
The primary distinction between power strip types lies in their design, features, and intended application. A Desktop Power Strip provides accessible ports and integrated functionalities for convenient desk-level use. Conversely, traditional power strips focus on basic power extension and surge protection. People typically use them for general purposes, often in hidden locations. Understanding these core differences helps users select the optimal device for their specific power needs.
Key Takeaways
- Traditional power strips extend outlets. They often hide behind furniture.
- Desktop power strips sit on your desk. They have USB ports and look nice.
- Never plug big appliances like heaters into any power strip. Use a wall outlet.
- Surge protectors keep your devices safe from power spikes. Check their joule rating.
- Replace surge protectors every few years. They wear out over time.
- Do not plug one power strip into another. This is dangerous and can cause fires.
- Always look for UL certification. This means the power strip is safe to use.
- Choose a power strip based on your needs. Think about where you will use it.
Traditional Power Strips: Design and Core Functionality

Understanding Traditional Power Strip Design
Long, Flat Form Factor
Traditional power strips typically feature a long, flat form factor. This design allows them to fit easily behind furniture or along baseboards. Their elongated shape accommodates multiple outlets in a linear arrangement.
Robust and Durable Construction
Manufacturers build traditional power strips with robust and durable materials. They often use sturdy plastic or metal casings. This construction ensures the strips can withstand daily use and provide reliable power distribution.
Placement Considerations for Traditional Power Strips
Users often place traditional power strips in discreet locations. They are suitable for areas where aesthetics are not the primary concern. Their design allows for hidden placement, keeping cables out of sight.
Core Functions of Traditional Power Strips
Basic Power Outlet Extension
The primary function of a traditional power strip is basic power outlet extension. It expands a single wall outlet into multiple outlets. This allows users to power several devices from one source.
Essential Surge Protection Capabilities
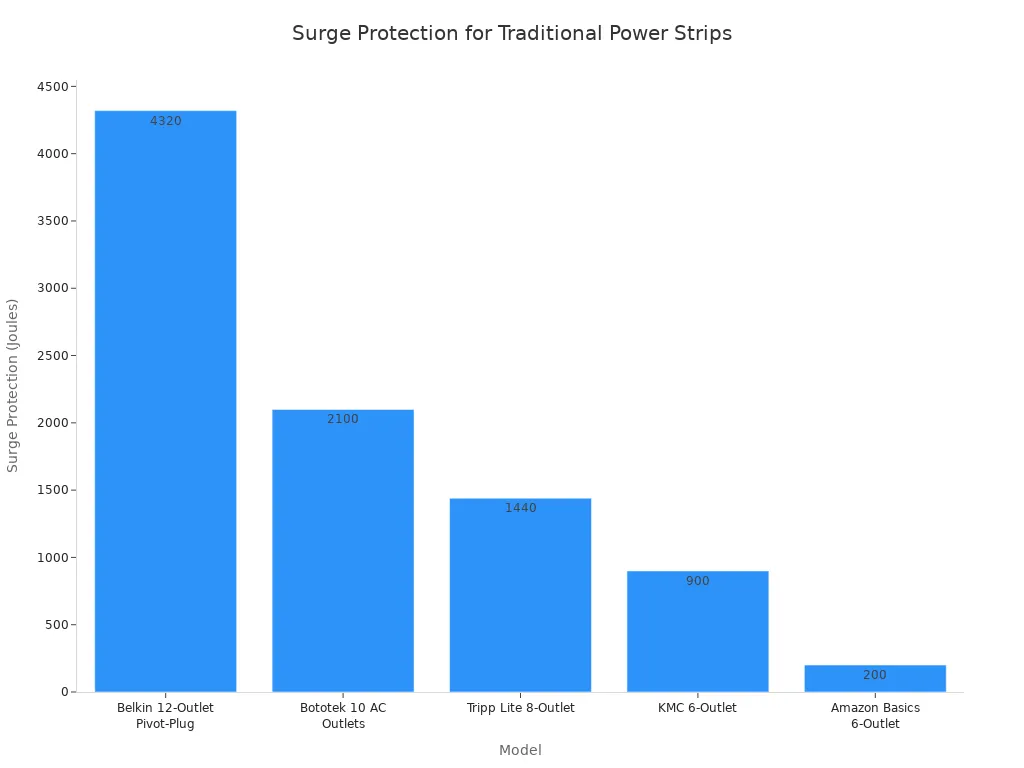
Many traditional power strips offer essential surge protection capabilities. These devices protect connected electronics from voltage spikes. True surge protectors typically have a joule rating, starting from around 400 joules. High-end consumer surge protectors can even be rated at 5000 joules or more. A higher joule rating indicates a greater capacity for the protector to absorb excess spike and surge energy. For most sensitive electronics, a surge protector with 1000-2000 joules of protection is considered adequate. However, for more sensitive, expensive, or important equipment, a rating higher than 2000 joules is recommended.
| Model | Style | Surge Protection (Joules) |
|---|---|---|
| Belkin 12-Outlet Pivot-Plug | Traditional | 4320 |
| CRST 10-Outlet Heavy Duty | Heavy duty | 2800 |
| Bototek 10 AC Outlets | Traditional | 2100 |
| Tripp Lite 8-Outlet | Traditional | 1440 |
| KMC 6-Outlet | Traditional | 900 |
| Amazon Basics 6-Outlet | Traditional | 200 |
Standard On/Off Switches and Indicator Lights
Traditional power strips often include standard on/off switches. These switches allow users to control power to all connected devices. Indicator lights typically show when the strip is powered on or when surge protection is active.
