
Comparing power distribution unit features is crucial for 2025. Understanding these specific features directly impacts an infrastructure’s performance. For example, a French Type E power distribution unit PDU offers unique regional benefits. This knowledge allows for an informed selection. An optimal Basic PDU then ensures reliable power distribution, safeguarding connected equipment.
Key Takeaways
- Choose the right number and type of outlets for your devices. Plan for future growth to avoid power shortages.
- Match the PDU’s input plug and amperage to your building’s power. This prevents electrical problems and ensures safety.
- Select a PDU form factor that fits your space. Vertical PDUs save rack space for IT equipment.
- Pick a PDU with a power cord long enough to reach the outlet. Avoid using extension cords for safety.
- Look for surge protection and EMI/RFI filtering. These features protect your equipment from power issues.
- Consider the PDU’s construction material and build quality. Durable materials like steel or aluminum ensure long life.
- Check for safety certifications like UL and CE. These ensure the PDU meets important safety rules.
- Research the vendor’s reputation and support. Good support helps solve problems quickly.
Basic PDU Outlet Configuration and Density
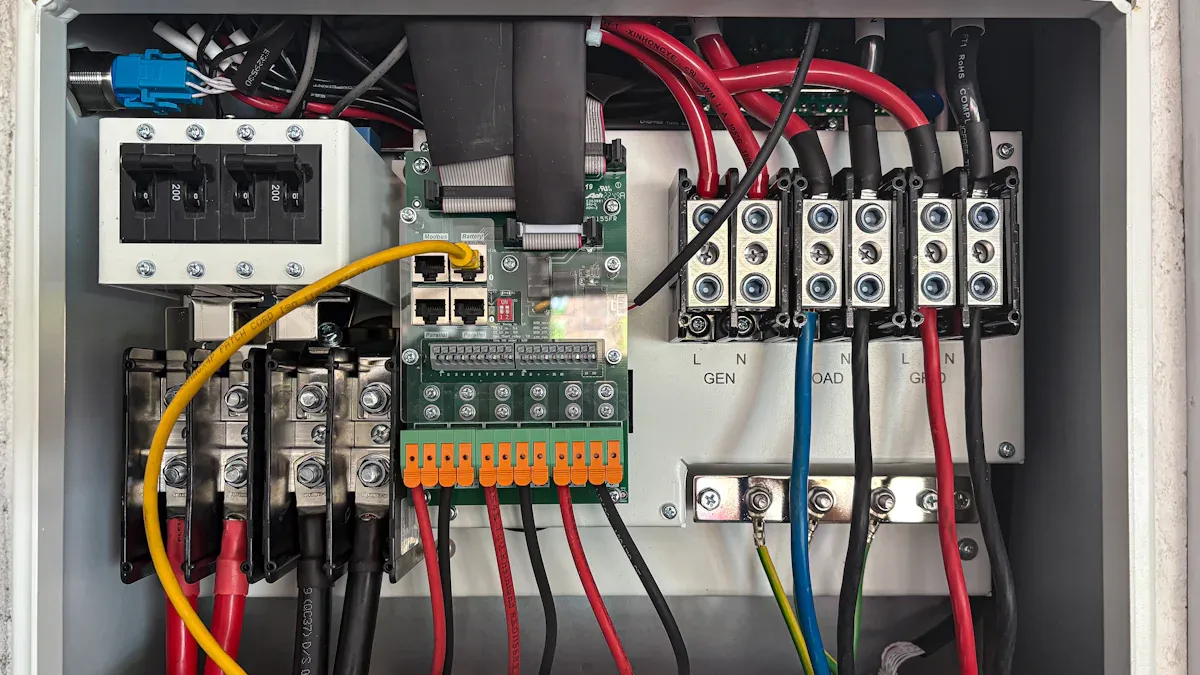
The outlet configuration and density of a Power Distribution Unit (PDU) directly influence its utility and efficiency within any setup. Careful consideration of these factors ensures optimal power delivery to all connected devices.
