
Smart Power Distribution Units (PDUs) significantly reduce data center energy costs. They provide granular power monitoring, remote management, and advanced control capabilities. This enables optimized power usage and identifies inefficiencies. A Smart PDU helps data centers achieve substantial savings. For instance, an Intelligent PDU, when integrated with comprehensive DCIM systems, often reduces energy costs by 20-30% compared to a Basic PDU or conventional setups. These capabilities ensure efficient power distribution and management, directly impacting operational expenses.
Key Takeaways
- Smart PDUs help data centers save money on electricity.
- They show how much power each device uses.
- You can turn devices on or off from far away with Smart PDUs.
- Smart PDUs help find devices that waste power or are not used enough.
- They make sure power is used well, which helps the data center run better.
- Smart PDUs stop power problems and keep equipment working longer.
- They help plan for future power needs without buying too much equipment.
Understanding Data Center Energy Challenges

The High Cost of Data Center Power
Substantial Energy Consumption
Data centers consume vast amounts of energy. They operate continuously, powering servers, storage, and networking equipment. Cooling systems also demand significant power to maintain optimal operating temperatures. This constant energy demand creates a substantial operational challenge for data center managers.
Financial Burden of Electricity
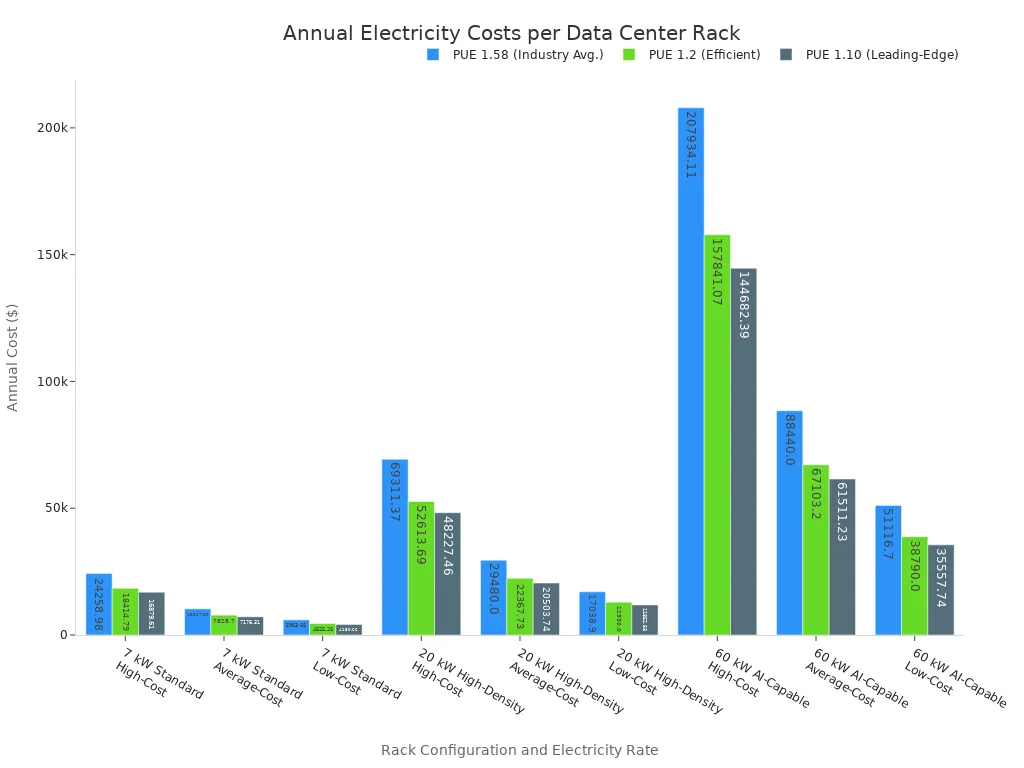
Electricity costs represent a major financial burden for data centers. Electricity typically constitutes 20-30% of their total operating costs. This significant proportion highlights electricity as a key factor influencing profitability and location decisions. Hyperscale operators, for example, spend billions annually on electricity. The annual cost to power one data center rack can be calculated using the formula: Annual Cost = Rack IT Power (kW) × PUE × 8760 hours/year × Electricity Rate ($/kWh). This calculation accounts for the IT equipment’s power consumption, cooling overhead, power infrastructure losses, and other facility overheads. The following chart illustrates the varying annual electricity costs per data center rack based on power density, electricity rates, and Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) levels.