Ideal Applications for Traditional Power Strips
Behind Entertainment Centers and Media Consoles
Traditional power strips are ideal for use behind entertainment centers and media consoles. They provide power for multiple devices like TVs, gaming consoles, and sound systems. Their flat design helps keep wiring tidy.
Under Desks and Furniture for Discreet Power
Users frequently place these strips under desks and furniture. This placement provides discreet power access. It helps maintain a clean and organized appearance in living or working spaces.
Workshops, Garages, and Utility Areas
Traditional power strips are well-suited for workshops, garages, and utility areas. They offer robust power extension for tools and equipment. Their durable construction handles demanding environments.
Powering Appliances and Heavy-Duty Equipment
These power strips are effective for powering appliances and heavy-duty equipment. They provide reliable power for items that do not require advanced charging features. Common applications include:
- Server rooms
- Homes (under counters in kitchens, behind headboards in bedrooms)
- Garages (on workbenches)
- Home offices
- Living rooms
Desktop Power Strips: Modern Solutions for Accessible Power

Innovative Design of Desktop Power Strips
Compact and Aesthetically Pleasing Shapes
Modern Desktop Power Strip units feature compact and aesthetically pleasing shapes. Manufacturers design these units to complement contemporary workspaces. They often come in sleek designs, moving beyond the utilitarian look of traditional strips.
Designed for Visible Placement on Desktops
Unlike their traditional counterparts, designers intend desktop power strips for visible placement. They integrate seamlessly into a desk setup. This design philosophy prioritizes user convenience and visual appeal.
Non-Slip Bases for Stability
Many desktop power strips include non-slip bases. These bases ensure stability on smooth surfaces. They prevent the strip from sliding or shifting during use, keeping connections secure.
Enhanced Features of Desktop Power Strips
Easily Accessible Top and Side Outlets
Desktop power strips offer easily accessible top and side outlets. This configuration makes plugging and unplugging devices simple. Users avoid reaching awkwardly under desks.
Integrated USB-A and USB-C Charging Ports
A significant enhancement includes integrated USB-A and USB-C charging ports. These ports allow direct charging of smartphones, tablets, and other gadgets. They eliminate the need for bulky wall adapters.
Convenient Wireless Charging Pads
Some advanced models feature convenient wireless charging pads. Users can simply place compatible devices on the pad for effortless power. This adds another layer of modern convenience.
Smart Features and Connectivity Options
Modern desktop power strips often incorporate smart features. These include Wi-Fi connectivity for remote control via smartphone apps. Users can turn outlets on or off and schedule power usage. Some models offer energy monitoring, tracking power consumption of individual devices. This helps inform energy-saving decisions. Other features include master and controlled outlets, which automatically shut down peripherals when the primary device is off. Auto-shutoff timers and motion sensor activation further enhance energy efficiency.
Optimal Use Cases for Desktop Power Strips
Office Desks and Home Workstations
Desktop power strips are perfect for office desks and home workstations. They provide centralized power for computers, monitors, and charging devices. This keeps the workspace organized and efficient.
Nightstands and Bedside Charging Hubs
These strips also serve as excellent nightstand and bedside charging hubs. They power lamps, alarm clocks, and personal devices. Their compact size fits well in smaller spaces.
Kitchen Counters for Appliance and Device Power
Kitchen counters benefit from desktop power strips. They provide convenient power for small appliances and charging devices. This keeps essential gadgets ready for use.
Portable Setups and Travel Convenience
Their compact design makes desktop power strips suitable for portable setups and travel. They offer multiple power options in a small package. This ensures users have power wherever they go.
Key Differentiating Factors: Traditional vs. Desktop Power Strips
Accessibility and Port Orientation
Ease of Plugging and Unplugging Devices
Traditional power strips often feature outlets arranged in a linear fashion. Users typically place these strips on the floor or behind furniture. This placement can make plugging and unplugging devices inconvenient. Users often bend or reach into tight spaces. In contrast, desktop power strips prioritize user convenience. They offer easily accessible outlets, often on the top or sides. This design allows users to connect and disconnect devices without effort.
Outlet Spacing and Configuration
Outlet spacing also distinguishes these two types. Traditional power strips sometimes have closely spaced outlets. This can lead to "wall wart" issues, where large adapters block adjacent outlets. Desktop power strips frequently feature wider spacing or rotating outlets. This thoughtful configuration ensures users can utilize every available port. It prevents bulky plugs from obstructing other connections.
