
A PDU plays a crucial role in professional environments by offering advanced power management and enhanced durability. While a Basic PDU or ordinary power strip meets everyday consumer needs with fundamental features, the demand for Intelligent PDU solutions is rapidly increasing in industrial settings. The table below highlights significant growth in the use of Intelligent PDUs within industrial sectors, whereas data on consumer power strips remains limited.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2025) | $630 million |
| CAGR (2025-2033) | 3.5% steady growth |
| Projected Market Size (2033) | Over 30 million units |
| Annual Growth Rate (Industrial) | Exceeding 5% in industrial automation and data centers |
| Dominant Segments | Data centers, industrial automation, healthcare |
Key Takeaways
- PDUs offer advanced power management, remote monitoring, and higher durability, making them ideal for data centers and industrial environments.
- Ordinary power strips provide basic power distribution and surge protection, best suited for homes, offices, and light commercial use.
- Choosing the right device depends on power needs, safety features, and environment to ensure reliable and efficient operation.
PDU: Definition and Key Features
What Is a PDU?
A PDU, or Power Distribution Unit, serves as a device that distributes electrical power to multiple devices in environments like data centers, server rooms, and industrial facilities. Companies use PDUs to manage and control the flow of electricity to critical equipment. PDUs come in several forms, including rackmount, floor-mounted, cabinet, and portable models. The industry divides PDUs into two main categories: basic and intelligent. Basic PDUs provide simple power distribution, while intelligent PDUs offer advanced features such as real-time monitoring, remote access, and outlet-level control. These devices help organizations maintain reliable power delivery and support the growing demand for energy efficiency and remote management.
Note: Intelligent PDUs play a key role in data centers, educational labs, and commercial network closets by supporting reliable and efficient power management.
Main Functions of a PDU
PDUs perform several essential functions that go beyond what ordinary power strips can offer. Their main functions include:
- Distributing electrical power safely to multiple devices.
- Monitoring power usage at the device or outlet level.
- Providing remote control and management of power outlets.
- Tracking power consumption to support energy efficiency.
- Offering environmental monitoring, such as temperature and humidity sensing.
- Sending alerts when power thresholds are exceeded or when environmental conditions change.
Technical documents highlight that intelligent PDUs support data center efficiency by enabling cooling optimization, capacity planning, and identifying underutilized equipment. These features help prevent overheating and improve uptime, making PDUs a vital part of modern IT infrastructure.
Ordinary Power Strip: Definition and Key Features
What Is an Ordinary Power Strip?
An ordinary power strip is a device that allows users to connect multiple electronic devices to a single electrical outlet. Manufacturers design these products for home, office, and light commercial environments. Most power strips feature a row of sockets, a main power switch, and a cord that plugs into a wall outlet. Many models include surge protection to guard against voltage spikes, as well as USB ports for charging mobile devices. Safety remains a top priority, so manufacturers often add overcurrent protection, thermal fuses, and fire-resistant materials. Regulatory standards in the United States and Europe require power strips to meet strict safety and performance criteria. Recent trends show that companies now offer power strips with fast-charging capabilities, child-proof designs, and certifications from independent testing organizations.
Note: Power strips come in several styles, such as basic strips, rack-mount units, under-monitor models, and direct plug-in types. Some versions, like furniture power distribution units (FPDUs) and relocatable power taps (RPTs), provide additional features for specialized use.
Main Functions of an Ordinary Power Strip
Ordinary power strips serve several important functions in everyday settings:
- Distribute electrical power from one outlet to multiple devices.
- Protect connected equipment from power surges and overloads using built-in circuit breakers and surge suppressors.
- Offer USB charging ports, including USB-C, for phones and tablets.
- Provide wide outlet spacing to fit large adapters and chargers.
- Include LED indicators to show power status and outlet activity.
- Feature on/off switches for easy control of all connected devices.
- Support advanced options like remote control, outlet scheduling, and real-time power monitoring in smart models.
Technical reviews highlight that some power strips deliver up to 2700 joules of surge protection and use fire-resistant shells rated for high temperatures. Safety certifications such as ETL and UL help ensure reliability and consumer trust. These features make ordinary power strips a practical choice for powering and protecting electronics in homes and offices.
PDU vs. Ordinary Power Strip: Side-by-Side Comparison

Usage Environments
PDUs and ordinary power strips serve different environments.
- Data centers, server rooms, and industrial automation facilities rely on PDUs for advanced power management.
- Home offices, classrooms, and small businesses use ordinary power strips for basic device connectivity.
PDUs support remote monitoring, power metering, load balancing, and remote outlet control. Intelligent PDUs allow real-time monitoring at the outlet level, which helps optimize energy use and prevent overloads. These features improve operational efficiency and reliability in complex IT environments. Power strips do not offer these capabilities.
Smart PDUs can reduce energy waste by up to 30% through improved monitoring and control. Switched PDUs provide remote power control, which is valuable in remote or edge data centers.
Physical Build and Durability
PDUs feature robust construction designed for demanding environments. Manufacturers use industrial-grade materials and reinforce enclosures to withstand heat, vibration, and heavy use.