Limitations of Traditional PDUs
Lack of Energy Insights
Traditional Power Distribution Units (PDUs) present significant limitations in energy monitoring. Basic PDUs, for instance, lack any monitoring capabilities. They cannot track energy consumption or detect potential issues. Metered PDUs offer some power data, but they lack remote monitoring or management capabilities. This requires physical presence to access power data, making real-time analysis difficult.
Inability to Optimize Power
Traditional PDUs also hinder effective power optimization. They do not offer remote access or control features. This means manual intervention is necessary for troubleshooting or power cycling equipment. Furthermore, these PDUs offer limited integration with advanced infrastructure management systems. This prevents comprehensive power management strategies. A Smart PDU addresses these limitations by providing granular data and remote control.
Defining a Smart PDU
A Power Distribution Unit (PDU) serves as a crucial component in managing and distributing electrical power within data centers, server rooms, and other critical environments. Its primary function is to take power from a source, typically a main electrical supply, and distribute it to multiple devices such as servers, networking equipment, and storage systems. The application of PDUs is essential in maintaining a reliable and organized power infrastructure. By consolidating power distribution, PDUs ensure that each device receives the required amount of electricity to operate efficiently. This centralized management simplifies monitoring and control, allowing for better resource allocation and troubleshooting.
A Smart PDU goes beyond basic power distribution. It integrates advanced features for monitoring, managing, and controlling power consumption across multiple devices. These intelligent units provide real-time data and remote capabilities. They offer significant advantages over traditional PDUs, which only distribute power without providing any insights or control.
Key Features of Smart PDUs
Smart PDUs offer a suite of features that enhance power management and operational efficiency in data centers. These capabilities allow administrators to gain granular control and visibility over their power infrastructure.
Individual Outlet Metering
Smart PDUs provide precise power consumption monitoring at the individual outlet level. This feature allows users to track real-time power usage, including voltage, current, and power consumption, for each connected device. Outlet-level metering helps identify power hogs and underutilized equipment. It also enables accurate energy cost calculations for specific devices.
Remote Power Cycling
Remote power cycling is a critical feature of Smart PDUs. It allows administrators to remotely turn individual outlets on or off. This capability helps troubleshoot unresponsive equipment without requiring physical presence in the data center. It also facilitates power conservation by shutting down idle devices.
Environmental Monitoring
Many Smart PDUs include built-in or external environmental sensors. These sensors monitor critical conditions such as temperature and humidity within the rack. They provide valuable data for maintaining optimal operating environments. Proactive monitoring helps prevent equipment damage from overheating or excessive moisture.
Network Connectivity
Smart PDUs feature network connectivity. This allows remote management and monitoring through a web interface or networked systems. Users can access real-time power and environmental data from anywhere. Network connectivity also supports integration with Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) solutions. This provides comprehensive insights and centralized control.
Types of Smart PDUs
Smart PDUs come in various configurations, each offering different levels of monitoring and control. Data center managers choose a type based on their specific needs and budget.
Metered Smart PDUs
Metered Smart PDUs provide local current monitoring. They typically feature a digital display on the unit. This display shows real-time load information. This allows data center staff to monitor power usage directly at the rack. Metered PDUs help prevent overloads and ensure balanced power distribution. However, they do not offer remote monitoring capabilities.
Monitored Smart PDUs
Monitored Smart PDUs offer remote monitoring capabilities. IT staff can track power consumption, voltage, and other critical parameters from any location. These PDUs provide data at the PDU level or, in more advanced versions, at the outlet level. They send alerts when power usage or environmental conditions exceed predefined thresholds. This enables proactive management and troubleshooting.
Switched Smart PDUs
Switched Smart PDUs combine remote monitoring with the ability to remotely control individual outlets. This type of PDU allows users to power cycle devices from a remote location. It optimizes energy usage by turning off idle equipment. Switched PDUs also facilitate efficient maintenance and troubleshooting. They offer the highest level of control among Smart PDU types.