Integrated Charging Capabilities
USB-A and USB-C Power Delivery
A significant difference lies in integrated charging capabilities. Traditional power strips primarily offer AC outlets. They require users to supply their own USB wall adapters for charging mobile devices. Modern desktop power strips often include built-in USB-A and USB-C ports. These ports provide direct power delivery for smartphones, tablets, and laptops. This eliminates the need for extra adapters, reducing clutter.
Wireless Charging Integration
Some advanced desktop power strip models further enhance convenience with wireless charging pads. Users simply place compatible devices on the pad to initiate charging. This feature is almost exclusively found in desktop-oriented designs. Traditional power strips do not typically incorporate wireless charging technology. This integration highlights the focus on modern device charging needs for desktop solutions.
Aesthetic Appeal and Placement Strategy
Design for Visible vs. Hidden Use
The intended placement dictates the design philosophy for each power strip type. Manufacturers design traditional power strips for hidden use. Their long, flat form factor and utilitarian appearance suit placement behind entertainment centers or under desks. They do not prioritize visual appeal. Conversely, a Desktop Power Strip features a design for visible placement. These units often boast compact, aesthetically pleasing shapes and finishes. They complement modern office or home decor.
Impact on Workspace Aesthetics
The choice of power strip significantly impacts workspace aesthetics. A traditional floor strip can contribute to a cluttered, unprofessional look. It often lies on the floor, potentially in the way. This can lead to tangled messes of wires. An under-desk power strip, often a type of desktop power solution, promotes a clean, minimalist desk and floor. It keeps all cables neatly contained and organized.
Consider the following comparison:
| Feature | Under Desk Power Strip | Traditional Floor Strip |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Mounted out of sight under the desk | Lies on the floor, often in the way |
| Aesthetics | Promotes a clean, minimalist desk and floor | Contributes to a cluttered, unprofessional look |
| Cable Management | Keeps all cables neatly contained and organized | Leads to tangled messes of wires |
| Safety | Eliminates trip hazards from cords | Creates a significant trip hazard |
| Protection | Safe from kicks, spills, and accidental unplugs | Vulnerable to damage, dust, and spills |
| Cleaning | Makes sweeping and vacuuming effortless | Obstructs cleaning crews, gathers dust bunnies |
For visible placement, users can choose outlets that complement the desk’s materials and finishes, such as wood, metal, or glass. They can opt for outlets with clean lines and neutral colors to blend seamlessly. Some solutions even offer customizable outlet covers that align with branding or personal style. Desk designs can also conceal outlets when not in use, using features like sliding panels or retractable options.
Effective placement strategies for desktop units include positioning outlets within easy reach but out of sight. This maintains a clean aesthetic. Placing outlets in the corners of the desk keeps cords out of the way and reduces clutter. For standing desks, users should position outlets at a convenient height for both sitting and standing. Zoning helps group outlets near areas where devices are frequently used, such as near the monitor or laptop. Users should also include extra outlets for future devices or upgrades.
Cable Management Solutions
Built-in Cable Organization Features
Power strips often include features to help manage cables. Traditional power strips usually offer basic solutions. These might include mounting holes on the back. Users can screw the strip to a wall or desk. This keeps it off the floor. Some traditional strips have simple cable ties or clips. These help bundle cords together. Desktop power strips, however, often have more advanced features. They might include integrated cable channels. These channels guide cords away from the desk surface. Some models have removable covers. These covers hide excess cable length. Other designs feature rotating outlets. These outlets allow cables to exit in different directions. This prevents tangles.
Reducing Desk Clutter
Both types of power strips aim to reduce clutter. Traditional strips achieve this by hiding power connections. They keep cables out of sight. This makes the area look neater. Desktop power strips focus on visible organization. Their design helps keep the desk surface clear. Integrated USB ports reduce the need for many wall adapters. Wireless charging pads remove charging cables entirely. These features create a clean and functional workspace. They make it easier to work without distractions.
Safety Features and Certifications
Surge Protection Levels and Joule Ratings
Safety is a critical factor for any power strip. Surge protection levels vary greatly. A joule rating tells you how much energy a surge protector can absorb. A higher joule rating means better protection. It also means a longer lifespan for the protector. For general use, a rating of 200-600 joules is a good start. Sensitive electronics, like computers, need more. They require at least 1000 joules. Many experts recommend 2000 joules or higher for maximum protection.
Clamping voltage is another important measure. It shows the voltage level at which the surge protector activates. A lower clamping voltage offers better protection.
- 330V: This provides excellent protection. You rarely find this in consumer units.
- 400V: This offers good protection. It is typical for quality Type 3 Surge Protective Devices (SPDs).
- 500V: This is acceptable protection. It is common in budget SPDs.
- 600V+: This offers marginal protection. Avoid these for sensitive electronics.
