
Data centers rely on a robust PDU to ensure consistent power delivery to critical equipment. Frequent failures often stem from poor maintenance, incorrect load balancing, or overheating. Regular monitoring, balanced loads, and prompt attention to electrical faults help prevent outages and minimize equipment risk.
Key Takeaways
- Regularly inspect and maintain PDUs by performing monthly visual checks and scheduled cleaning to prevent overheating and equipment failure.
- Balance power loads evenly across all outlets and circuits to avoid overloads, reduce heat, and extend the lifespan of your power distribution units.
- Use smart PDUs with real-time monitoring, surge protection, and firmware updates to improve reliability, security, and prepare your data center for future growth.
1. PDU Installation Best Practices

Tool Preparation and Safety Protocols
Technicians should gather all necessary tools before starting installation. Common tools include screwdrivers, torque wrenches, and cable ties. Safety gloves and eye protection help prevent injuries. Always disconnect power sources before handling electrical components. Following safety protocols reduces the risk of accidents and equipment damage.
Verifying PDU Compatibility
Selecting the right PDU starts with understanding the rack’s power requirements. Technicians determine if the rack uses single-phase or three-phase power. They calculate the total power consumption of all devices in the rack and choose a PDU with a higher power rating. Matching the PDU plug to the input power source ensures proper operation. Locking outlets prevent accidental disconnections, while advanced features like metering and remote monitoring support efficient power management.
Optimal PDU Placement in Server Racks
Proper placement of the PDU improves accessibility and airflow. Industry standards recommend positioning PDUs within arm’s reach for easy maintenance. Vertical mounting maximizes outlet count and saves rack space. Horizontal mounting works best when vertical placement blocks airflow or when the rack’s power load is low. Technicians avoid blocking other equipment and ensure the PDU does not obstruct airflow, which helps maintain effective heat dissipation.
Secure Mounting and Structural Support
Mounting brackets provide secure attachment for both vertical and horizontal installations. Detachable brackets allow flexibility for rack, surface, or under-table mounting. Toolless mounting simplifies the process and reduces installation time. Reversible housings on horizontal PDUs let technicians place outlets at the front or back of the rack. Secure mounting prevents movement and minimizes strain on power cords, supporting long-term reliability.
2. PDU Load Balancing Techniques
Even Distribution of Equipment
Proper load balancing stands as a critical factor in extending the operational lifespan of power distribution units. When technicians distribute equipment evenly across all available outlets and circuits, they prevent overloads and reduce thermal stress. Electrical engineering studies highlight the risks of neglecting this practice:
Uneven power distribution across phases or circuits caused by skipping load balancing leads to reliability issues and reduces overall efficiency, which negatively affects the operational lifespan of PDUs.
Technicians should avoid clustering high-power devices on a single circuit. Instead, they should assess the power draw of each device and plan placement to achieve symmetry. This approach minimizes the risk of overheating and false circuit breaker trips. Even distribution also supports consistent airflow, which helps maintain safe operating temperatures.
Monitoring and Adjusting Load Levels
Continuous monitoring allows data center staff to detect imbalances early. Smart PDUs with outlet-level metering provide real-time data on voltage, frequency, and load. Staff can use this information to make timely adjustments and prevent overloads. Best practices for maintaining optimal load levels include:
- Assess power requirements to ensure the PDU meets device needs efficiently.
- Implement load balancing to distribute power evenly and avoid overloads.
- Monitor PDU performance regularly to detect and resolve issues early.
- Use advanced load management features for real-time adjustments.
Improper load balancing causes power quality problems such as harmonics, which lead to equipment malfunctions and increased operational temperatures. By following these techniques, organizations can enhance reliability and maximize the lifespan of their power infrastructure.
3. PDU Inspection and Maintenance
Routine Visual Checks for Wear and Damage
Technicians perform routine visual checks to spot early signs of wear or damage. Manufacturers recommend monthly inspections to look for frayed cables, loose connections, or physical deformities. These checks help prevent unexpected failures and keep equipment running smoothly. Scheduling maintenance every six months allows teams to identify potential issues early and maintain efficient operation. A well-documented inspection schedule reduces downtime and supports long-term reliability.
Tip: Consistent visual inspections help catch minor problems before they become major failures.