Direct Energy Cost Reduction with Smart PDUs
Smart PDUs directly contribute to significant energy cost reductions in data centers. They provide detailed insights and control over power consumption. This allows managers to make informed decisions. These decisions lead to lower electricity bills and improved operational efficiency.
Granular Power Monitoring and Measurement
Granular power monitoring offers deep visibility into energy use. This helps data center operators find and fix inefficiencies. It moves beyond overall facility metrics like PUE. PUE shows overall data center efficiency. However, it does not show the efficiency of individual racks, servers, or applications. This lack of detail makes it hard to find specific sources of energy waste. Smart PDUs provide this missing detail. They use built-in power meters to track energy use by connected equipment. This allows for precise identification of energy issues.
Identifying Phantom Loads
Phantom loads are devices that consume power even when they are not actively working. Smart PDUs help identify these hidden energy drains. They provide real-time power consumption data for each outlet. This data shows which devices draw power unnecessarily. Operators can then take action to eliminate this wasted energy.
Detecting Underutilized Servers
Many data centers have servers that run but do little work. These are underutilized servers. Switched PDUs collect detailed data like amperage, voltage, kilowatts, kilovolt-amps, and kilowatt-hours from individual outlets. This data helps identify servers suitable for decommissioning or virtualization. It also reveals times when production servers are not busy. This allows for remote power cycling, turning them off and on as needed. This reduces IT power consumption. It also lowers the energy needed for cooling these idle servers.
Pinpointing Power Hogs
Some equipment uses much more power than others. These are “power hogs.” Smart PDUs help pinpoint these devices. They provide energy consumption reports. These reports highlight high-energy usage areas across different sites or business units. This allows data center managers to compare device-level consumption. They can then make decisions about upgrades or virtualization. This also helps in creating ghost server reports to identify and decommission idle servers.
Remote Power Management and Control
Remote power management and control features of Smart PDUs offer substantial energy savings. They allow data center staff to manage power without being physically present.
Eliminating Idle Equipment Power
Smart PDUs give control over power down to the individual outlet. Technicians can switch the PDU on and off from any location. They can also restart equipment after outages. This maximizes runtime efficiently. In lab or test environments, not every server needs continuous power. Remote power control PDUs allow organizations to save energy. They simply power off servers and equipment when not needed. This can be done manually or automatically at set times. Using intelligent PDUs, data center managers can schedule power cycling of unused IT equipment remotely. This reduces energy consumption.
Facilitating Efficient Maintenance
Remote power control also makes maintenance easier. If a server freezes, technicians can remotely power cycle it. This avoids a trip to the data center. This saves time and labor costs. It also ensures quicker resolution of issues. Switched PDUs offer a full view of critical IT equipment power usage. This view is available at the rack and remotely. They also provide the ability to remotely turn on, turn off, or reboot power at each outlet. This function is perfect for data centers that need to limit power use at the outlet. It prevents accidental overloads. It also helps remote data centers. It allows quick and easy power cycling of equipment in large facilities or across an entire network.
Optimizing Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE)
Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) measures a data center’s energy efficiency. It is the ratio of total facility energy consumed to the energy used by IT equipment. A PUE closer to 1.0 means higher energy efficiency. Total facility energy includes all power used by the data center. This covers IT equipment, cooling, lighting, and power delivery. IT equipment energy refers to power for computing, storage, networking, and control hardware.
Improving PUE with Smart PDU Data
Smart PDU data helps improve PUE. It provides detailed information about power consumption at the device level. This data helps identify areas of inefficiency. For example, it can show if cooling systems are working harder than needed. It can also show if certain IT equipment uses too much power. This granular data allows for targeted improvements. These improvements directly lower the “Total facility energy usage” part of the PUE calculation.
Rectifying Power Inefficiencies
Smart PDUs help rectify power inefficiencies. They detect system imbalances. They also identify inefficiencies in motor-driven systems. This data helps improve setpoints for environmental systems. For example, it can inform better temperature, humidity, or pressure settings. This leads to non-CAPEX savings. It also guides smart CAPEX decisions. This includes replacing inefficient equipment like old HVAC units. It also identifies opportunities for advanced controls and automation. These actions directly reduce wasted energy.
Capacity Planning and Avoiding Over-provisioning
Data centers require careful planning to ensure efficient resource utilization. Intelligent PDUs play a crucial role in this process. They provide the necessary data to prevent both over-provisioning and under-provisioning of infrastructure.