Number of Outlets for Your Basic PDU
Selecting the correct number of outlets prevents power shortages and supports future growth.
Assessing current device count needs
Organizations must first identify the exact number of devices requiring power. This includes servers, network switches, storage arrays, and other essential equipment. An accurate count prevents immediate shortfalls.
Planning for future expansion
Future expansion plans significantly impact PDU selection. Consider potential additions to the infrastructure over the next few years. For a vertical PDU in a standard server rack, experts recommend 40 or more outlets. The PDU’s length often dictates the number of outlets, primarily limited by the server cabinet’s height. This proactive approach avoids the need for additional PDUs later.
Basic PDU Outlet Types
Different regions and equipment types require specific outlet connectors.
NEMA 5-15R and 5-20R standards
North American data centers frequently use NEMA 5-15R and 5-20R outlets. The NEMA 5-15R supports 15 amps, while the NEMA 5-20R handles 20 amps, often found in commercial buildings and as wall outlets within data centers.
IEC C13 and C19 connectors
IEC C13 and C19 connectors are prevalent in modern data centers globally.
- IEC 60320 C13 and C14: These are the most common connector types in modern data centers. They also see wide use in home electronics.
- IEC 60320 C19 and C20: While less common than C13/C14, they are still frequently used in data centers. PDUs offer various combinations of C13 and C19 receptacles to accommodate diverse equipment.
Regional and specialized Basic PDU connectors
Other common Basic PDU outlet types include:
- NEMA L5-20R
- NEMA L5-30R
- NEMA L6-20R
- NEMA L6-30R
These specialized connectors cater to higher amperage requirements or specific regional standards.
Basic PDU Outlet Spacing
Proper outlet spacing prevents physical interference and ensures all ports remain accessible.
Standard vs. wide spacing for power bricks
Standard spacing works well for devices with traditional power cords. However, many modern devices use bulky power bricks. Wide spacing accommodates these larger adapters, preventing them from blocking adjacent outlets.
Preventing outlet blockage in Basic PDUs
Choosing a PDU with adequate spacing ensures every outlet is usable. This maximizes the PDU’s efficiency and prevents the need for inconvenient workarounds or additional power strips.
Basic PDU Input Plug Type and Amperage
The input plug type and amperage rating of a PDU are critical considerations. They ensure compatibility with the facility’s power infrastructure and prevent electrical issues.
Basic PDU Input Plug Standards
Different regions and power requirements dictate specific input plug standards. Selecting the correct plug ensures a secure and compliant connection.
NEMA 5-15P, 5-20P, L5-20P, L5-30P
NEMA connectors are common in North America. They include various types designated by "P" for plug. For instance, the NEMA 5-15P handles 15 amps, while the 5-20P supports 20 amps. Locking types, such as L5-20P and L5-30P, provide a more secure connection, preventing accidental disconnections in critical environments. These NEMA connectors are prevalent in many data center and office setups.
IEC 60320 C14, C20 for Basic PDUs
Globally, IEC 60320 connectors are widely adopted. The IEC 60320 C14 plug pairs with a C13 receptacle, commonly found on computer power supplies. The IEC 60320 C20 plug, a larger variant, pairs with a C19 receptacle. These are often used for higher power devices. Both C14 and C20 plugs are essential for connecting many modern IT devices to a Basic PDU.
Regional variations in Basic PDU plugs
Beyond NEMA and IEC 60320, other plug standards exist. IEC 60309 connectors, for example, are common in industrial settings. They are designated by pole, earth/ground, and neutral pins, such as 2P+E or 3P+N+E. Other NEMA locking types like L6-20P, L6-30P, L15-20P, L15-30P, L21-20P, and L-30P also cater to specific voltage and amperage needs. These regional and specialized plugs ensure compatibility with diverse power grids worldwide.
Basic PDU Amperage Rating
The amperage rating of a PDU determines the maximum current it can safely handle. This rating is crucial for operational safety and efficiency.