Ordinary power strips use lighter materials and target less demanding settings. Their design focuses on portability and convenience rather than durability.
| Feature | PDU (Power Distribution Unit) | Ordinary Power Strip |
|---|---|---|
| Build Quality | Industrial-grade, reinforced | Consumer-grade, lightweight |
| Durability | High, for 24/7 operation | Moderate, for occasional use |
| Mounting Options | Rack, cabinet, wall, floor | Desktop, wall, under-desk |
Outlet and Inlet Configurations
Technical documents from leading manufacturers show that PDUs offer a wide range of outlet and inlet configurations.
- PDUs include specialized outlets such as HDOT and HDOT Cx, which combine multiple plug types.
- They provide metering accuracy at both inlet and outlet levels, supporting precise power monitoring.
- PDUs come in rackmount, vertical, and horizontal forms, with input power options for global compatibility.
Ordinary power strips usually feature a fixed number of standard outlets, often with a single input plug. They rarely offer metering or advanced outlet types.
Voltage and Current Ratings
PDUs support higher voltage and current ratings than ordinary power strips.
- Smart PDUs provide real-time voltage and current monitoring with billing-grade accuracy.
- They record advanced power quality metrics, such as total harmonic distortion and peak/minimum voltage/current values.
- Metered and monitored PDUs display local and remote data for voltage, current, and load levels.
Ordinary power strips supply power without monitoring or management. They operate at standard household voltages and currents, suitable for non-critical devices.
The progression from basic power strips to advanced PDUs highlights the increase in measurement precision and control.
Safety Features
PDUs meet strict safety standards, including UL Listed Mark, CE Mark, IEC 60950-1, IEC 62368-1, and the EU Low-Voltage Directive.
- These certifications ensure protection against electrical shocks and fire hazards.
- PDUs include overload protection, surge suppression, and circuit breakers.
- Some models feature 2-pole 50A circuit breakers for over-voltage, over-current, and short-circuit protection.
Ordinary power strips offer basic safety features, such as simple circuit breakers and surge protection. They do not meet the rigorous standards required for critical environments.
Compliance with international certifications guarantees reliable and safe operation in data centers and industrial settings.
Advanced Functions
PDUs, especially intelligent models, provide advanced functions not found in ordinary power strips.
- Intelligent PDUs offer remote monitoring and control down to individual outlets.
- They integrate environmental sensors and analytics for power and temperature data.
- Advanced PDUs identify the specific outlet causing a breaker trip, reducing troubleshooting time.
- Automated waveform capture helps diagnose power quality issues.
- Multi-level power monitoring delivers detailed metrics for current, voltage, power factor, and harmonic distortion.
- Outlet-level monitoring identifies idle or inefficient devices, supporting power optimization.
Ordinary power strips lack these advanced features. They do not support remote management, detailed analytics, or environmental monitoring.
These advanced functions in PDUs lead to measurable outcomes, such as improved uptime, faster fault resolution, and better energy efficiency.
PDU and Power Strip: Typical Applications

Home and Office Use
Power strips remain the most common choice for homes and small offices. People use them to connect computers, lamps, chargers, and entertainment devices. Many models include USB ports, surge protection, and child safety locks. Smart power strips now offer WiFi connectivity and voice assistant integration, making it easy to schedule devices and monitor energy use. These features help families and office workers save energy and protect electronics from voltage spikes.
| Environment | Key Features | Performance & Reliability Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Home Use | Compact design, USB ports, smart home integration, surge protection, child lock | Enhances convenience and safety, enables energy savings, protects devices, reliable for daily use |
| Office Use | More outlets, transformer-friendly sockets, high surge protection, remote monitoring | Supports multiple devices, prevents overloads, enables remote management, ensures durability |
Data Center and Server Room Use
Data centers and server rooms require advanced power management. PDUs provide reliable power distribution to racks of servers and networking equipment. Metered and monitored PDUs allow real-time tracking of voltage and load, which helps prevent overloads. Switched PDUs enable remote control of individual outlets, so technicians can reboot equipment without visiting the site. Customizable features, such as triple-output voltage transformers and isolated designs, support evolving power needs and reduce downtime risks. These solutions ensure continuous operation and high reliability for critical infrastructure.
PDUs in data centers often include environmental sensors for temperature and humidity, helping operators optimize cooling and energy use.
Industrial and Specialized Environments
Factories, telecom sites, and research labs need robust power solutions. Industrial PDUs offer high outlet counts, strong aluminum housings, and precise metering. Real-time monitoring and outlet-level control increase power efficiency and reduce downtime. Features like open neutral protection and GFCI compliance enhance safety. Custom PDUs support renewable energy integration and harsh conditions, ensuring reliable operation in manufacturing and green energy sectors. These advanced capabilities make PDUs essential for demanding environments.