Preventing Infrastructure Over-provisioning
Intelligent PDUs offer granular power usage data. This data is essential for effective capacity planning. It enables monitoring and management of power distribution. This helps identify overloaded or underutilized areas within the data center. For instance, circuits nearing capacity limits become detectable. This allows for load redistribution to prevent outages. Similarly, underutilized resources are identified and reallocated to maximize efficiency. By using intelligent PDUs, data centers avoid risks like equipment failure from overloading. They also prevent wasted resources from underutilization. This leads to improved efficiency and optimal resource use. These PDUs also send alerts for power threshold breaches. This ensures prompt action and continuous operations.
Reducing Capital Expenditure
Accurate capacity planning directly impacts capital expenditure. Intelligent PDUs are crucial for this planning. They evaluate power usage and distribution. This pinpoints areas for optimization. It also facilitates future expansion. This ensures data centers maximize their resource utilization. They prevent both over-provisioning and under-provisioning. This avoids unnecessary purchases of equipment. It also reduces the need for additional power infrastructure. Their role is vital in maintaining data center efficiency. It also supports growth and sustainability. This strategic approach saves significant capital.
Load Balancing and Phase Optimization
Effective load balancing and phase optimization are critical for data center stability and efficiency. Intelligent PDUs provide the tools to achieve these goals.
Distributing Loads Evenly
Intelligent PDUs enable load balancing across phases or circuits. They offer remote switching of power outlets. They also provide power sequencing and alarm notifications. These features are suitable for high-density and high-complexity applications. They require granular visibility and control over power distribution. Evenly distributing electrical loads reduces stress on circuits. It also prevents overloads. This ensures a stable power supply for all connected equipment.
Maximizing Infrastructure Efficiency
Three-phase PDUs provide superior load balancing. They evenly distribute electrical loads. This reduces stress on circuits and prevents overloads. They enhance energy efficiency through improved power factor and reduced losses. This leads to lower utility costs and better thermal performance. These PDUs ensure optimal energy distribution in high-demand environments. They balance the load across three phases. This maintains consistent power usage and reduces waste. Monitored three-phase PDUs offer insights into power consumption patterns. This aids in identifying areas for improvement. It also prevents system overloads to minimize downtime. This comprehensive approach maximizes the efficiency and reliability of the data center’s power infrastructure.
Indirect Cost Savings from Smart PDUs
Data centers realize significant indirect cost savings through the implementation of intelligent PDUs. These savings extend beyond direct energy reduction, impacting operational stability, efficiency, and equipment longevity.
Enhanced Uptime and Reliability
Preventing Costly Downtime
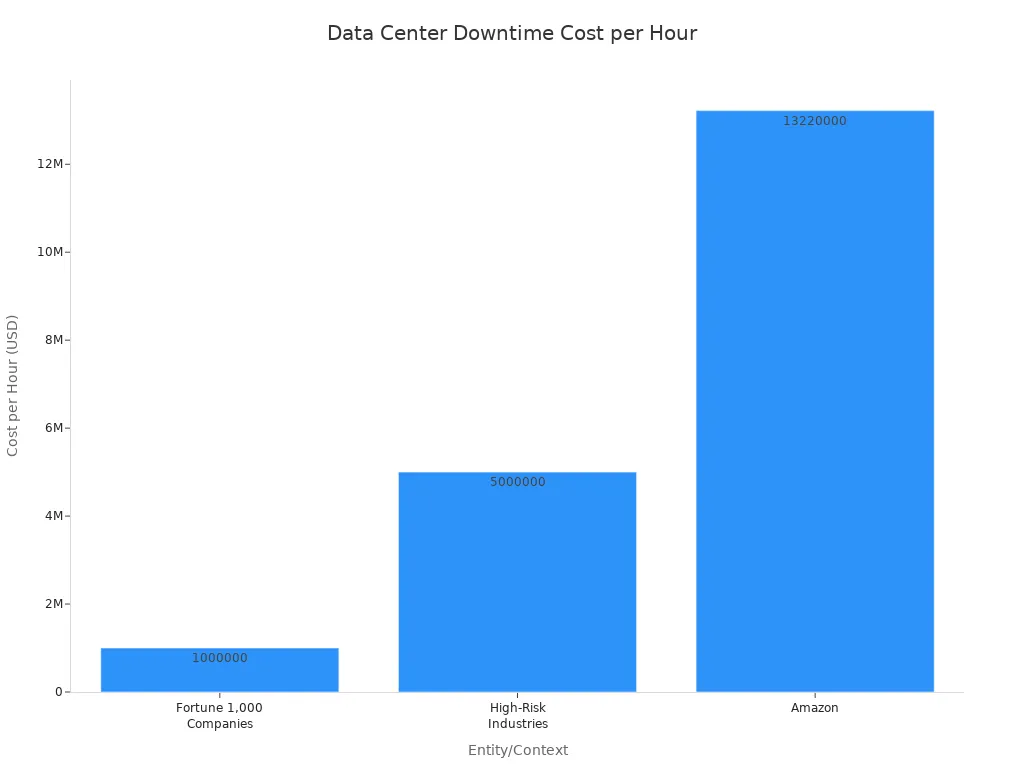