Matching circuit breaker capacity
Always match the PDU’s amperage rating to the circuit breaker capacity in the electrical panel. A 20A PDU requires a 20A circuit breaker. This prevents the PDU from drawing more power than the circuit can safely provide, which could trip the breaker or cause electrical hazards.
Preventing overload in Basic PDU setups
Selecting a PDU with an appropriate amperage rating prevents overloading. Overloading occurs when connected devices draw more current than the PDU can supply. This can lead to power outages, equipment damage, or even fires. Typical amperage ratings for basic PDUs in enterprise environments range from 15A, 20A, and 30A, going up to 100A for high-density applications.
Future power requirements for your Basic PDU
Consider future power needs when choosing a PDU’s amperage. While a basic, standard PDU might offer 15A-30A at 120V-208V, supporting 1.4kW-4.9kW, future expansion could require more. Over-provisioning slightly can accommodate new equipment without needing a PDU replacement. This proactive approach ensures the power infrastructure remains scalable.
Basic PDU Form Factor and Mounting Options

The physical design and installation methods of a power distribution unit significantly impact its integration into any environment. Choosing the correct form factor ensures efficient space utilization and proper cable management.
Rack Mount Basic PDUs
Rack-mounted PDUs are common in data centers and server rooms. They offer organized power distribution within standard equipment racks.
Horizontal 1U/2U Basic PDU options
Horizontal PDUs fit within the standard width of a server rack. They typically occupy 1U or 2U of vertical rack space. While compact, these units consume rack space that could otherwise house IT equipment. This can create capacity management challenges in high-density data centers. However, horizontal PDUs offer a compact design that maximizes the use of available rack space by fitting horizontally within a single rack unit (1U). This allows for more vertical space for essential IT equipment, simplifies cable management, and improves airflow, which enhances cooling efficiency.
Vertical 0U Basic PDU solutions
Vertical PDUs, often called 0U PDUs, mount vertically along the side or rear of a server rack. They do not consume any horizontal rack units, making them ideal for maximizing space for IT equipment. This design allows for a higher density of outlets within the rack without sacrificing valuable equipment space.
Non-Rack Basic PDU Mounting
Not all power distribution needs occur within a server rack. Various mounting options exist for different environments.
Under-desk and wall mount Basic PDUs
Under-desk and wall-mount PDUs provide power distribution in offices, control rooms, or other non-rack settings. Users can securely attach these units to walls or under desks, keeping power accessible yet out of the way. This helps maintain a tidy workspace and prevents accidental disconnections.
Space-saving Basic PDU solutions
These non-rack mounting options are crucial for space-constrained environments. They offer flexible power solutions where traditional rack mounting is not feasible or desired. Their design focuses on minimizing footprint while providing reliable power access.
Basic PDU Mounting Hardware
Proper mounting hardware ensures secure installation and long-term reliability. Manufacturers often include necessary components with the PDU.
Included brackets and screws
Most PDUs come with standard mounting brackets and screws. These components allow for secure attachment to rack rails, walls, or other surfaces. Users should verify compatibility with their specific rack or mounting surface before installation.
Tool-less installation for Basic PDUs
Many modern PDUs feature tool-less installation options. These designs simplify deployment and reduce installation time. For example, some units include detachable toolless mounting buttons. These buttons allow users to snap the PDU into place without needing additional tools, making setup quick and efficient.
Basic PDU Cord Length and Orientation
The power cord’s length and its exit orientation are critical factors for efficient and safe power distribution. These features directly impact cable management and overall infrastructure aesthetics. Careful consideration prevents clutter and ensures reliable power delivery.
Basic PDU Input Cord Length
The input cord connects the Basic PDU to the main power source. Its length is a practical concern.
Reaching the power source effectively
Operators must ensure the Basic PDU’s input cord can comfortably reach the designated power outlet. This outlet might be a wall receptacle, a floor box, or an uninterruptible power supply (UPS). Measuring the distance from the PDU’s intended mounting location to the power source prevents installation issues. A cord that is too short creates tension and potential disconnections. A cord that is excessively long contributes to cable clutter.