Testing Outlets, Connections, and Power Cords
Testing outlets and connections ensures safe and reliable power delivery. Staff verify that each outlet supplies the correct voltage and that connections remain tight. They also check power cords for signs of overheating or brittleness. Quarterly maintenance includes cleaning dust, tightening connections, and testing circuit breakers. Annual reviews involve infrared scans and firmware updates. The following schedule aligns with manufacturer guidelines:
- Monthly: Visual inspection, load verification, temperature checks, cable management.
- Quarterly: Dust removal, tightening connections, testing breakers, verifying network settings.
- Annual: Infrared scans, firmware updates, load data review, monitoring tests, grounding checks.
- Every three years: Evaluate replacement, technology upgrades, power quality analysis, capacity reassessment.
Identifying Signs of Overheating or Failure
Overheating remains a leading cause of equipment failure. Technicians look for discoloration, melted insulation, or a burning smell. They monitor temperature and humidity to prevent environmental stress. The table below highlights common maintenance issues found during inspections:
| Maintenance Issue Category | Description and Impact |
|---|---|
| Overheating in Components | Evidence of overheating, especially in bolted connections, indicating potential electrical faults. |
| Dust Accumulation | Dust buildup reduces energy efficiency and can affect equipment performance. |
| Environmental Factors | Humidity, temperature extremes, and vibration can jeopardize electrical components’ reliability. |
| Missing or Worn Components | Components showing wear or missing parts require repair or replacement to maintain functionality. |
| Calibration and Verification | Monitoring, alarm, and operational components need regular calibration to ensure proper operation. |
Regular inspection and maintenance help maximize the lifespan of every PDU in the data center.
4. PDU Cleaning and Ventilation
Dust and Debris Removal Methods
Technicians recognize that dust and debris can quickly accumulate in server racks. This buildup restricts airflow and increases the risk of overheating. Regular cleaning forms the foundation of effective maintenance. Staff use antistatic cloths and vacuum cleaners with HEPA filters to remove dust from surfaces and vents. Compressed air helps dislodge particles from tight spaces, but technicians avoid blowing debris deeper into equipment. Cleaning schedules often align with quarterly or monthly maintenance routines. Staff also inspect cooling fans and filters, replacing or cleaning them as needed to maintain optimal performance.
Tip: Always power down equipment before cleaning to prevent accidental damage or electrical hazards.
Maintaining Unobstructed Airflow
Proper ventilation prevents hot air from recirculating and raising equipment temperatures. In high-density server environments, standard comfort cooling systems often fall short, providing only about 100 CFM per kilowatt. Experts recommend increasing airflow to 150 CFM per kilowatt to avoid temperature spikes of 5–15°F, which can trigger emergency shutdowns. Dedicated IT cooling systems and airflow containment strategies, such as hot aisle and cold aisle configurations, help maintain stable temperatures.
To ensure effective ventilation, technicians follow these best practices:
- Keep vents and fans clear by avoiding the placement of objects nearby.
- Use perforated rack doors and raised floors to enhance airflow.
- Arrange equipment in hot and cold aisle layouts to optimize cooling.
- Inspect and clean cooling fans and filters regularly.
- Monitor temperature near equipment with sensors to detect hotspots early.
- Organize cables with ties or trays to prevent airflow blockages.
These steps help maintain a safe operating environment and extend the lifespan of critical power infrastructure.
5. PDU Cable Management Strategies
Using Velcro Straps and Cable Organizers
Technicians rely on Velcro straps and cable organizers to keep power cords neat and secure. Velcro straps allow for easy adjustments and prevent cables from tangling or sagging. Cable organizers, such as trays or rings, help route cords along designated paths. This organization maintains proper airflow around equipment, which reduces heat buildup and the risk of overheating. Organized cabling also supports dual cord power supply configurations, making it possible to perform maintenance without shutting down servers.
Tip: Neat bundling of cables with Velcro straps reduces physical stress on connectors and prevents accidental disconnections.
Labeling Cables for Easy Identification
Labeling each cable during installation saves time during maintenance and troubleshooting. Clear labels help staff quickly identify and replace cables, minimizing downtime and preventing confusion. Proper labeling also prevents misuse that could cause shorts or failures at termination points. Infrared scanning of labeled connections helps detect hot spots caused by loose connections or overloads before they lead to failure.
