed for rack or cabinet mounting. They can be installed both horizontally and vertically, optimizing space in server rooms or data centers.
What features should I look for in a smart PDU?
When selecting a smart PDU, look for features like remote monitoring, energy usage analytics, and outlet control. These capabilities enhance power management and improve operational efficiency.
Post time: Sep-04-2025