Avoiding extension cords with Basic PDUs
Using extension cords with power distribution units is generally discouraged. Extension cords can introduce voltage drops, increase resistance, and pose fire hazards. They are not designed for continuous, high-power loads typical of data center equipment. Selecting a Basic PDU with an appropriate input cord length eliminates the need for these unsafe workarounds. This ensures a direct, secure, and compliant power connection.
Basic PDU Cord Exit Orientation
The direction in which the power cord exits the PDU affects cable routing and space utilization.
Straight vs. right-angle plugs
Input plugs typically come in two main orientations: straight or right-angle. Straight plugs extend directly out from the PDU. They require more clearance space behind the unit. Right-angle plugs, however, bend immediately after exiting the PDU. This design allows equipment to sit closer to walls or other rack components. The choice depends on the available space and cable management strategy.
Cable management considerations for Basic PDUs
Effective cable management is vital for airflow, maintenance, and safety within any IT environment. Right-angle plugs offer significant advantages in this area.
- Space-saving: Angled power cords are ideal for tight spaces. They allow equipment to be placed closer to walls or other objects.
- Improved cable management: They help keep cables neat and untangled. This simplifies equipment organization and maintenance tasks.
- Enhanced safety: Right/left-angle AC cables prevent accidental disconnections. They ensure a secure power supply and reduce tripping hazards.
- Extended lifespan: Minimizing strain on cables and ports contributes to the longevity of equipment.
- Optimized performance: The design of these cables promotes better airflow and flexibility. This leads to more efficient power delivery.
Choosing the correct cord orientation streamlines cable routing. It also improves the overall organization and safety of the power infrastructure.
Basic PDU Surge Protection and Filtering
Power quality significantly impacts equipment longevity and performance. Power Distribution Units (PDUs) often include features to protect connected devices from electrical disturbances. Surge protection and EMI/RFI filtering are two crucial elements.
Basic PDU Surge Suppression
Power surges can damage sensitive electronic equipment. Surge suppression within a PDU diverts excess voltage away from connected devices.
Joule rating and response time
A surge suppressor’s effectiveness is often measured by its joule rating. This rating indicates the amount of energy the suppressor can absorb before failing. Higher joule ratings offer greater protection. The value and sensitivity of equipment directly influence the required joule rating. More valuable and sensitive electronics necessitate a higher rating for adequate protection. Response time is also critical. A faster response time means the suppressor reacts more quickly to a surge, providing immediate defense.
Here are recommended joule ratings for various applications:
| Application Scenarios | Recommended Joule Rating (J) |
|---|---|
| Small Electronic Devices | 1,000–2,000J |
| Home Entertainment Equipment | 2,000–3,000J |
| High-End Electronics & Workstations | 3,000–6,000J |
Protecting connected equipment with Basic PDUs
Selecting a PDU with robust surge suppression safeguards valuable IT assets. A high joule rating, such as 2000 joules, provides robust defense against power surges for sensitive server equipment. This protection prevents costly downtime and hardware failures. It ensures continuous operation of critical systems.
Basic PDU EMI/RFI Filtering
Electrical noise can disrupt sensitive electronics. Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) and Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) are common forms of this noise.
Reducing electrical noise
PDUs can incorporate EMI/RFI filtering as a protective measure for devices against electrical noise. This feature, alongside others like circuit breakers and surge protection, helps to mitigate the risk of equipment damage and contributes to a safer operational environment. The filters work by blocking or reducing unwanted electrical signals that travel along power lines. This creates a cleaner power supply for connected devices.
Ensuring clean power delivery from Basic PDUs
Clean power is essential for optimal performance of IT equipment. EMI/RFI filtering prevents data corruption, system errors, and premature equipment wear. It ensures that devices receive stable and consistent power. This leads to greater reliability and efficiency within the data center or office environment.
Basic PDU Construction Material and Durability
The physical construction of a power distribution unit significantly influences its lifespan and performance. Material choices and overall build quality determine how well a unit withstands operational demands.