Benefits of Cable Labeling:
- Quick identification during emergencies
- Reduced risk of accidental unplugging
- Streamlined maintenance and upgrades
Preventing Overcrowding and Strain
Overcrowded or tangled cables block airflow and increase the risk of overheating. Technicians avoid bending, crushing, or twisting cables, as these actions can damage the cable structure and interrupt power supply. They separate power and data cables to reduce electrical interference and use only high-quality, compatible cables. Regular inspection and proper routing prevent tension, kinks, and accidental disconnections. By following these practices, teams reduce physical stress on cables and connectors, supporting efficient power distribution and extending equipment lifespan.
6. PDU Environmental Controls
Managing Temperature and Humidity
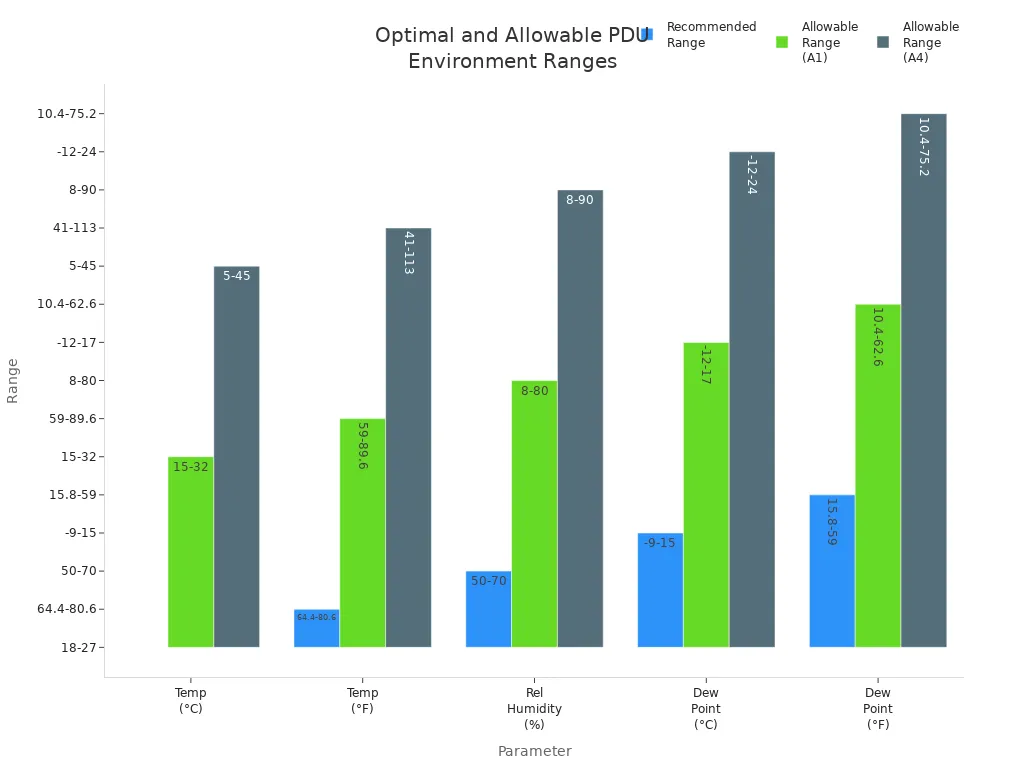
Data center operators must maintain stable temperature and humidity to protect sensitive equipment. Leading manufacturers recommend following ASHRAE guidelines for optimal performance. The ideal temperature range sits between 18°C and 27°C (64.4°F to 80.6°F), while relative humidity should remain between 40% and 60%. These conditions help prevent electrostatic discharge and condensation, both of which can damage hardware. Intelligent monitoring systems often include sensors that track these parameters in real time, alerting staff to any deviations.