Data center outages carry substantial financial consequences. A majority of data center outages cost businesses over $100,000, with many exceeding $1 million. Larger organizations and operations incur higher costs. For example, Amazon lost an estimated $34 million in revenue in 2021 due to data center outages. Facebook lost an estimated $100 million, and Alibaba faced an estimated $1 billion loss in revenue during the same year. The percentage of outages costing over $100,000 increased from 39% in 2019 to over 60% in recent years. Outages costing over $1 million rose from 11% to 15%.
| Cost Threshold | 2019 | Recent Years |
|---|---|---|
| Over $100,000 | 39% | Over 60% |
| Over $1 million | 11% | 15% |
The cost per hour of downtime for Fortune 1,000 companies can reach up to $1 million, while high-risk industries like banking and finance face upward of $5 million.
Intelligent PDUs are engineered for durability. They undergo rigorous testing and use robust materials to ensure consistent performance. This design prevents outages. Features like full-color displays and clear phase identification also reduce human error during equipment installation. This contributes to higher uptime.
Proactive Monitoring Benefits
These units offer high-accuracy metering at various levels. This allows precise real-time monitoring of power data. This capability is crucial for preventing outages. Advanced power management provides visibility into available power per phase and outlet. When combined with DCIM software, this enables configuration of specific alerts and automation rules. This optimizes power usage and prevents issues. Some intelligent PDUs include built-in failover power capabilities. This maintains connectivity if one PDU loses power. This allows immediate alerts and remote access. Responsive, rule-based alerting for potential issues can transfer to BMS or DCIM software, preventing downtime.
Improved Operational Efficiency
Reducing Manual Intervention
Remote management capabilities reduce the need for physical presence in the data center. This saves time and minimizes human error. Real-time power usage monitoring allows for identification and correction of excessive power consumption. Scheduling power cycles for non-essential equipment during off-peak hours further reduces costs.
Lowering Labor Costs
The reduction in manual intervention directly translates to lower labor costs. Technicians spend less time on site for routine checks or troubleshooting. This frees them for more strategic tasks.
Extended Equipment Lifespan
Optimized Power Delivery
Intelligent PDUs extend the lifespan of data center equipment. They deliver stable and reliable power. This protection against power fluctuations ensures consistent power distribution. This is crucial for sensitive equipment. It also reduces the need for costly repairs or replacements.
Environmental Monitoring Benefits
Plug-and-play environmental sensors integrate with intelligent PDUs. They allow comprehensive monitoring of conditions like temperature and humidity. This data acts as warnings and alerts. It helps maintain optimal operating environments. This prevents equipment failures. AI integration in these units also contributes to extending equipment life. It uses machine learning to detect early signs of equipment degradation. This enables proactive maintenance, preventing failures and prolonging operational life.
Implementing Smart PDUs: Best Practices

Implementing intelligent power distribution units requires careful planning. Data centers can maximize their benefits by following best practices. These practices ensure efficient energy management and operational stability.