Basic PDU Chassis Material
The chassis material provides the structural integrity for the power distribution unit. Different materials offer distinct advantages.
Steel vs. aluminum for durability
Manufacturers often choose steel for its exceptional strength and robustness. Steel chassis units resist physical impact and bending, making them suitable for industrial settings or environments where rough handling might occur. Aluminum, while lighter, also offers good durability. It resists corrosion effectively, which benefits units in humid or outdoor conditions.
Heat dissipation properties of Basic PDUs
Effective heat dissipation is crucial for maintaining optimal operating temperatures within a PDU and the surrounding equipment.
| Material Type | Thermal Properties |
|---|---|
| Metal (including Steel and Aluminum) | Good thermal conductivity |
| Plastic | Poor thermal conductivity, may require vents or heat sinks for heat dissipation |
Aluminum excels in heat dissipation. Its excellent thermal conductivity makes it a preferred material in high-density environments. Effective cooling is crucial for PDUs in these settings. Steel also conducts heat well, but aluminum’s properties are often highlighted for superior thermal management.
Basic PDU Build Quality
High build quality ensures a PDU performs reliably over time. It also protects connected devices.
Robustness for demanding environments
A robust PDU withstands harsh conditions. This includes environments with vibrations, dust, or extreme temperatures. Manufacturers use high-grade components and secure assembly methods to achieve this robustness. Such units prevent failures and maintain consistent power delivery in challenging operational settings.
Longevity and reliability of Basic PDUs
A well-built PDU offers long-term reliability. It reduces the need for frequent replacements and maintenance. This translates into lower operational costs and less downtime for critical systems. Investing in a unit with superior build quality ensures a stable and dependable power infrastructure for many years.
Basic PDU Agency Certifications and Compliance
Agency certifications and compliance are essential for power distribution units. These certifications ensure safety, reliability, and adherence to environmental standards. They provide assurance to users regarding product quality and regulatory conformity.
Basic PDU Safety Standards
Safety standards protect both equipment and personnel. They confirm a PDU meets rigorous testing requirements.
UL, cUL, CE, RoHS compliance
Various certifications apply to PDUs for international distribution. The UL Listed Mark primarily applies to electrical products sold in the U.S. and Canada. It ensures products are free from risks like electric shock and fire. UL Standards include UL 60950-1 for Information Technology Equipment and UL 62368-1 for Audio/Video, Information and Communication Technology Equipment. UL 1363 also covers Relocatable Power Taps. The CE Mark is required for electronic devices sold in the European Union (EU). Manufacturers typically self-certify compliance for this mark. The EU low-voltage directive (LVD) also covers PDUs.
The IEC CB Scheme offers a global standard. National certification bodies recognize each other’s testing. This facilitates multi-country certification. The IEC 62368-1 standard applies to PDUs. IEC 60950-1 for Information Technology Equipment – Safety and IEC 60320 for Appliance Couplers are also relevant. FCC Compliance certifies a device’s electromagnetic emissions do not cause interference or safety hazards. PDUs for business/industrial use are Class A digital devices. The UKCA Mark is a new certification for products marketed in Great Britain. It became effective on January 31, 2020. Its requirements are similar to the CE mark. NEMKO Certification provides additional approval for universal PDUs. SGS NRTL Certification comes from a Nationally Recognized Test Laboratory. OSHA recognizes SGS, which conducts third-party testing. This ensures products meet relevant U.S. and Canadian standards, material safety, and consistent manufacturing quality.
Meeting regulatory requirements for Basic PDUs
Meeting these regulatory requirements is crucial for market access and user confidence. These certifications demonstrate a manufacturer’s commitment to product safety and quality. They also help avoid legal issues and product recalls.
Basic PDU Environmental Compliance
Environmental compliance focuses on a PDU’s impact on the environment. This includes energy efficiency and hazardous material reduction.
Energy efficiency ratings
Energy efficiency ratings indicate how effectively a PDU converts input power to usable output power. Higher efficiency means less wasted energy and lower operating costs.