| Parameter | Recommended Range | Allowable Range (varies by equipment class) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 18 to 27 | A1: 15 to 32; A4: 5 to 45 |
| Temperature (°F) | 64.4 to 80.6 | A1: 59 to 89.6; A4: 41 to 113 |
| Relative Humidity (%) | 50 to 70 | A1: 8 to 80; A4: 8 to 90 |
| Dew Point (°C) | -9 to 15 | A1: -12 to 17; A4: -12 to 24 |
| Dew Point (°F) | 15.8 to 59 | A1: 10.4 to 62.6; A4: 10.4 to 75.2 |
Ensuring Adequate Rack Airflow
Proper airflow management prevents hot spots and reduces the risk of thermal stress. Operators should use perforated doors, blanking panels, and raised floors to direct cool air where it is needed. Regular monitoring with temperature sensors helps detect abnormal heat patterns early. Smart monitoring systems can send alerts when temperatures rise, allowing for quick intervention. Without effective airflow, equipment faces increased failure rates and reduced mean time between failures.
Note: Environmental incidents account for over half of unplanned downtime in data centers, highlighting the importance of proactive airflow management.
Spacing Devices to Prevent Heat Exchange
Technicians should avoid crowding devices within racks. Adequate spacing allows air to circulate freely, minimizing heat buildup between components. Placing high-heat devices apart from each other reduces the chance of localized hot spots. Operators should also consider the direction of airflow when arranging equipment. Consistent spacing, combined with regular maintenance, helps maintain a stable environment and extends the lifespan of all hardware.
7. PDU Firmware and Software Updates
Checking for Manufacturer Updates
Manufacturers regularly release firmware and software updates to address performance issues and security risks. Technicians should check for these updates on a set schedule, such as quarterly or after any major vulnerability announcement. Many manufacturers provide email alerts or dashboards that notify users about new releases. Staying current with updates helps maintain device stability and ensures compatibility with evolving data center technologies. ISO/IEC 27001 certification signals that a manufacturer follows strict information security management practices. This certification means the company uses secure development methods and reduces the risk of introducing exploitable flaws. By choosing certified vendors and monitoring for updates, organizations can strengthen their infrastructure against emerging threats.
Applying Security Patches
Security patches play a vital role in protecting intelligent power devices from cyberattacks. Unpatched devices may contain critical vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Some documented risks include:
- Authentication bypass flaws, such as CVE-2023-3259, which allow remote attackers to gain full administrative control without authentication.
- Operational disruption, where attackers remotely power off servers or racks, causing outages and possible data loss.
- Physical destruction risks from malicious rapid power cycling, which can damage sensitive hardware.
- Compromised devices acting as stealthy entry points for attackers to move laterally within the network.
Timely application of security patches helps prevent these threats. Additional best practices include isolating devices on secure networks and enforcing strong authentication. Regular patching, combined with proactive monitoring, keeps systems resilient and reduces the risk of costly downtime.
8. PDU Surge Protection Measures
Installing Surge Protection Devices
Surge protection stands as a vital defense against unexpected voltage spikes in enterprise IT environments. Technicians often select hydraulic-magnetic breakers for their consistent performance, even when temperatures fluctuate. These breakers maintain reliability, which is crucial for data centers that operate around the clock. Thermal breakers, while more affordable, can react unpredictably to temperature changes and may not offer the same level of protection. Resettable breakers provide a practical advantage by allowing quick recovery after a surge event, reducing downtime compared to single-use fuses.
Many modern power distribution units feature built-in surge suppression. This technology shields sensitive hardware from voltage spikes caused by lightning, grid instability, or internal electrical faults. Selecting units with clearly rated surge protection levels helps minimize the risk of equipment failure. Devices like the Ubiquiti PDU Pro offer advanced surge protection, remote power control, and individual outlet management, making them well-suited for demanding enterprise environments.
Tip: Always verify the surge protection rating before installation to ensure compatibility with critical equipment.
Monitoring for Electrical Anomalies
Continuous monitoring helps identify electrical anomalies before they escalate into major problems. Technicians use monitoring systems to track voltage, current, and frequency in real time. These systems alert staff to irregularities such as voltage sags, swells, or unexpected surges. Early detection allows for immediate intervention, which protects hardware and prevents costly outages.
A simple checklist for monitoring includes:
- Reviewing surge event logs weekly
- Setting up automated alerts for abnormal readings
- Inspecting breaker status indicators regularly
Proactive monitoring, combined with robust surge protection, forms a comprehensive strategy for safeguarding IT infrastructure.