Response time is also crucial. It measures how quickly the protector reacts to a surge. It is measured in nanoseconds (ns). Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) respond very fast. They typically react in less than 1 nanosecond. Gas Discharge Tubes (GDTs) are slower. They take 100+ ns. However, GDTs can handle higher currents. For most home uses, MOV-based SPDs with sub-nanosecond response are sufficient.
Overload Protection Mechanisms
Power strips also include overload protection. This mechanism prevents too much current from flowing through the strip. It usually involves a circuit breaker. If too many devices draw too much power, the breaker trips. This cuts power to the strip. It protects connected devices from damage. It also prevents electrical fires. This feature is essential for all power strips. It ensures safe operation.
UL Certification and Safety Standards
Always look for UL certification. Underwriters Laboratories (UL) tests products for electrical safety. A UL mark means the product meets strict safety standards. These standards cover fire, electrical shock, and personal injury hazards. It is important to know the difference. A product listing joules, clamping voltage, and UL 1449 is a true surge protector. If it only lists a ’15A circuit breaker’ and ’6 outlets,’ it is just a power strip. It does not offer surge protection.
For essential safety, ensure any power strip or surge protector is UL certified. This shows compliance with safety standards. Also, check the electrical rating. This rating is in watts or amps. Make sure the power strip’s capacity matches your devices. For surge protectors, a lower suppressed voltage rating is better. For example, 330 volts protects better than 4,000 volts.
Here is a comparison of different surge protector types:
| Feature | Power Strip Surge Protector | Whole-House Surge Protector | High-End Power Strip Surge Protector |
|---|---|---|---|
| Joule Rating | 600-2,000 | 2,000-6,000 | 3,000-6,000 |
| UL Certification | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Clamping Voltage | 400V or less | 400V or less | 400V or less |
| Response Time | < 1 nanosecond | < 1 nanosecond | < 1 nanosecond |
| Number of Outlets | 4-12 outlets | Protects entire home | 8-12 outlets |
| Additional Features | USB ports, noise filtering | Whole-house protection | USB ports, coaxial protection |
Price Point and Value Proposition
Cost of Basic Functionality vs. Added Features
The price of power strips varies widely. Traditional power strips offer basic functionality. They extend power outlets and provide surge protection. These models are generally more affordable. They represent a budget-conscious choice. Desktop power strips often cost more. They include advanced features. These features are USB charging ports, wireless charging, and smart capabilities. These added features increase the price.
Long-Term Value of Investment
Consider the long-term value when choosing. A traditional power strip offers reliable basic power. It serves its purpose well for many years. A higher-priced desktop power strip provides more convenience. It also offers better organization. It reduces the need for separate chargers. This can save money over time. It also creates a more efficient workspace. The investment in a feature-rich strip pays off through enhanced productivity and reduced clutter. It also offers better protection for valuable electronics.
Advanced Features and Considerations for Power Strips
Smart Power Strip Functionality
Wi-Fi Connectivity and App Control
Smart power strips offer advanced control. Users can manage multiple outlets remotely through Wi-Fi. A smartphone app or voice commands enable actions like turning devices on or off. They also allow scheduling operations. These devices seamlessly integrate with smart home networks and popular platforms. This provides easy integration.
Scheduling and Remote Power Management
Users gain significant control with smart power strips. They can set automation rules. For example, devices can turn off after a certain time. They can also turn off when no activity is detected. Users build on-off schedules and routines for specific devices. This allows remote control of plugged-in devices. It also helps create routines via smartphone apps or voice commands. Many smart power strips offer independent control of each outlet. This allows precise management of connected devices.
Voice Assistant Integration
Smart power strips enhance home automation. They are compatible with broader smart home systems. This allows seamless integration with voice assistants. Alexa or Google Assistant provide voice control and scene automation. This enables advanced automation scenarios. Users can schedule coffee makers or dim lights automatically.
USB Power Delivery (PD) Technology
Fast Charging for Compatible Devices
Modern power strips often include USB Power Delivery (PD) technology. This feature provides fast charging for compatible devices. USB-C ports with PD can deliver higher wattages. This charges smartphones, tablets, and even some laptops much faster than standard USB ports.
Understanding Wattage Output
Understanding wattage output is crucial for efficient charging. USB PD ports specify their maximum wattage. For instance, a 60W USB-C PD port charges a laptop quickly. A 15W port suits smaller devices like phones. Users should match the power strip’s output to their device’s charging needs.
Environmental Impact and Energy Efficiency
Reducing Standby Power Consumption
Power strips contribute to energy efficiency. Advanced power strips, also known as smart strips, reduce standby power consumption. This "vampire power" comes from devices like computers and TVs. These devices consume power even when not in use but still plugged in. Tier 1 advanced power strips feature Master, Energy-Saving, and Always-On outlets. They use an energy usage sensor. This sensor detects when the main device is off. It then cuts power to peripherals in the Energy-Saving outlets. Tier 2 advanced power strips include Energy-Saving and Always-On outlets. An infrared (IR) smart sensor controls them. This sensor detects remote control activity. If no activity is sensed for a set period, power is cut to devices in the Energy-Saving outlets.