Green initiatives for Basic PDUs
Green initiatives for PDUs often involve several aspects.
- RoHS Compliance: This ensures products are free from hazardous materials.
- Remote monitoring and control: This allows access to real-time power usage data and historical trends. It enables proactive energy management, like powering off unused equipment.
- Dual-power inputs and network redundancy options: These features ensure reliability, especially in challenging environments.
| Certification | Description |
|---|---|
| UL Certification | Verifies safety and performance through rigorous testing. |
| CE Marking | Indicates adherence to EU health, safety, and environmental regulations. |
| RoHS Compliance | Ensures products are free from hazardous materials. |
These initiatives contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally responsible data center operation.
Basic PDU Color Coding and Labeling
Effective power management in data centers and server rooms relies heavily on clear visual cues. Color coding and labeling on power distribution units (PDUs) simplify identification and prevent critical errors.
Basic PDU Outlet Color Coding
Color coding outlets provides an immediate visual reference for power configurations. This helps technicians quickly understand the power infrastructure.
Identifying different power phases
Basic PDU outlet color coding helps differentiate between power feed settings. For instance, colored LCD console panels, available in yellow, red, purple, blue, and green, make it easier to distinguish power phases. This feature speeds up troubleshooting when failures occur. Color-coded PDUs and their outlets assist operators in identifying different power phases. They discern which phase powers each PDU, simplifying load balancing.
Preventing misconnections in Basic PDUs
Color coding significantly reduces the risk of misconnections. Operators can quickly identify the correct power source for specific equipment. This prevents accidental plugging of devices into incompatible power phases or circuits. Additionally, color-coded, locking receptacles can organize individual outlets by sub-circuits. This provides detailed power infrastructure organization and enhances safety.
Clear Basic PDU Labeling
Beyond color coding, clear and concise labeling offers essential information about the PDU’s specifications and connections.
Input and output specifications
Labels clearly display critical input and output specifications. These include voltage, amperage, and outlet types. This information helps technicians verify compatibility before connecting equipment. It also assists in capacity planning and ensures the PDU operates within its safe limits. Accurate labeling prevents overloading and potential damage to connected devices.
Easy identification in dense racks
Server racks often contain many cables and devices. Clear labeling on PDUs makes identification easy, even in dense configurations. Labels indicate the PDU’s unique identifier, its power source, and the specific equipment it powers. This streamlines maintenance tasks, reduces human error, and improves overall operational efficiency. Technicians can quickly locate the correct PDU and its associated connections without extensive searching.
Basic PDU Price Point and Warranty
Organizations consider the price and warranty of power distribution units (PDUs) when making purchasing decisions. These factors influence both initial expenditure and long-term operational costs.
Cost-Effectiveness of Basic PDUs
Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of a PDU involves more than just the sticker price. It includes balancing features with budget and understanding the long-term value.
Balancing features with budget
Choosing a PDU requires a careful balance between desired features and available funds. While advanced features like remote monitoring increase cost, basic models offer essential power distribution at a lower price point. For small businesses or home offices, cost-effective options exist. For example, NBYOSUN PDUs typically range from $120 to $350. More established brands also offer competitive pricing for their basic models. An APC Rack PDU AP9568, a basic model, costs around $289.99, while the AP9571A and AP9570 are priced at $399.99 and $409.00 respectively. Eaton Mini Switched PDUs fall between $272 and $416, and Vertiv Basic Switched PDUs range from $400 to $600. These price points allow businesses to select a PDU that meets their immediate needs without overspending.
| Brand/Model | Price Range |
|---|---|
| NBYOSUN | $120 – $350 |
| Eaton Mini Switched PDU | $272 – $416 |
| Vertiv Basic Switched PDU | $400 – $600 |
Long-term value of your Basic PDU investment
A PDU’s long-term value extends beyond its purchase price. A durable, reliable unit reduces the need for frequent replacements and minimizes downtime. Investing in a quality PDU protects connected equipment from power fluctuations, preventing costly repairs or data loss. This proactive approach ensures consistent power delivery and contributes to overall system stability.