Choosing Between a PDU and an Ordinary Power Strip
Key Factors to Consider
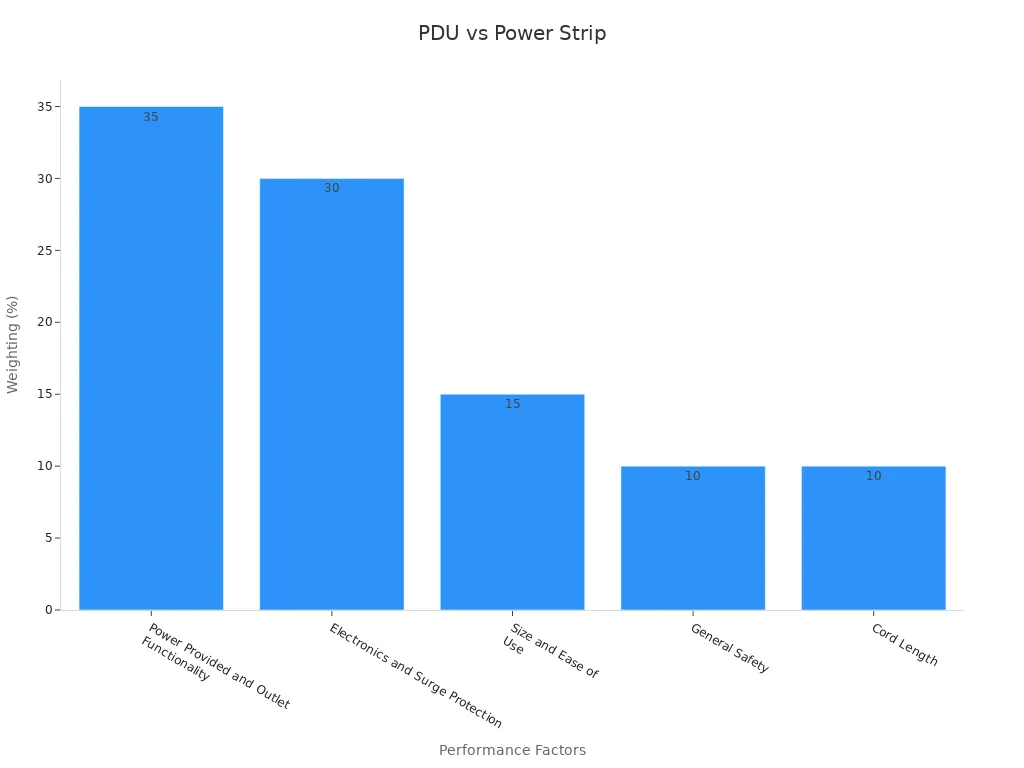
Selecting the right power distribution device depends on several important factors. Buyers should evaluate performance metrics, safety, and compatibility with their environment. Expert reviews often highlight the following performance metrics when comparing devices:
| Performance Metric | Weighting (%) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Power Provided and Outlet Functionality | 35 | Ability to reliably supply power and support multiple outlets without failure. |
| Electronics and Surge Protection | 30 | Quality of surge protection and electronic components to safeguard devices. |
| Size and Ease of Use | 15 | Physical dimensions and user-friendliness of setup and operation. |
| General Safety | 10 | Safety certifications, fire-resistant materials, and overall device safety. |
| Cord Length | 10 | Length of power cord to suit different installation needs. |
A detailed comparison also considers these factors:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Capacity | Match the device’s capacity with equipment power needs and plan for future expansion. |
| Number and Type of Outlets | More outlets and varied types increase flexibility for different devices. |
| Durability and Build Quality | Sturdy design ensures longevity and resistance to wear and tear. |
| Safety Features | Surge protection, overload prevention, and other protections safeguard equipment. |
| Compatibility | Ensure size, mounting options, and outlet types fit existing infrastructure. |
| Scalability and Future-Proofing | Choose devices that can grow with needs and support future devices. |
| Ease of Installation and Use | Simple setup and operation reduce complexity and downtime. |
| Cost and Value for Money | Balance price with features and durability for the best long-term investment. |
| Customer Support and Warranty | Reliable warranty and responsive support provide peace of mind. |
Tip: Safety certifications, such as UL and ISO9001, and durable materials like aluminum alloy housing, increase reliability and protect valuable equipment.
PDUs deliver advanced features and strong protection for critical environments, while power strips offer simple solutions for homes and offices. The table below highlights key differences in safety, capacity, and application. Users should always match their choice to power needs and environment for safety and reliability.
| Aspect | PDUs | Power Strips |
|---|---|---|
| Power Capacity | Higher amperage, built-in circuit breakers | 15-20 amps capacity |
| Application | Data centers, industrial use | Residential, office use |
| Advanced Features | Remote management, metering, alerting | Basic power delivery |
FAQ
What is the main reason to choose a PDU over a power strip?
A PDU offers advanced power management, higher durability, and better safety. Data centers and industrial sites use PDUs for critical equipment.
Can a power strip replace a PDU in a server room?
A power strip cannot replace a PDU in a server room. PDUs provide monitoring, control, and protection that power strips lack.
Do PDUs always include surge protection?
Not all PDUs include surge protection. Users should check product specifications before purchase to ensure the right level of protection.
Post time: Jun-18-2025