Energy Monitoring Capabilities
Many smart power strips offer energy-usage monitoring. They track energy consumption for each outlet. This provides insights into usage patterns and costs. It helps identify energy-intensive devices. This leads to energy savings and lower electricity bills. Users can save on electricity bills. They identify energy-intensive devices. They cut standby power and optimize device usage.
Durability and Build Quality Assessment
Materials Used in Construction
Manufacturers use specific materials to ensure power strip durability. These materials protect internal components and ensure safe operation. Many power strips feature fire-resistant materials. These materials prevent fire hazards. They also use a reinforced housing structure. This structure protects the strip from physical damage. A fire-resistant casing further enhances safety. This casing contains any potential internal issues. High-quality construction materials contribute significantly to a power strip’s overall robustness. They allow the device to withstand daily wear and tear.
Expected Lifespan and Reliability
Power strips offer a long operational life when built well. Advanced Power Strips (APS) typically have a lifetime expectancy of about 10 years. This long lifespan means users can rely on them for extended periods. Some APS models are also constructed from environmentally sustainable materials. Manufacturers design these for easy disassembly. This facilitates recycling at the end of their useful life. A power strip’s reliability depends on its internal components and external casing. Quality components ensure consistent power delivery. A sturdy build prevents premature failure. Investing in a well-constructed power strip provides long-term value. It also offers peace of mind regarding safety and performance.
Choosing the Right Power Strip for Your Specific Needs
Selecting the appropriate power strip requires careful consideration of specific requirements and usage environments. Users must weigh factors like budget, aesthetics, device types, and safety features. Understanding the distinct advantages of traditional versus desktop power strips guides this decision.
When to Opt for a Traditional Power Strip
Budget-Conscious Power Extension
Traditional power strips offer a cost-effective solution for basic power extension. They provide additional outlets without requiring significant investment. These strips are budget-friendly for straightforward, static power needs. They do not require additional customization or installation. People often choose them for temporary setups or quick fixes. They also suit areas needing additional outlets without permanent installation. Traditional strips are ideal for spaces with static and straightforward power needs.
Requirements for Hidden Power Sources
Traditional power strips excel in situations demanding discreet power access. Their long, flat form factor allows placement behind furniture or along baseboards. This keeps cables and outlets out of sight. Users often place them under desks or behind entertainment centers. This maintains a clean and uncluttered appearance in the visible areas of a room.
Powering High-Wattage Appliances
Power strips are specifically designed for a high concentration of low-powered devices. They are not for high-power appliances. High-wattage appliances can cause overloading due to high startup or surge loads. Never plug high-wattage appliances into power strips. These include space heaters, vacuum cleaners, microwave ovens, coffee makers, electric kettles, hair dryers, toaster ovens, portable air conditioners, dishwashers, washing machines, clothes dryers, refrigerators, freezers, and clothing irons. They require direct wall outlet connections. Always plug power tools directly into wall outlets.
When to Select a Desktop Power Strip
Prioritizing Desk Organization and Aesthetics
A Desktop Power Strip enhances desk organization and aesthetics. Its compact and often stylish design complements modern workspaces. These strips are designed for visible placement. They integrate seamlessly into a desk setup. This helps maintain a clean, minimalist desk and floor. Users can choose outlets that complement their desk’s materials and finishes. They can opt for clean lines and neutral colors to blend seamlessly. Some solutions even offer customizable outlet covers.
Need for Multiple Device Charging Options
Desktop power strips provide excellent solutions for charging multiple devices. They often include integrated USB-A and USB-C charging ports. Some models feature convenient wireless charging pads. These options eliminate the need for numerous wall adapters. They simplify charging for smartphones, tablets, and other gadgets. These strips are designed for a high concentration of low-powered devices. They are perfect for home office setups for charging gadgets and powering PCs, printers, or Wi-Fi routers. They also suit living room entertainment systems to accommodate large adapters for speakers, game consoles, and smart televisions.
Enhancing Workspace Convenience
Desktop power strips significantly enhance workspace convenience. They offer easily accessible top and side outlets. This makes plugging and unplugging devices simple. Users avoid reaching awkwardly under desks. They are ideal for environments with numerous devices requiring continuous power. These strips connect multiple devices securely, especially in home offices, entertainment centers, or workstations.
Essential Safety Considerations for All Power Strips
Understanding Surge Protection Ratings
Understanding surge protection ratings is crucial for device safety. A joule rating indicates the amount of energy a surge protector can absorb. Higher joule ratings offer better protection and a longer lifespan. For sensitive electronics, a rating of 1000-2000 joules is adequate. More critical equipment benefits from ratings above 2000 joules. Clamping voltage shows the voltage level at which the protector activates. A lower clamping voltage, such as 330V or 400V, provides superior protection. Response time, measured in nanoseconds, indicates how quickly the protector reacts to a surge. Faster response times are always better.