9. PDU Documentation and Record-Keeping
Maintaining Detailed Service Records
Accurate service records form the backbone of reliable power management. Technicians document every inspection, repair, and upgrade. This habit ensures that teams can trace the history of each device. Well-kept records help identify recurring issues and support warranty claims. Many organizations use digital logs to store maintenance data. These logs often include dates, technician names, and descriptions of work performed. A clear record-keeping process reduces confusion and speeds up troubleshooting.
Note: Consistent documentation helps teams comply with industry regulations and internal policies.
Tracking Configuration and Maintenance Changes
Large organizations benefit from structured methods for tracking changes. Managed power units with real-time monitoring allow staff to view device status and power usage at the outlet level. Alerting systems notify teams when thresholds are exceeded or faults occur. Remote management features enable maintenance and troubleshooting without physical presence.
Teams often integrate power units with data center infrastructure management (DCIM) software. This integration centralizes configuration data and automates monitoring. Audit logs record every action, ensuring traceability and compliance. Security controls, such as role-based access and strong authentication, protect configuration integrity. Regular firmware updates and inspections keep devices secure and functional. Staff also monitor environmental conditions, like temperature and humidity, to prevent failures. Training ensures everyone follows proper protocols and emergency procedures.
Best Practices for Change Tracking:
- Use real-time monitoring and alerting systems
- Maintain audit logs of all actions
- Integrate with DCIM software for centralized management
- Enforce security controls and regular training
10. PDU Scalability and Future-Proofing
Assessing Future Power Requirements
Data center teams must anticipate future growth to ensure reliable power delivery. They start by evaluating current and projected power consumption. This process includes reviewing equipment roadmaps and business objectives. Teams consider the installation type, such as rack-mounted or floor units, and select the orientation that fits their space. They choose devices with more outlets than currently needed, allowing for expansion without major upgrades. Matching outlet types to device plugs prevents the need for adapters. Teams also review power source compatibility and ensure the selected units meet safety certifications like UL or CE. Budget flexibility and compliance with industry standards support long-term scalability.
Note: Partnering with vendors who offer flexible contracts and responsive support can simplify future upgrades.
Selecting Modular or Expandable PDUs
Modular and expandable units offer significant advantages over traditional models. These intelligent devices provide real-time monitoring, outlet-level metering, and remote control. Their robust construction and advanced safety features contribute to long-term reliability. Intelligent models adapt to high-density environments, supporting growth without frequent replacements. Integration with management tools enables centralized control and proactive maintenance. In contrast, basic models require manual intervention and lack flexibility, making them less suitable for evolving infrastructure needs.
- Modular units allow teams to add capacity as needed.
- Advanced monitoring reduces downtime and supports sustainable operations.
- Centralized control streamlines maintenance and enhances adaptability.
Considering Smart PDU Features
Smart features extend device lifespan and improve monitoring. Real-time power monitoring at both outlet and unit levels helps detect overloads early. Remote management enables administrators to reboot or shut down equipment without being onsite. Environmental sensors track temperature and humidity, maintaining safe conditions and preventing failures. Load balancing ensures stable operations by distributing power evenly. Alarms and reminders alert teams to issues before they escalate. Integration with management software centralizes insights and automates alerts, supporting efficient planning and compliance.
Tip: Smart features can improve power efficiency by up to 20% and reduce downtime by 30%, making them essential for future-ready data centers.
Proactive PDU maintenance and smart installation deliver long-term savings by reducing downtime and costly repairs. Organizations that follow best practices achieve improved reliability, energy efficiency, and scalability. With consistent care, a PDU can last up to 15 years, supporting future IT growth and ensuring stable power for critical infrastructure.
FAQ

How often should technicians inspect PDUs?
Technicians should perform visual inspections monthly. They should schedule comprehensive maintenance every six months to ensure optimal performance and early detection of potential issues.
What is the ideal temperature range for PDU operation?
ASHRAE recommends maintaining temperatures between 64.4°F and 80.6°F. This range helps prevent overheating and supports reliable, long-term PDU operation.
Do smart PDUs require regular firmware updates?
Yes. Regular firmware updates help address security vulnerabilities and improve device performance. Technicians should check for updates quarterly or after major manufacturer announcements.
Post time: Jul-28-2025