Basic PDU Warranty Coverage
Warranty coverage provides peace of mind and protects against manufacturing defects. It is a crucial aspect of any PDU purchase.
Manufacturer’s guarantee and support
A strong manufacturer’s guarantee indicates confidence in product quality. It assures buyers of support if issues arise. Manufacturers often provide technical assistance and troubleshooting resources. This support helps users resolve problems quickly and efficiently.
Replacement policies for Basic PDUs
Replacement policies outline the terms for exchanging a faulty PDU. These policies typically cover defects in materials or workmanship for a specified period. For instance, Panduit offers a three-year standard warranty for their PDUs. This warranty can be extended by up to three additional years with product registration. Raritan states their products are covered by the most extensive standard warranty in the industry. Understanding these policies ensures businesses can quickly replace a malfunctioning unit, minimizing service interruptions.
Basic PDU Vendor Reputation and Support
A vendor’s reputation and the quality of their support significantly influence the long-term satisfaction with a power distribution unit. Customers often consider these factors as important as the PDU’s technical specifications. A reliable vendor provides peace of mind and ensures operational continuity.
Basic PDU Brand Reliability
The reliability of a brand reflects its commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. This reliability builds trust among users.
Industry standing and track record
A vendor’s industry standing and track record offer insights into their product quality and consistency. Established companies with years of experience often produce more dependable PDUs. Their long history in the market suggests they understand customer needs and have refined their products over time. A strong track record indicates a vendor consistently delivers high-performing and durable power solutions. This history helps buyers make informed decisions.
User reviews and testimonials for Basic PDUs
User reviews and testimonials provide real-world feedback on PDU performance and reliability. These insights come directly from other customers who have used the products in various environments. Several brands consistently receive high praise for their offerings:
- Tripp Lite: Users frequently rate Tripp Lite highly for durability and ease of use. Their PDUs offer diverse outlet configurations, providing flexibility. Many consider them simple, durable, and reliable.
- CyberPower: This brand receives praise for its budget-friendly options. CyberPower PDUs offer essential protections, making them a popular choice for cost-conscious buyers.
- Eaton: Customers value Eaton for its versatility. Their PDUs suit diverse setups, from small offices to large data centers.
- Vertiv Geist: Vertiv Geist earns recognition for its robust build and strong safety features. These qualities make their PDUs particularly beneficial for critical environments where reliability is paramount.
Basic PDU Technical Support
Effective technical support is crucial for resolving issues quickly and minimizing downtime. A vendor’s support system can be a deciding factor.
Availability and responsiveness
The availability and responsiveness of technical support are vital. Customers need access to help when problems arise, whether during installation or operation. Vendors offering 24/7 support or quick response times demonstrate a strong commitment to their users. Prompt assistance can prevent minor issues from escalating into major disruptions. This ensures continuous power delivery to critical equipment.
Documentation and resources for Basic PDUs
Comprehensive documentation and readily available resources empower users to troubleshoot issues independently. This includes detailed user manuals, installation guides, FAQs, and online knowledge bases. Good documentation helps users understand their PDU’s features and functions. It also provides solutions to common problems. Vendors who invest in clear, accessible resources enhance the user experience and reduce the need for direct support calls.
Prioritizing Basic PDU Features for Your Needs
Selecting the right power distribution unit requires careful consideration of specific environmental demands. Different settings necessitate distinct features to ensure optimal power delivery and equipment protection. This section explores PDU selection for various operational scales and specialized applications.
Basic PDU Selection for Small Business and Home Office
Small businesses and home offices often operate with limited budgets and space. Their PDU choices reflect these constraints.
Budget-friendly Basic PDU options
Cost-effective PDU solutions are paramount for smaller operations. These units provide essential power distribution without unnecessary advanced features. They focus on core functionality, offering reliable power outlets at an accessible price point. Many manufacturers offer entry-level models specifically designed for these environments.