Importance of UL Listing
Always prioritize power strips with UL certification. Underwriters Laboratories (UL) tests products for electrical safety. A UL mark signifies the product meets strict safety standards. These standards cover fire, electrical shock, and personal injury hazards. A product listing joules, clamping voltage, and UL 1449 is a true surge protector. If it only lists a ’15A circuit breaker’ and ’6 outlets,’ it is just a power strip. It does not offer surge protection.
Proper Usage Guidelines to Prevent Hazards
Proper usage prevents hazards and ensures longevity for all power strips.
- Placement: Position power strips on a stable and elevated surface. Avoid placing them directly on carpeting or under rugs. Keep the area around the power strip clear of objects that can impede airflow. Position all electrical connections in visible, accessible locations. Avoid hiding them behind furniture or underneath rugs. Position power strips at least three feet away from any window opening to avoid moisture exposure. Keep power strips in a dry environment, away from water or any other type of liquid.
- Appliance Use: Never plug high-wattage appliances into power strips. These include space heaters, vacuum cleaners, microwave ovens, coffee makers, electric kettles, hair dryers, toaster ovens, portable air conditioners, dishwashers, washing machines, clothes dryers, refrigerators, freezers, and clothing irons. They require direct wall outlet connections.
- Daisy-Chaining: Do not daisy-chain power strips together. Connecting multiple power strips in series can cause overheating and is a serious safety violation.
- Wattage Matching: Choose a power strip that supports the combined wattage of the devices you plan to connect.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect power strips for signs of damage. Look for discoloration (blackened marks), unusual warmth, burning odors, frayed cords, burnt or melted plastic, and loose connections. Replace faulty power strips immediately.
- Unplugging: Unplug power strips when not actively in use. This eliminates standby electrical flow and potential malfunction. Users can also switch off the integrated circuit breaker.
- Mounting: Always use proper mounting procedures. Utilize tabs or hangers often molded into power strip housings. Avoid drilling or stapling.
- Environment: Never use power strips outdoors, particularly during damp weather. Avoid using power strips in applications or facilities, such as a healthcare environment, where power is critical.
Installation, Setup, and Maintenance Tips
Optimal Placement Strategies for Power Strips
Avoiding Overheating and Airflow Obstruction
Proper placement of power strips prevents overheating and ensures optimal airflow. Users must avoid cable overcrowding. Overcrowded cables restrict airflow. This restriction leads to overheating. Organize cables to enhance airflow and reduce fire risk. Regularly monitor cabling to keep it clutter-free. Map out power strip placement. Distribute power strips evenly across racks. This prevents overloading and minimizes cable clutter. Strategic positioning maintains airflow. Airflow is crucial for preventing overheating in high-density environments. Ensure proper mounting. Mount power strips at an elevated height, such as on a rack or wall. This prevents obstruction of airflow. It also reduces tripping hazards. Mounting protects strips from dust and moisture.
Effective Cable Routing Techniques
Effective cable routing techniques contribute to a tidy and safe environment. Use cable ties or sleeves to bundle wires together. Route cables along the edges of desks or walls. This keeps them out of the way. Proper routing prevents tangles. It also makes cleaning easier. A well-organized cable system improves airflow around devices. This reduces the risk of overheating.
Maximizing Outlet Usage Efficiency
Preventing Blocked Outlets
Users must maximize outlet usage efficiency. Avoid overloading power strips with too many devices. Do not daisy-chain multiple power strips together. This practice creates fire hazards. Place power strips in well-ventilated areas. Keep them away from flammable materials and moisture. Understand the power requirements of each connected device. Ensure the total load does not exceed the strip’s capacity. Avoid plugging in high-power devices like microwaves or space heaters into power strips. These appliances require direct wall outlet connections.
Utilizing Angled Plugs and Adapters
Angled plugs and adapters help prevent blocked outlets. These accessories allow bulky power bricks to fit side-by-side. They ensure users can utilize every available port on a power strip. Some power strips feature rotating outlets. These outlets offer flexibility for various plug sizes.
Regular Maintenance and Care for Longevity
Cleaning and Dust Removal
Regular maintenance extends a power strip’s lifespan. Perform quarterly maintenance. Remove dust and debris with compressed air. Dust accumulation can impede airflow. It also increases the risk of electrical shorts. Verify proper placement and usage during cleaning.
Inspecting for Damage and Wear
Inspect power strips for damage and wear. Unplug the power strip and remove all connected devices. Examine the housing for cracks, melting, or distortion. Check outlet openings for damage or foreign objects. Look for discoloration. Discoloration indicates overheating. Feel the entire cord for damage. Examine cord entry points for stress. Inspect plug prongs for straightness and secure attachment. Verify cord flexibility. Ensure it is not pinched. Check the status of the protection indicator light. Press the test button if available. Replace damaged or faulty products immediately. Do not attempt repairs.