Assessing Current Power Consumption
Conducting an Initial Power Audit
Before deploying new equipment, data centers must understand their existing power usage. An initial power audit helps identify current consumption patterns. Operators measure actual usage with metered PDUs. They also account for peak loads, which are maximum power draws during busy times. It is wise to include a safety margin, typically 20-30%, for unexpected surges or future growth. This audit identifies rack power consumption at the inlet, outlet, and circuit breaker levels. Inlet metering shows overall server power. Outlet metering clarifies individual device consumption. Circuit breaker metering provides early warnings for heavily loaded circuits.
Choosing the Right Smart PDU
Selecting Based on Data Center Needs
Choosing the correct Smart PDU involves several considerations. First, confirm the infrastructure voltage. This includes 120V single phase, 208V single phase, 208V three phase, or 400V three phase for North America. Next, establish the rack kilowatt budget. Estimate the total power needed, including a buffer for future growth. Determine the circuits, phase, and amperage for the rack. This dictates the PDU plug type. Find out what devices will be in the rack. This determines the necessary PDU outlet types and number of outlets. Decide if switching is desired and what level of metering is required. Consider remote power control for rebooting servers. Also, assess if inlet-level or outlet-level metering is preferred. Learn the rack PDU installation options. This includes form factor, power inlet location, and cord length. Finally, figure out if advanced features are needed. These include environmental monitoring, specific LAN connectivity, daisy chaining capabilities, or color-coded PDUs. Features like outlet control, hot-swappable design, and Ulock outlets also enhance functionality.
Budget Considerations
Budget plays a role in PDU selection. Data centers must balance desired features with financial constraints. Investing in advanced features often yields greater long-term savings.
Integrating Smart PDUs with DCIM Solutions
Comprehensive Insights with DCIM
Integrating intelligent PDUs with Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) solutions enhances their capabilities. DCIM turns collected data into actionable information. It uses business intelligence dashboards and visual analytics. This provides real-time visibility into device status and update compliance.
Centralized Management Benefits
DCIM solutions offer centralized management benefits. They automate update processes. This minimizes manual effort and human error. This reduces downtime risks by maintaining a secure and updated infrastructure. DCIM enables remote management and power actions. It facilitates bulk firmware updates, cloning configurations, and restoring from backups through a single user interface. This integration bridges the gap between IT and facilities. It optimizes data centers from cost centers into value-generating assets.
Smart PDUs are indispensable for modern data centers. They significantly reduce energy costs, improve operational efficiency, and help achieve sustainability goals. These units enable savings through granular monitoring, remote control, PUE optimization, and informed capacity planning. They track energy usage, provide alerts for power anomalies, and allow remote management, which streamlines operations and reduces onsite visits. Investing in a Smart PDU is a strategic move for a more sustainable and cost-effective data center future, enhancing reliability and future-proofing infrastructure.
FAQ
What is a Smart PDU?
A Smart PDU distributes power to data center equipment. It also monitors, manages, and controls power consumption. These units provide real-time data and remote capabilities. They offer significant advantages over traditional PDUs.
How do Smart PDUs reduce energy costs?
Smart PDUs provide granular monitoring. They identify phantom loads and underutilized servers. Remote control allows users to power off idle equipment. This optimizes power usage and lowers electricity bills.
What are the main types of Smart PDUs?
Three main types exist. Metered Smart PDUs offer local monitoring. Monitored Smart PDUs provide remote monitoring. Switched Smart PDUs add remote outlet control. Each type offers different levels of functionality.
Can Smart PDUs monitor individual outlets?
Yes, many Smart PDUs feature individual outlet metering. This allows precise tracking of power consumption for each connected device. It helps identify power hogs and underutilized equipment. This granular data is very valuable.
How do Smart PDUs help with capacity planning?
Smart PDUs provide detailed power usage data. This data helps prevent over-provisioning of infrastructure. It ensures optimal resource utilization. This reduces capital expenditure and improves efficiency.
Do Smart PDUs improve data center uptime?
Yes, Smart PDUs enhance uptime. They offer proactive monitoring and alerts for power issues. This prevents costly downtime. Their robust design also ensures reliable power delivery. This keeps operations smooth.
What is PUE, and how do Smart PDUs affect it?
PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness) measures data center energy efficiency. Smart PDUs provide data to identify inefficiencies. This allows targeted improvements. These actions directly lower the PUE value, making the data center more efficient.
Post time: Dec-02-2025