Essential protection for Basic PDUs
Even with budget constraints, protecting valuable electronics remains crucial. For small business or home office setups, critical PDU features include:
- Compact Design: This is essential for small offices with limited space. It allows for rack-mounted or wall-mounted installation.
- Basic or Metered Features: A basic PDU suffices for simple power sharing. A metered PDU is beneficial for tracking energy usage and preventing circuit overloads.
- Surge Protection: This feature is crucial for safeguarding sensitive electronic devices like computers and printers from power spikes.
Basic PDU Selection for Enterprise Data Centers
Enterprise data centers demand high performance, density, and unwavering reliability from their power infrastructure.
High density and scalability for Basic PDUs
Data centers require PDUs that maximize power delivery within minimal physical space. High-density PDUs offer numerous outlets in compact form factors, such as 0U vertical units. Scalability is also vital. Data centers frequently expand, so PDUs must accommodate future growth without extensive reconfigurations. This ensures efficient power distribution as equipment needs increase.
Advanced reliability for Basic PDUs
Continuous operation is non-negotiable in enterprise data centers. PDUs for these environments feature robust construction and advanced power conditioning. They often include redundant power feeds and hot-swappable components. These features minimize downtime and ensure consistent power delivery to critical servers and networking equipment.
Basic PDU Selection for Specialized Environments
Certain industries have unique power requirements and regulatory mandates. Their PDU selections reflect these specialized needs.
Industrial and medical Basic PDU applications
Industrial settings often expose PDUs to harsh conditions, including dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures. These environments require ruggedized PDUs with durable enclosures and enhanced ingress protection. Medical applications demand PDUs with specific safety certifications and isolation features to prevent electrical interference and ensure patient safety.
Unique compliance requirements for Basic PDUs
Specialized environments often adhere to stringent regulatory standards. Medical PDUs, for example, must comply with specific IEC standards for patient care equipment. Industrial PDUs might require certifications for hazardous locations. These compliance requirements dictate the PDU’s design, materials, and testing protocols. They ensure safe and reliable operation within their intended specialized contexts.
This guide highlights crucial Basic PDU features for 2025. Understanding power requirements, including voltage, amperage, and the choice between single-phase or three-phase power, is paramount. Mounting options, such as horizontal or vertical, also impact efficiency. Prioritizing quality certifications and reputable manufacturers ensures reliability. These insights empower informed decisions. Selecting the ideal unit guarantees optimal performance and robust protection for your infrastructure.
FAQ
What is a Basic PDU?
A Basic PDU distributes power to multiple devices. It provides reliable power delivery without advanced features. Users connect IT equipment to its outlets. This ensures organized power access in racks or other setups.
Why is outlet configuration important for a Basic PDU?
Outlet configuration determines how many devices a PDU supports. It also dictates the types of connectors available. Proper spacing prevents power bricks from blocking outlets. This ensures efficient use of all available ports.
What are common input plug types for Basic PDUs?
Common input plug types include NEMA 5-15P, 5-20P, and various IEC 60320 connectors like C14 and C20. These plugs match the facility’s power infrastructure. They ensure safe and compatible connections.
Do Basic PDUs include surge protection?
Some Basic PDUs offer surge protection. This feature safeguards connected equipment from power spikes. Users should check the joule rating for effective defense. It protects valuable electronics from damage. ⚡
What is the difference between horizontal and vertical PDU mounting?
Horizontal PDUs mount across the rack, using 1U or 2U space. Vertical PDUs mount along the side of the rack. They use 0U space. Vertical options maximize space for IT equipment.
Why are agency certifications important for Basic PDUs?
Agency certifications like UL and CE ensure safety and compliance. They confirm the PDU meets rigorous standards. These certifications protect both equipment and personnel. They also guarantee product quality.
How does PDU amperage rating affect its use?
The amperage rating indicates the maximum current a PDU handles safely. Users must match it to the circuit breaker capacity. This prevents overloading and potential electrical hazards. It ensures stable power delivery.
Post time: Nov-04-2025