Common Misconceptions and Best Practices for Power Strips
Power Strips vs. Dedicated Surge Protectors
Understanding Their Distinct Roles
People often confuse power strips with surge protectors. A basic power strip simply expands one wall outlet into several. It provides more places to plug in devices. A dedicated surge protector, however, offers protection against voltage spikes. It safeguards connected electronics from damage caused by power surges. While many power strips include surge protection, not all do. Always check the joule rating and UL certification to confirm surge protection capabilities.
When to Use Each Device
Users should choose a basic power strip for simple power extension. This works well for devices that do not require surge protection, like lamps or phone chargers. For valuable or sensitive electronics, always use a dedicated surge protector. Computers, televisions, and gaming consoles benefit greatly from this added protection. A surge protector is essential in areas prone to lightning strikes or unstable power grids.
Dangers of Daisy Chaining Power Strips
Risks of Overloading Circuits
Daisy-chaining power strips means plugging one power strip into another. This practice creates significant risks. When multiple power strips connect, the one directly connected to the wall outlet often supplies power to far more outlets than its approved number. This electrical current overload can lead to significant risks. It can cause a fire or trip a circuit breaker. A tripped breaker de-energizes connected equipment. OSHA regulation 29 CFR 1910.304(b)(4) states that ‘outlet devices shall have an ampere rating not less than the load to be served.’ Overloading a power strip, which often occurs with daisy-chaining, is unsafe. It carries the risk of generating excess heat.
Fire and Electrical Hazards
Daisy-chaining power strips is against safety codes and standards. Organizations like OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), NFPA (National Fire Protection Association), and UL (Underwriters Laboratories) prohibit this practice. Richard Fairfax, OSHA Director, states:
“Manufacturers and nationally recognized testing laboratories determine the proper uses for power strips. For example, the UL Directory contains instructions that require UL-listed RPTs to be directly connected to a permanently installed branch circuit receptacle; they are not to be series-connected to other RPTs or connected to extension cords.”
This practice significantly increases the risk of electrical fires and other hazards.
Lifespan of Surge Protection Components
Degradation Over Time and Usage
Surge protectors do not simply wear out like mechanical devices. Instead, their protective capacity diminishes gradually with each power surge they absorb. The key component, a Metal Oxide Varistor (MOV), degrades incrementally. It continues until it can no longer provide adequate protection. Factors such as surge frequency and intensity, joule rating, build quality, and environmental conditions like heat, humidity, and dust can accelerate this degradation.
Recommendations for Replacement
Most manufacturers recommend replacing surge protectors every two to five years. Users should replace them sooner if exposed to frequent or severe surges. Surge protectors often continue to function as an electricity source even when their surge protection powers wane. This makes it difficult to tell if they are no longer working.
- Look for surge protectors with LED lights. These lights can alert you when the surge protection power has decreased, though these lights are not foolproof.
- Periodically examine the surge protector for any signs of damage; if found, unplug and replace it immediately.
- Replace the surge protector after a significant power surge event, such as a lightning storm. Its ability to absorb surge energy may be compromised.
- If the indicator light on a surge protector power strip has stopped working, especially after a significant storm or power surge, it may indicate that the surge protection has expired. Assume that if the light is out, the strip is no longer providing protection and should be replaced.
- Even if a strip appears functional, age is a factor. Repeated plugging/unplugging, temperature changes, and dust accumulation over 3-5 years can lead to internal wear. If you cannot recall when you purchased it, and it has been a long time, it is likely time for a replacement.
Top Brands and Models for Desktop Power Strips and Traditional Options
Choosing the right power strip involves considering reputable brands. These brands offer reliable products. They also provide features matching specific needs. Understanding leading manufacturers helps consumers make informed decisions.
Reputable Traditional Power Strip Brands
Key Features to Look For in Basic Models
Consumers often seek affordability and basic functionality in traditional power strips. Key features include multiple AC outlets and essential surge protection. A robust build ensures durability. Many models offer a long, flat form factor for discreet placement. They also feature standard on/off switches.
Belkin Power Strip Surge Protector is a trusted brand. It is known for long-lasting power strips. Philips 6 Outlet Surge Protector Power Strip offers good power organization. It has an attractive flat plug and braided cord. Amazon Basics provides super affordable and straightforward options. An example is the Amazon Basics Surge Protector Power Strip. GE (General Electric) is a legacy brand. It offers dependable, practical, and solid power strips. The GE Pro 6-Outlet Surge Protector is a good example. These are reasonably priced. They are also widely available. They often feature longer cables. Tessan is ideal for travel. It minimizes cable clutter. It is known for minimalist, space-saving designs. These designs often include built-in USB ports.
User Reviews and Reliability Ratings
User reviews and reliability ratings offer valuable insights. They help assess a product’s real-world performance. High ratings often indicate customer satisfaction. They also suggest consistent product quality. Consumers should check these ratings before purchasing.
Leading Desktop Power Strip Brands
Innovative Designs and Functionality
Leading desktop power strip brands focus on innovative designs. They prioritize functionality for modern workspaces. These designs are compact and aesthetically pleasing. They often include features for visible placement.
Huntkey is a leading brand. It is known for its quality power strips. It offers a variety of products. These products have unique features and reliability. The Huntkey SMD407C features 4 AC outlets. It also has 2 USB-A ports and 1 USB-C port. This USB-C port offers 30W high-speed charging. It includes a cradle ledge for smartphones. It has automatic device detection for optimal charging. It also boasts a 7-point safety system. This model has a stylish, sturdy, and compact design. The Huntkey SMD507 offers 5 AC outlets and 2 USB-A ports. It features a double break safety switch. It has an integral copper bar. It provides surge and overload protection. It comes in a stylish black design. It uses robust V0 fire-retardant material. The Huntkey SMC307 is a compact and portable power strip. It has 3 AC outlets and 3 USB ports. It includes a 5ft long thickened power cord. It features an intelligent charging chip. This chip provides automatic device detection. It supports fast charging (2.4A max). It has a compact cube design. It also includes multiple safety features.
Advanced Charging Capabilities and Smart Features
These brands integrate advanced charging capabilities. They also include smart features. This enhances user convenience. USB-A and USB-C ports are common. Fast charging support is also a key feature.
Future Trends in Power Strip Technology
Power strip technology continues to evolve, driven by demands for greater efficiency, flexibility, and intelligence. Future trends point towards more adaptable designs, smarter energy management, and environmentally conscious manufacturing. These innovations will transform how users power their devices and manage energy consumption.
Modular and Customizable Designs
Swappable Ports and Configurations
Future power strips will likely feature modular designs. These designs allow users to customize port types and configurations. Users can swap out standard AC outlets for USB-C ports, Ethernet connections, or even specialized charging modules. This flexibility means a power strip can adapt to changing device needs without requiring a complete replacement. This approach supports easy upgrades and maintenance without system downtime.
Adaptability to Evolving Needs
Modular and scalable designs enable power systems to expand and adapt flexibly. This adaptability is crucial as technology evolves rapidly. Users can easily add new modules or reconfigure existing ones. This ensures their power solutions remain relevant and efficient for years to come.
Enhanced Smart Features and AI Integration
Predictive Power Management
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) will significantly enhance power strip functionality. AI tools will predict energy usage patterns. They will optimize power distribution across connected devices. This leads to cost savings and increased reliability. IoT devices will provide real-time data for smarter energy management. This reduces waste and helps avoid grid issues.
Advanced Automation and Control
Future power strips will offer advanced automation and control capabilities. Users can manage devices remotely through sophisticated apps. These systems will integrate seamlessly with smart home ecosystems. They will also feature voice assistant compatibility. New power strips will incorporate enhanced safety and cybersecurity features. These features protect against both physical and online threats, ensuring system security and reliability. Machine learning will also help predict equipment failures, reducing downtime and extending the lifespan of power systems.
Sustainable Materials and Manufacturing
Eco-Friendly Production Practices
The industry is moving towards more sustainable practices. Manufacturers will increasingly use eco-friendly materials in power strip production. This includes recycled plastics and biodegradable components. Production processes will also focus on reducing waste and energy consumption.
Recyclability and Reduced Environmental Impact
Future power strips will prioritize recyclability. Designs will facilitate easy disassembly, allowing for the separation and recycling of components. This commitment to sustainability aims to reduce the overall environmental impact of these essential devices.
The "best" power strip ultimately depends on individual needs, environment, and specific use cases. By understanding the distinct design, features, and intended applications of both traditional and Desktop Power Strip options, readers can make an informed choice. This decision optimizes convenience, safety, and efficiency for their unique setup. Users can confidently select the right device for their specific requirements.
FAQ
What is the primary difference between desktop and traditional power strips?
Desktop power strips offer accessible ports and integrated features for desk convenience. Traditional power strips prioritize basic power extension and surge protection for general, often hidden, use.
Can users plug high-wattage appliances into any power strip?
No, users should never plug high-wattage appliances like space heaters or microwaves into power strips. These appliances require direct wall outlet connections. This prevents overloading and fire hazards.
How often should users replace a surge protector?
Manufacturers recommend replacing surge protectors every two to five years. Users should replace them sooner after significant power surges or if the indicator light shows reduced protection.
What does UL certification signify for a power strip?
UL certification means Underwriters Laboratories tested the product for electrical safety. It confirms the power strip meets strict safety standards for fire, electrical shock, and personal injury hazards.
Is daisy-chaining power strips a safe practice?
No, daisy-chaining power strips is unsafe and prohibited by safety standards. It overloads circuits. This creates significant risks of overheating, electrical fires, and tripped circuit breakers.
Do all power strips provide surge protection?
Not all power strips offer surge protection. Basic power strips only extend outlets. Users must check for a joule rating and UL 1449 certification to confirm true surge protection capabilities.
Why do desktop power strips often include USB charging ports?
Desktop power strips include USB-A and USB-C ports for convenience. These ports allow direct charging of smartphones, tablets, and other gadgets. They reduce the need for bulky wall adapters on the desk.
Post time: Jan-16-2026

